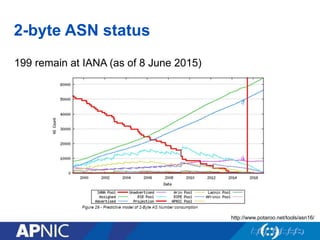
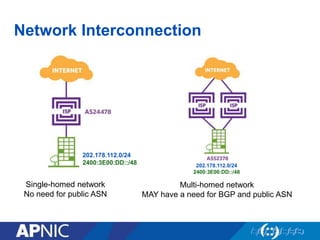
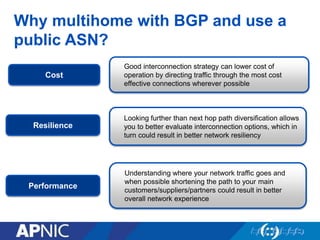
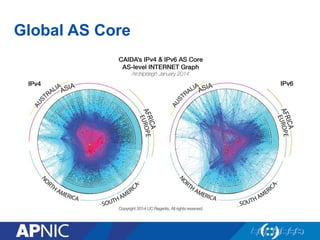
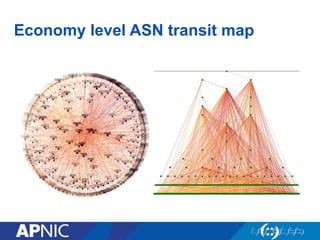
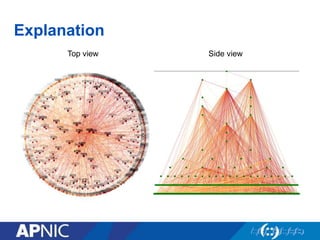
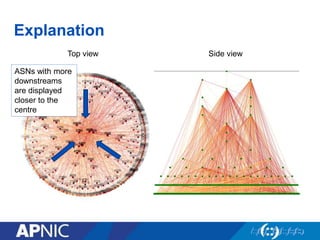
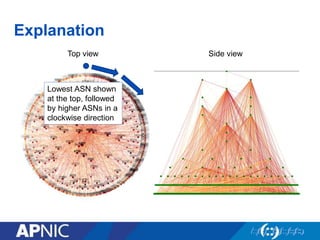
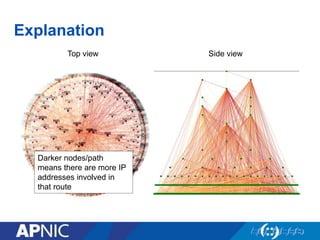
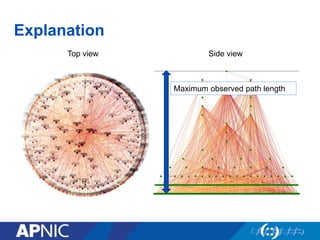
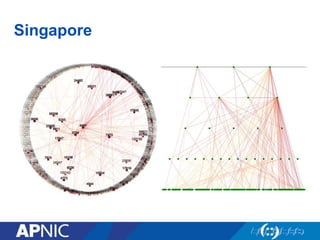
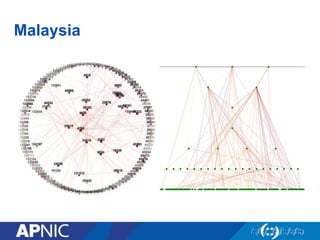
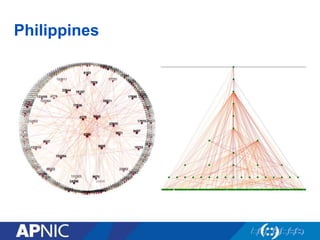
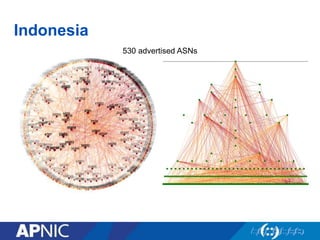
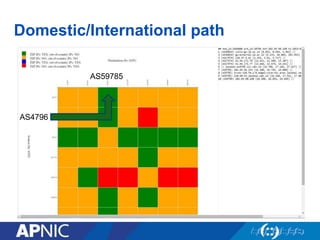
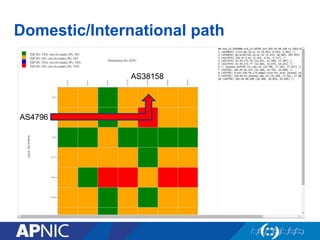
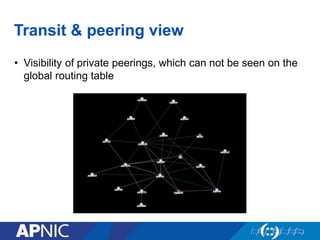
The document provides an overview of Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) including how they are distributed and used for interconnection in Indonesia. It notes that Indonesia currently has 530 advertised ASNs and discusses challenges around the adoption of 4-byte ASNs in the country. The document also visualizes Indonesia's position within the global routing ecosystem and provides recommendations around routing security, resource registration, and route aggregation.