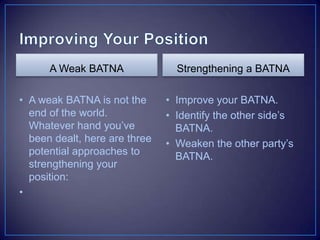
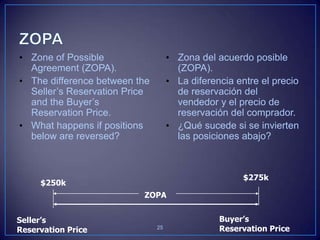
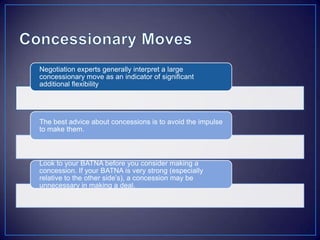
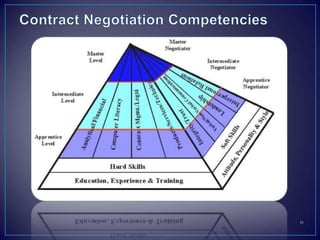
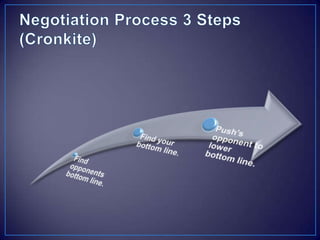
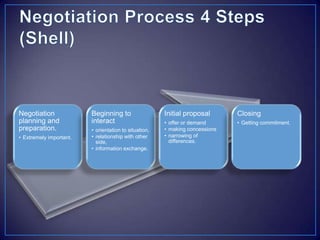
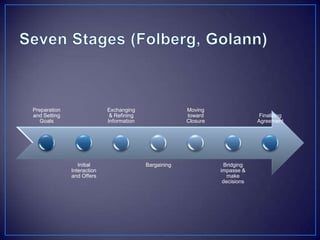
The document discusses various negotiation strategies and techniques, including when to negotiate and when not to, different negotiation styles, preparing for negotiation by understanding interests and alternatives, anchoring offers, expanding the negotiation issues, and tips for opening offers such as framing proposals optimistically within reason. It provides an overview of international negotiation concepts and best practices.