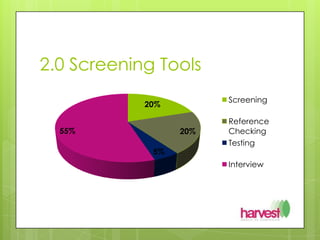
The document outlines a workshop on interview skills led by Maree Herath, focusing on the importance of effective interviewing in the hiring process. It covers selection procedures, screening techniques, and the significance of body language, along with common pitfalls and best practices for conducting interviews. Additionally, it highlights the benefits for both the employer and the candidate, and provides techniques for assessing and understanding candidates better.