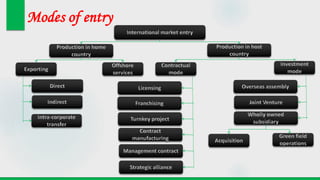
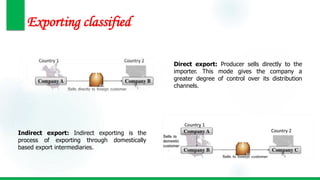
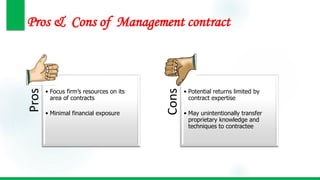
This document discusses various modes of international market entry for companies looking to expand globally. It describes exporting, both direct and indirect; offshore services; international licensing; franchising; turnkey projects; contract manufacturing; and management contracts. For each entry mode, it provides brief definitions and discusses their pros and cons. Management contracts, turnkey projects, and contract manufacturing are referred to as "specialized entry modes" since they involve shorter-term investments and less financial risk than other options. The document aims to help companies understand the different options available for entering international markets.