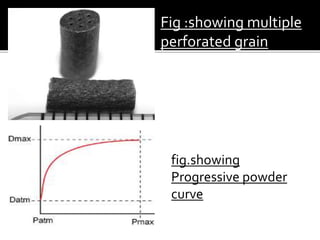
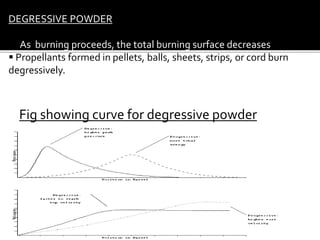
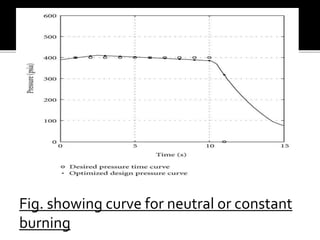
Internal ballistics is the study of what happens inside the barrel of a firearm from the moment of ignition until the projectile exits. When fired, the projectile is accelerated to high velocity by the burning of propellant gases trapped behind it in the barrel. There are three types of propellant powders - progressive powders increase burning surface as they burn, degressive powders decrease burning surface, and neutral powders maintain a constant burning surface.