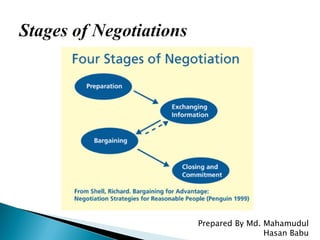
The document discusses various aspects of negotiation skills and techniques. It covers determining goals, presenting supporting reasons, win-win negotiating involving stating ideal outcomes, preparing for negotiations by gathering information and setting objectives, the importance of questions in understanding other parties, and exchanging terms and concessions during bargaining.