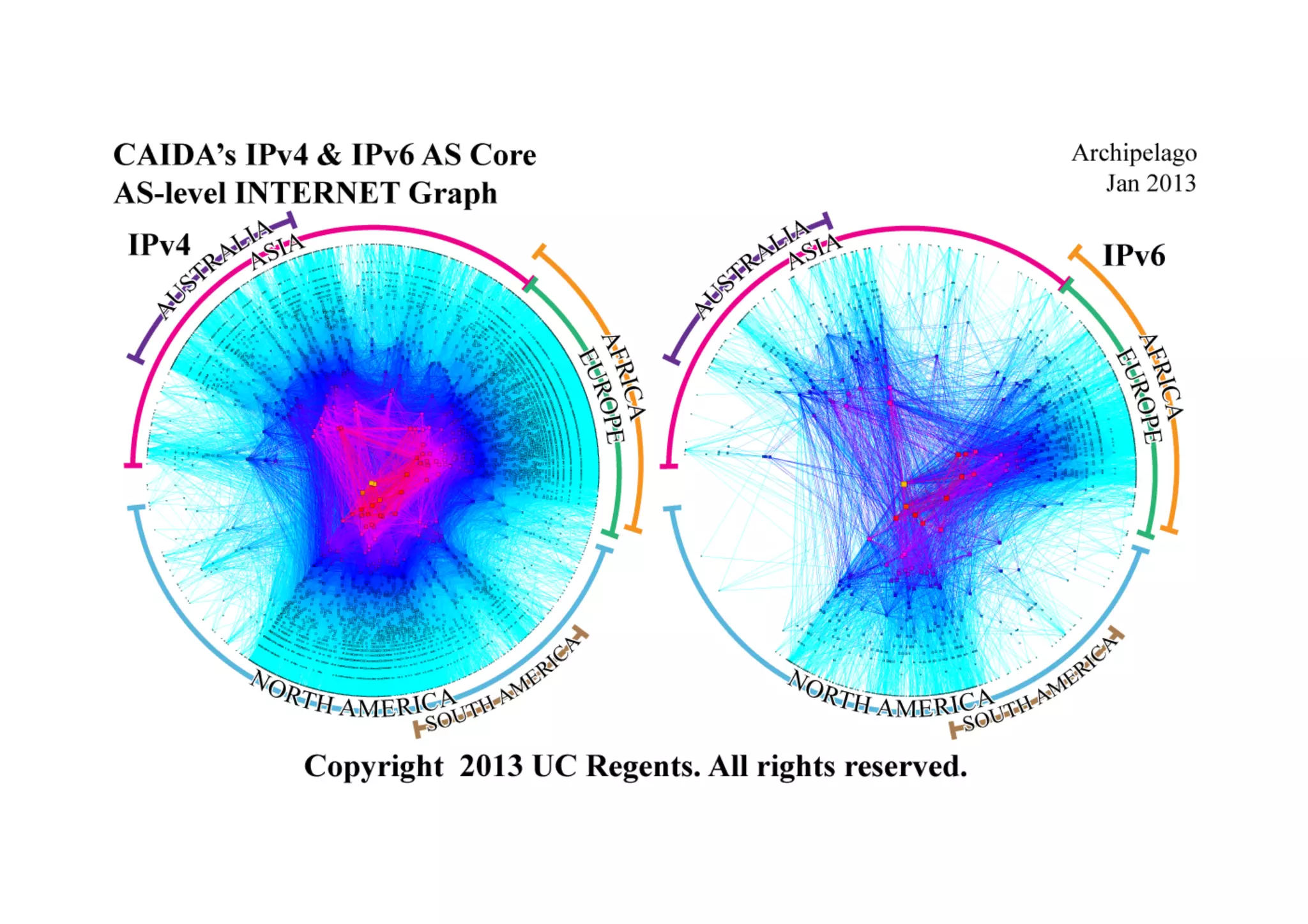
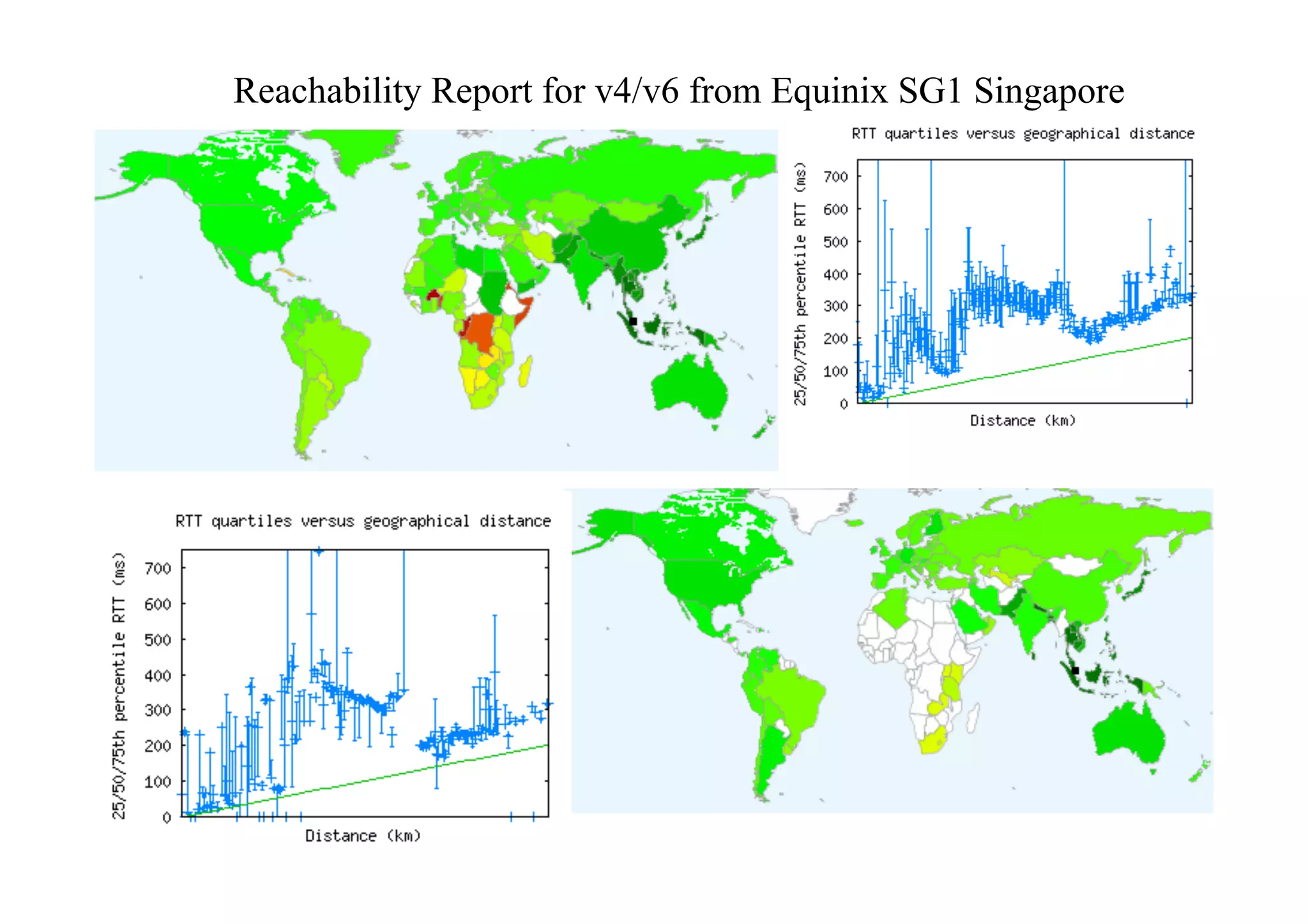
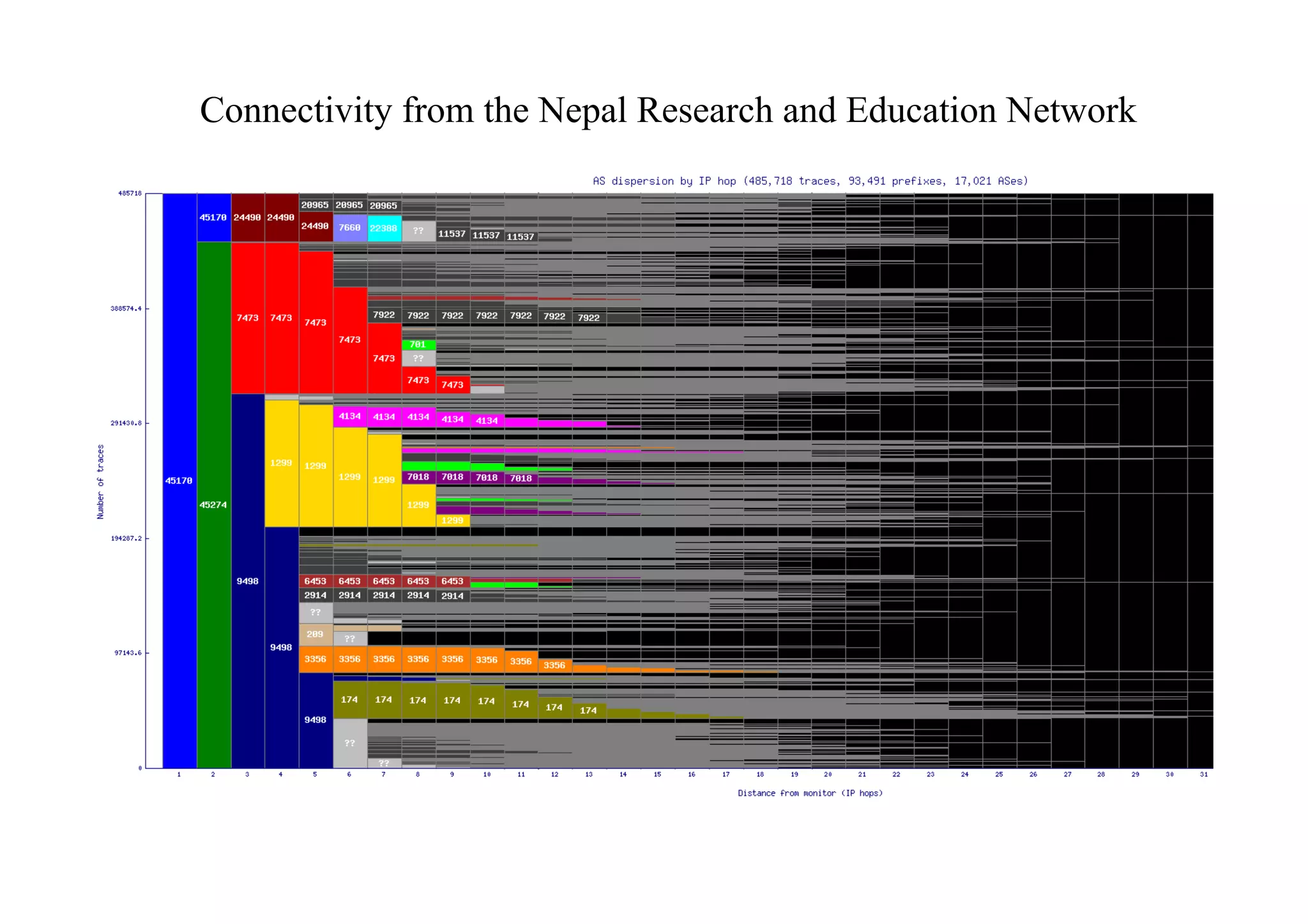
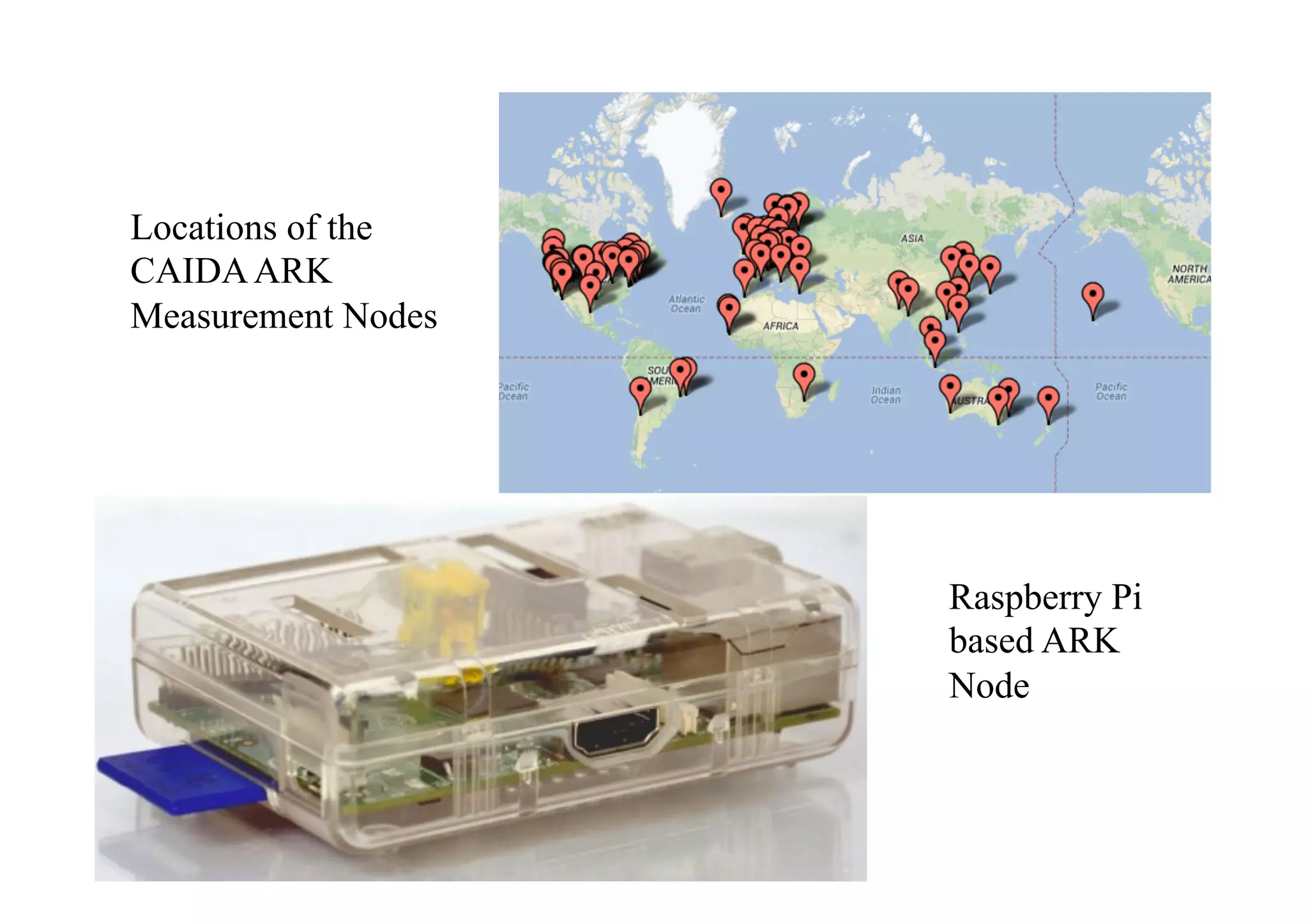
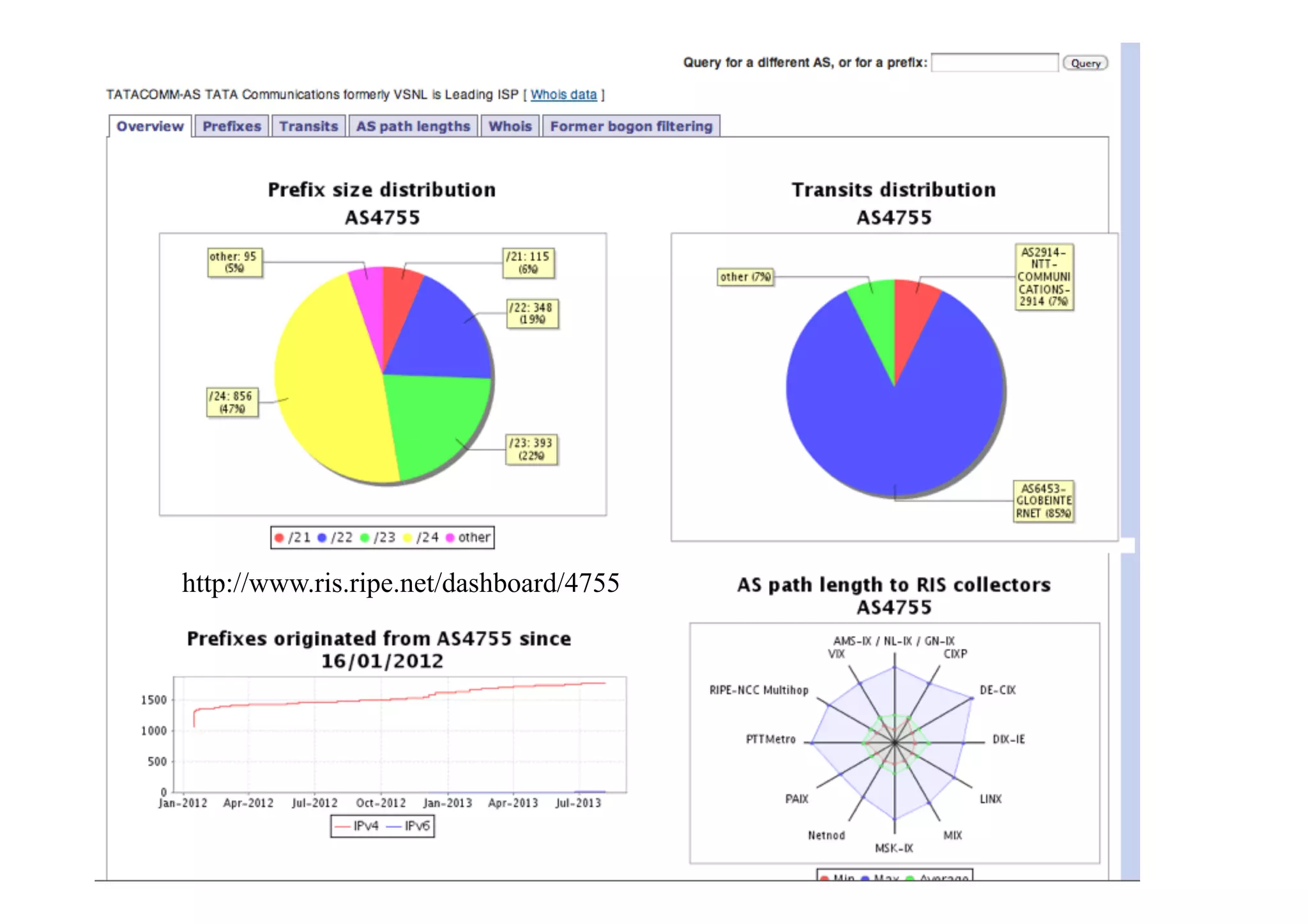
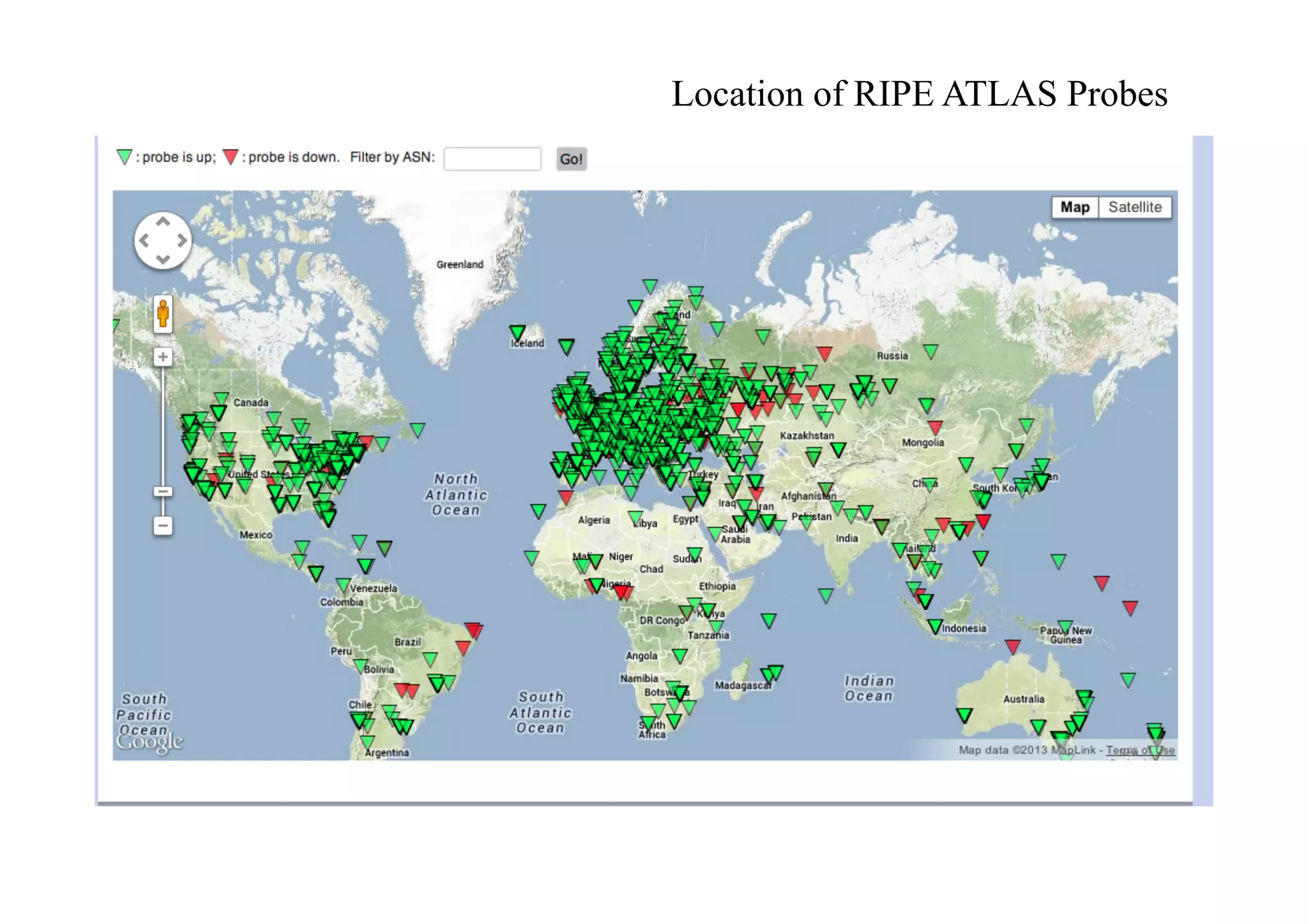
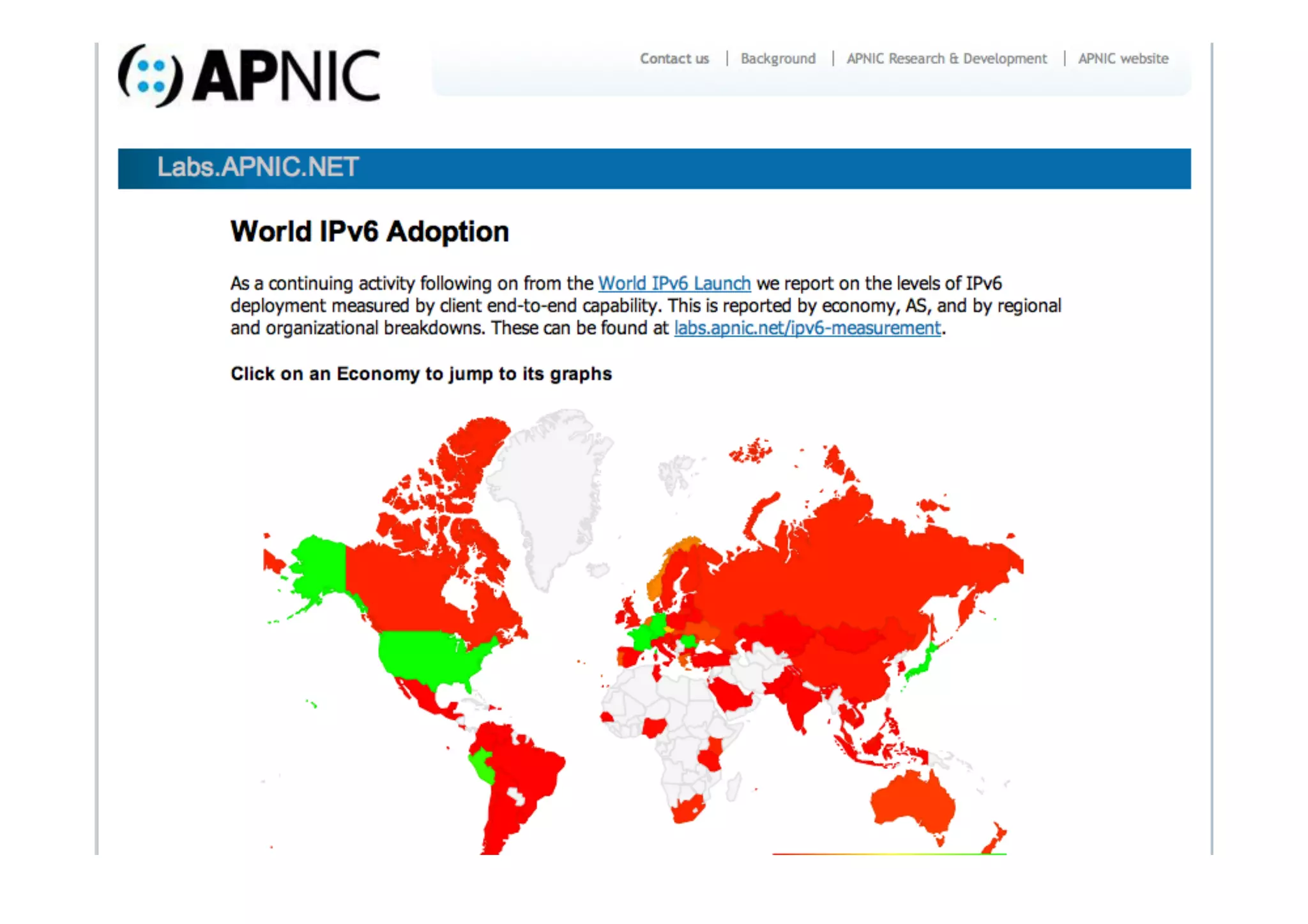
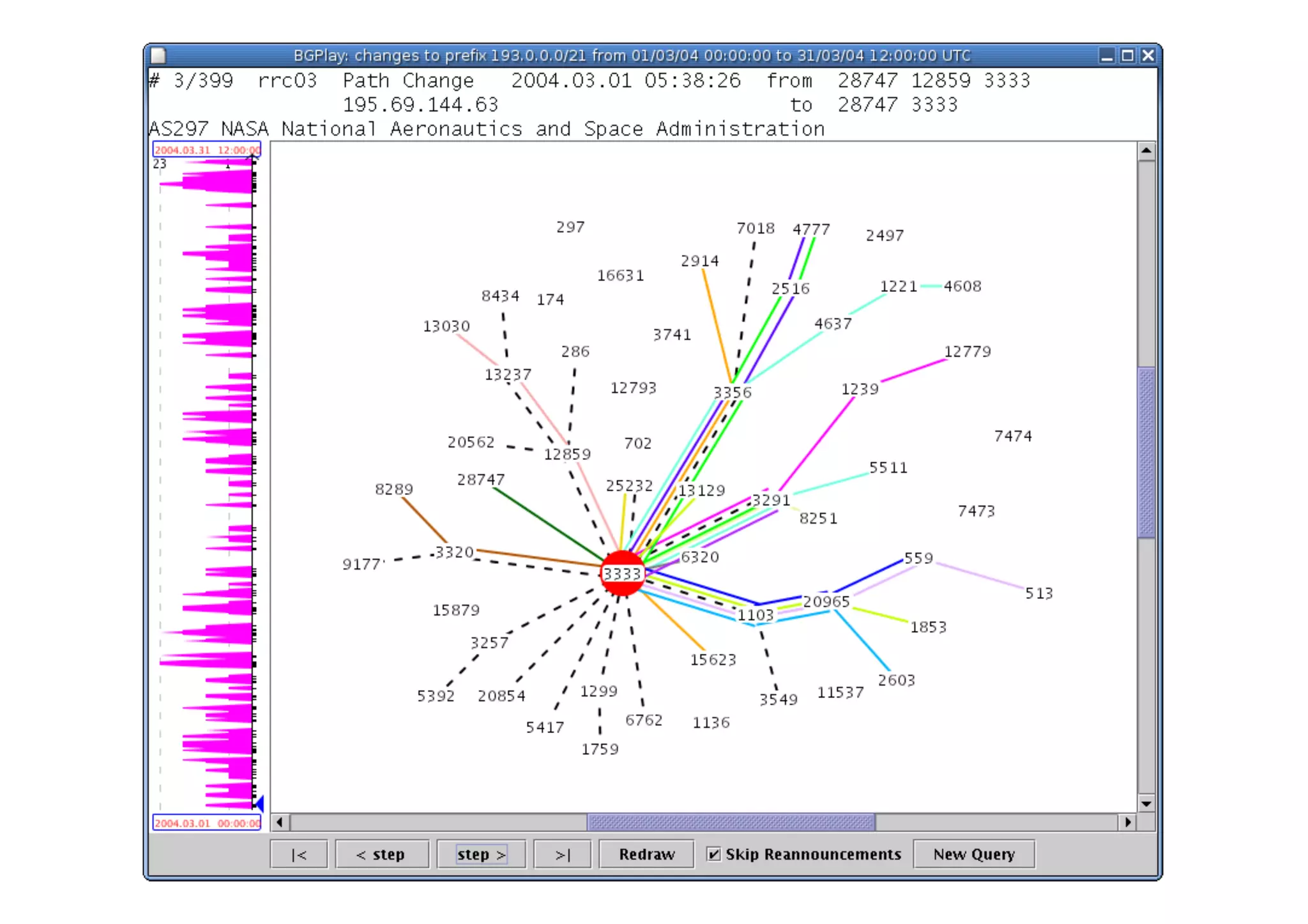
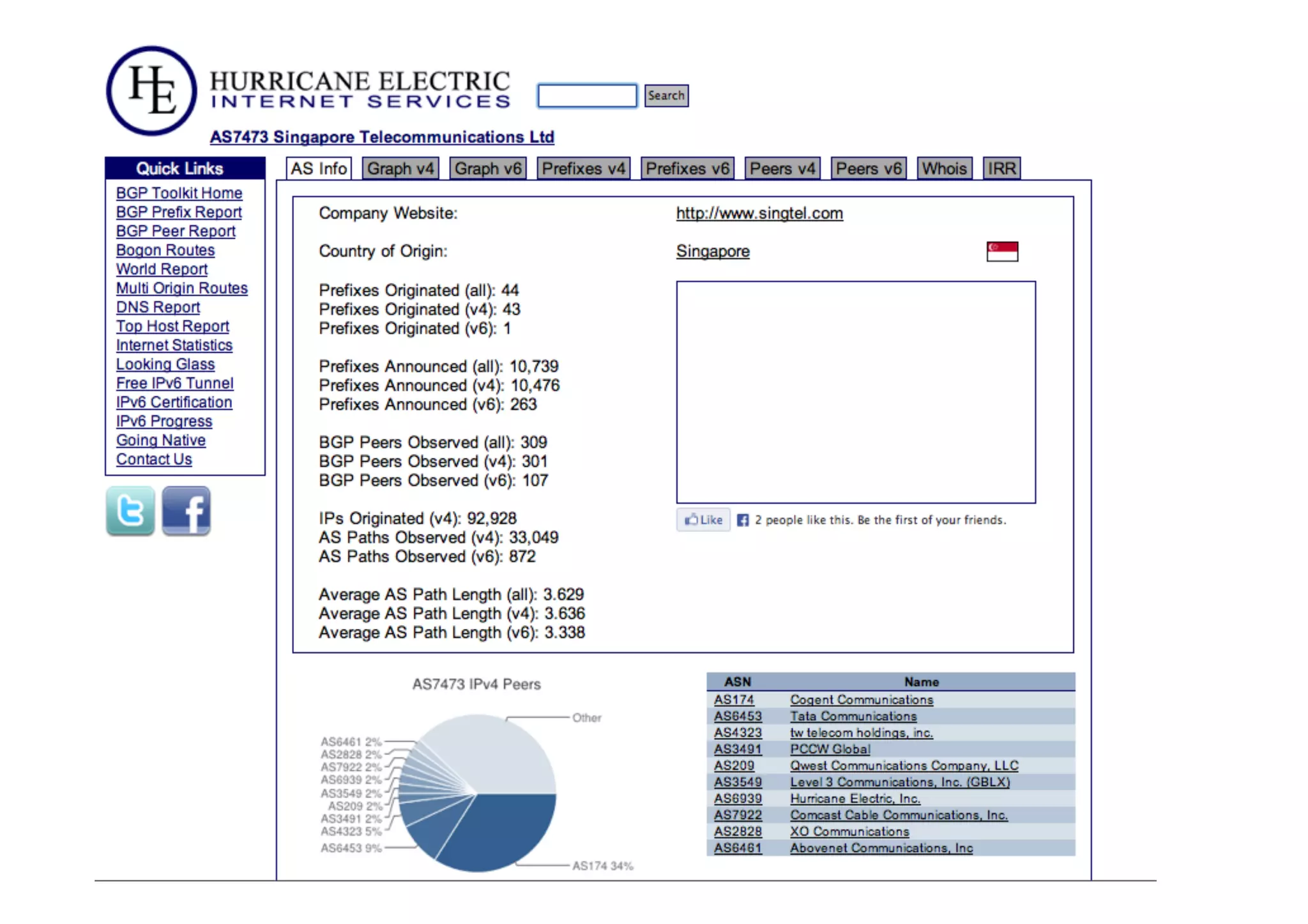
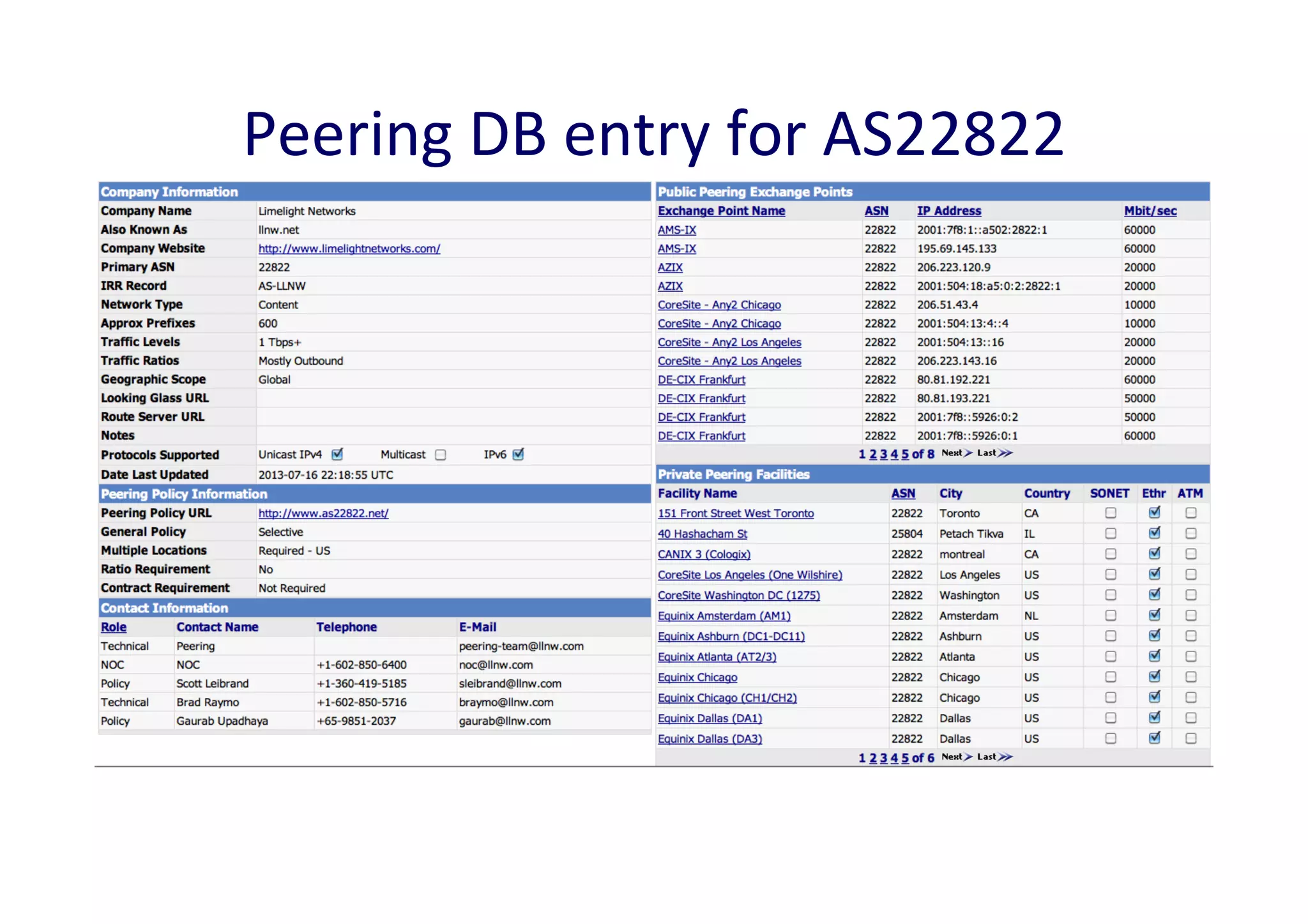
This document discusses various internet measurement tools and their usefulness for network engineers. It describes tools run by academic groups like CAIDA and RIPE, as well as community/industry tools like Routeviews, CIDR Report, and looking glasses. These tools provide continuous measurements of reachability, routing tables, latency, and BGP updates to help monitor and understand internet performance and stability.