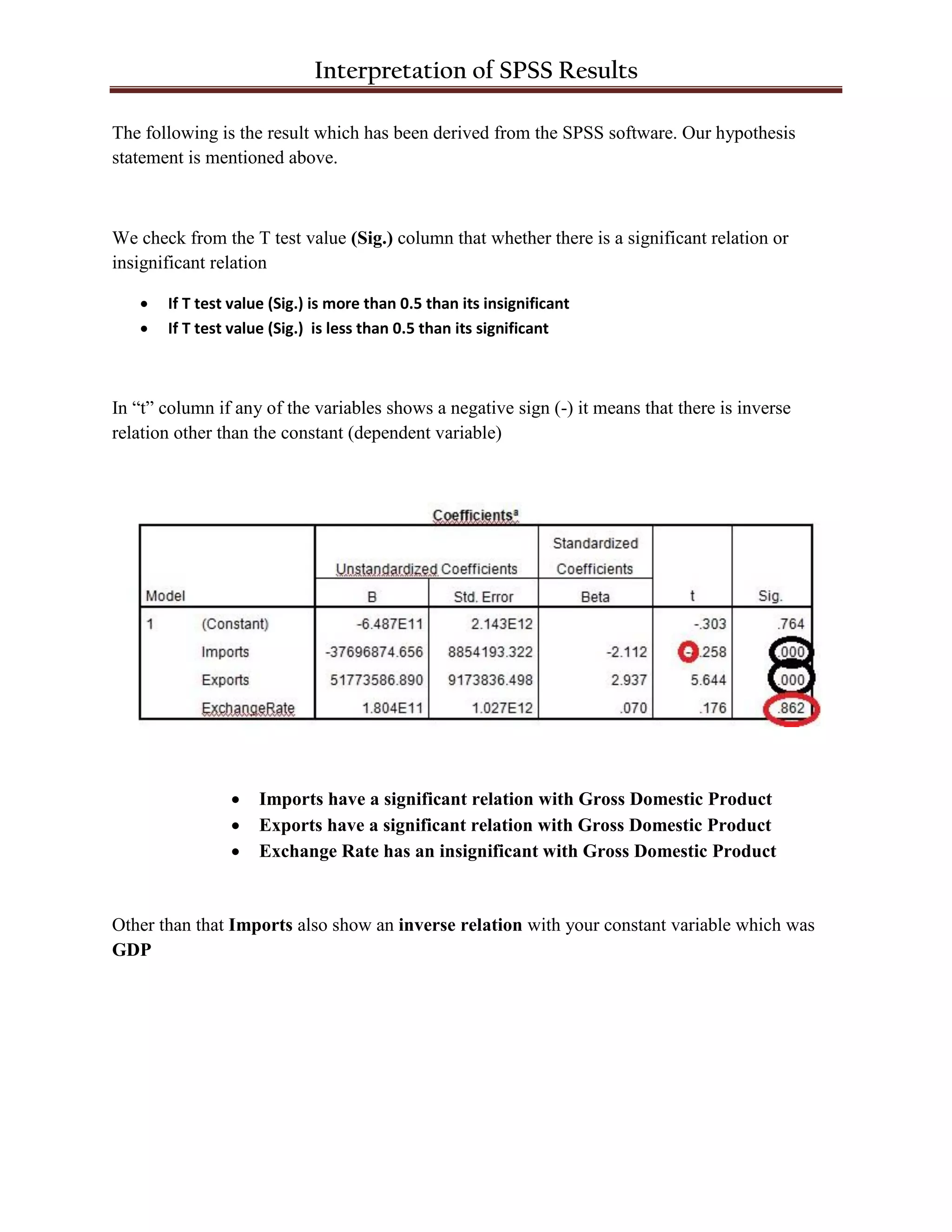
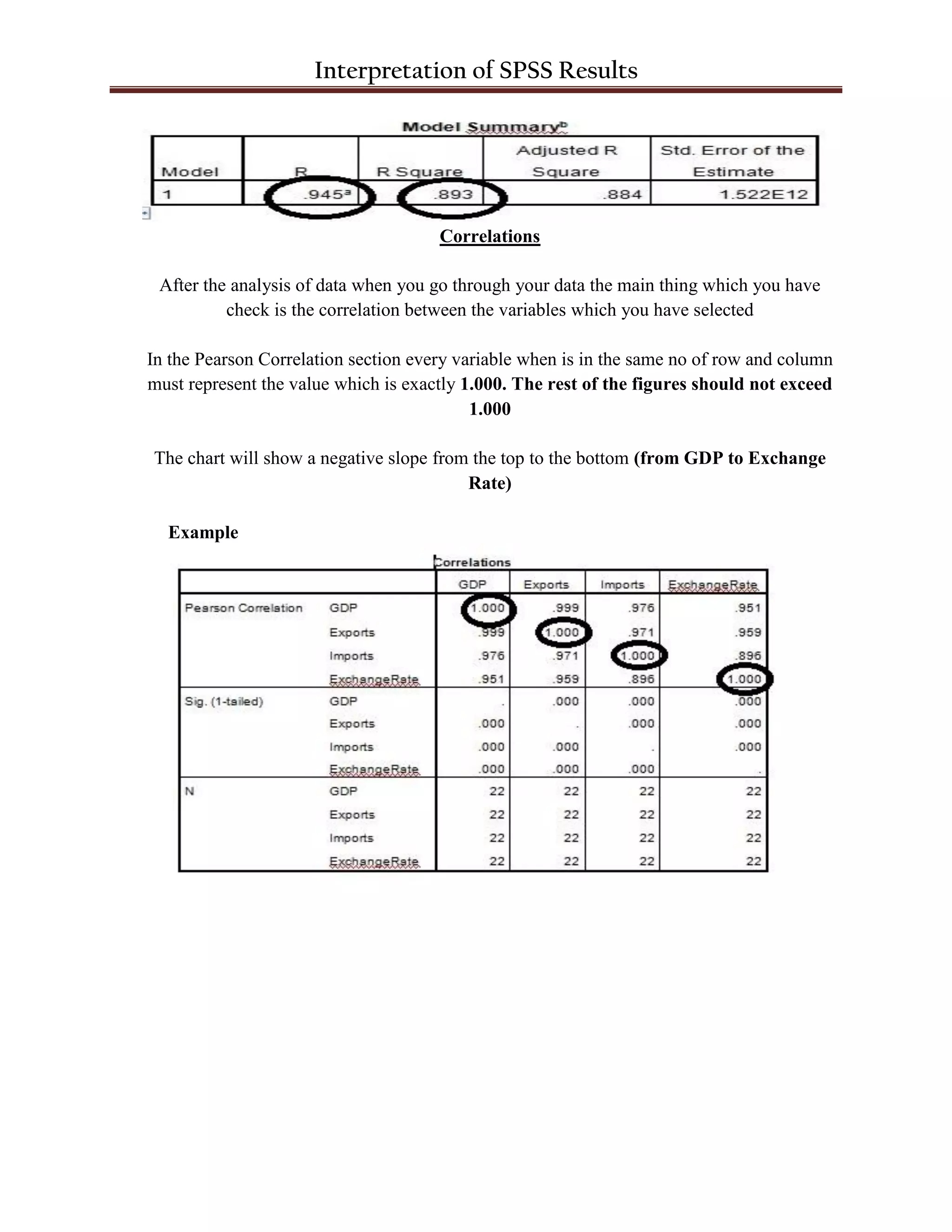
The document discusses interpreting results from SPSS analysis with GDP as the dependent variable and imports, exports, and exchange rate as independent variables. It states that imports and exports have a significant relationship with GDP based on their t-test values being less than 0.5, while exchange rate does not due to its t-test value being greater than 0.5. Imports also have an inverse relationship with GDP. The Durbin-Watson value of 1.856 is within the acceptable range of 1.7 to 2.0. R should be greater than 0.8 and R-square depends on R. Correlations between variables should be exactly 1.000.