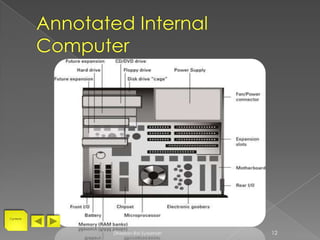
This presentation details the internal components of personal computers, including processors, memory types, adapter cards, storage devices, and input/output hardware. It aims to clarify concepts and enhance understanding of computer components, emphasizing technical specifications and functionalities. Key topics include CPU capabilities, types of RAM, and methods for connecting various devices.