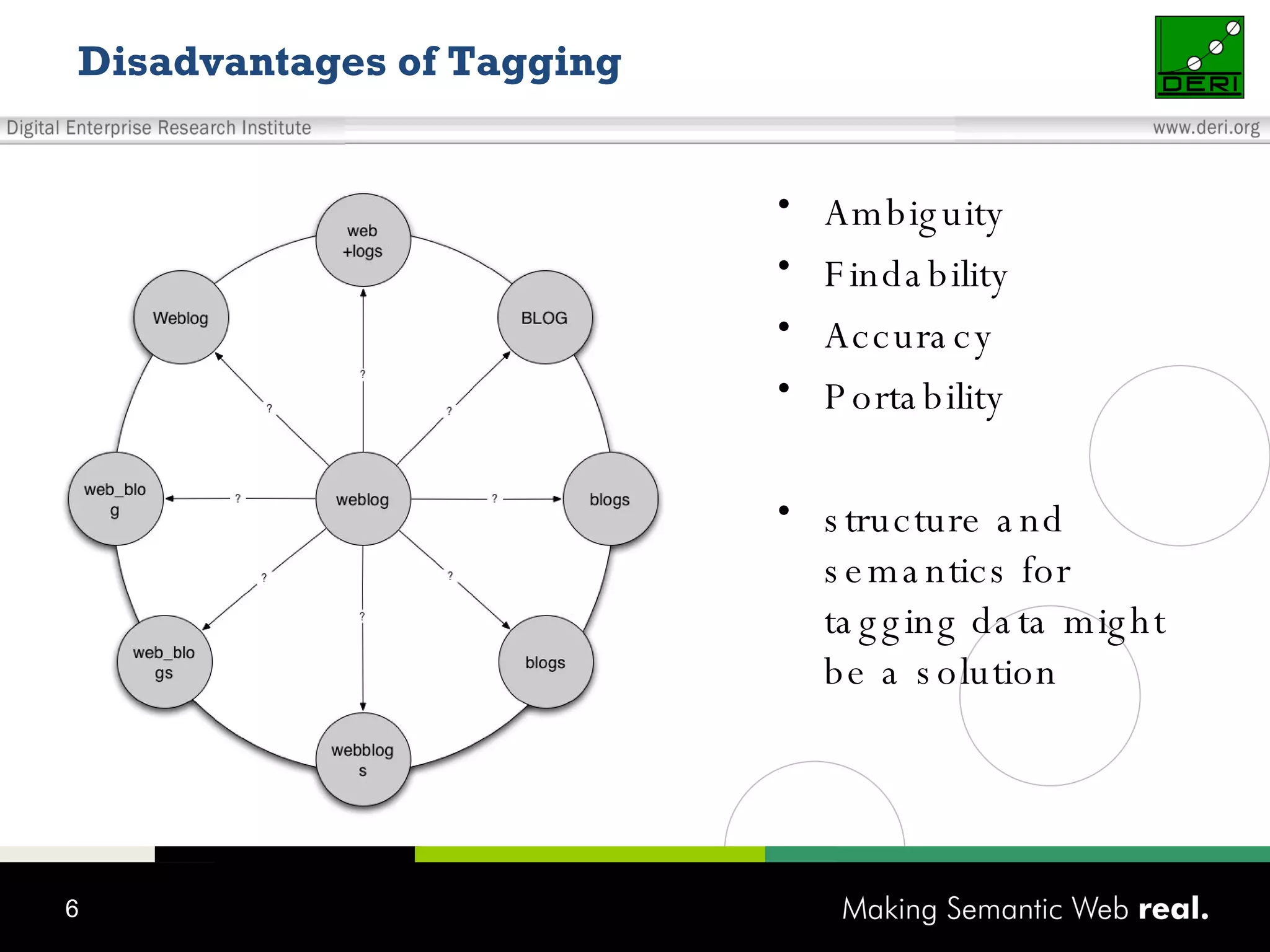
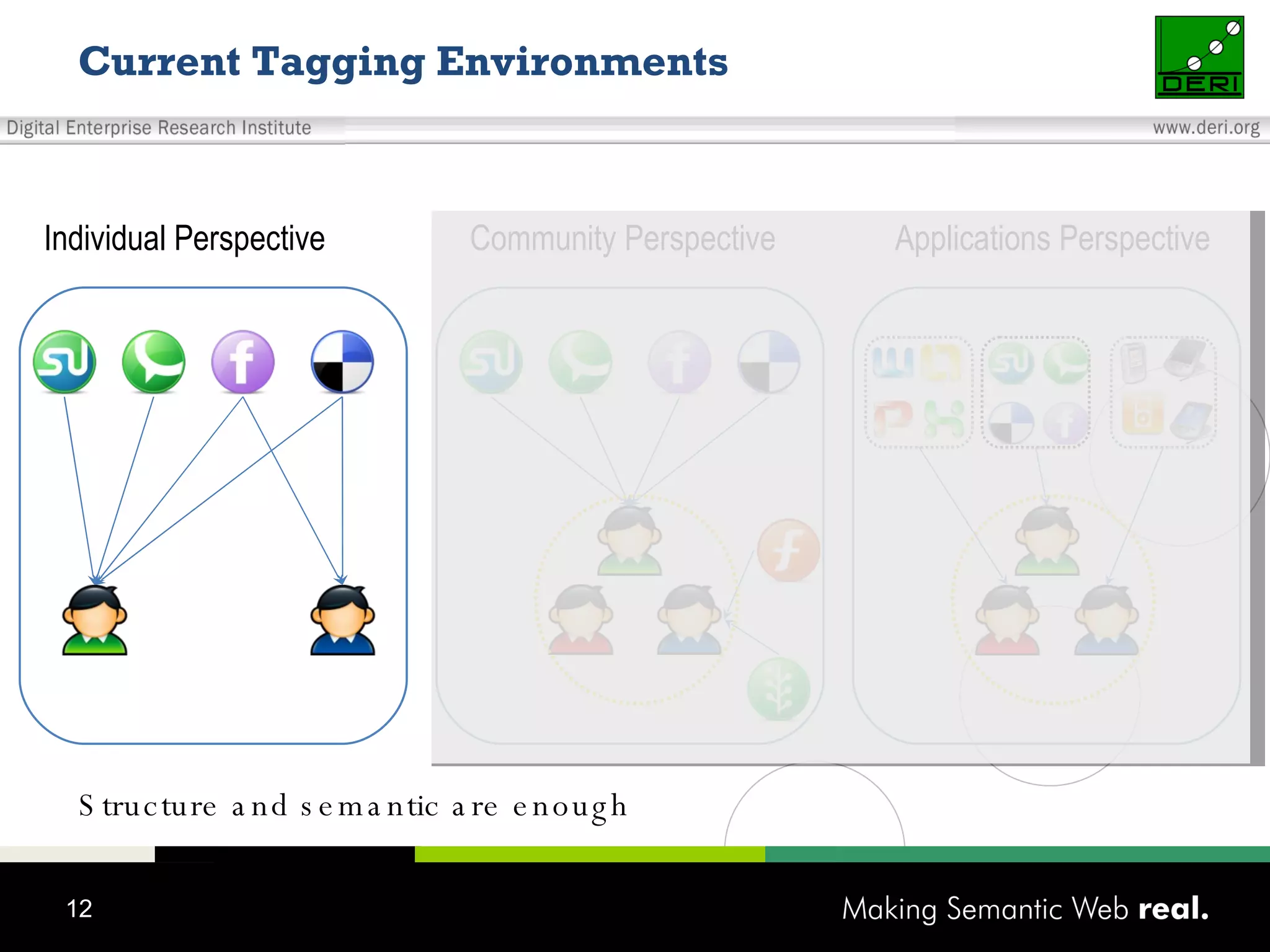
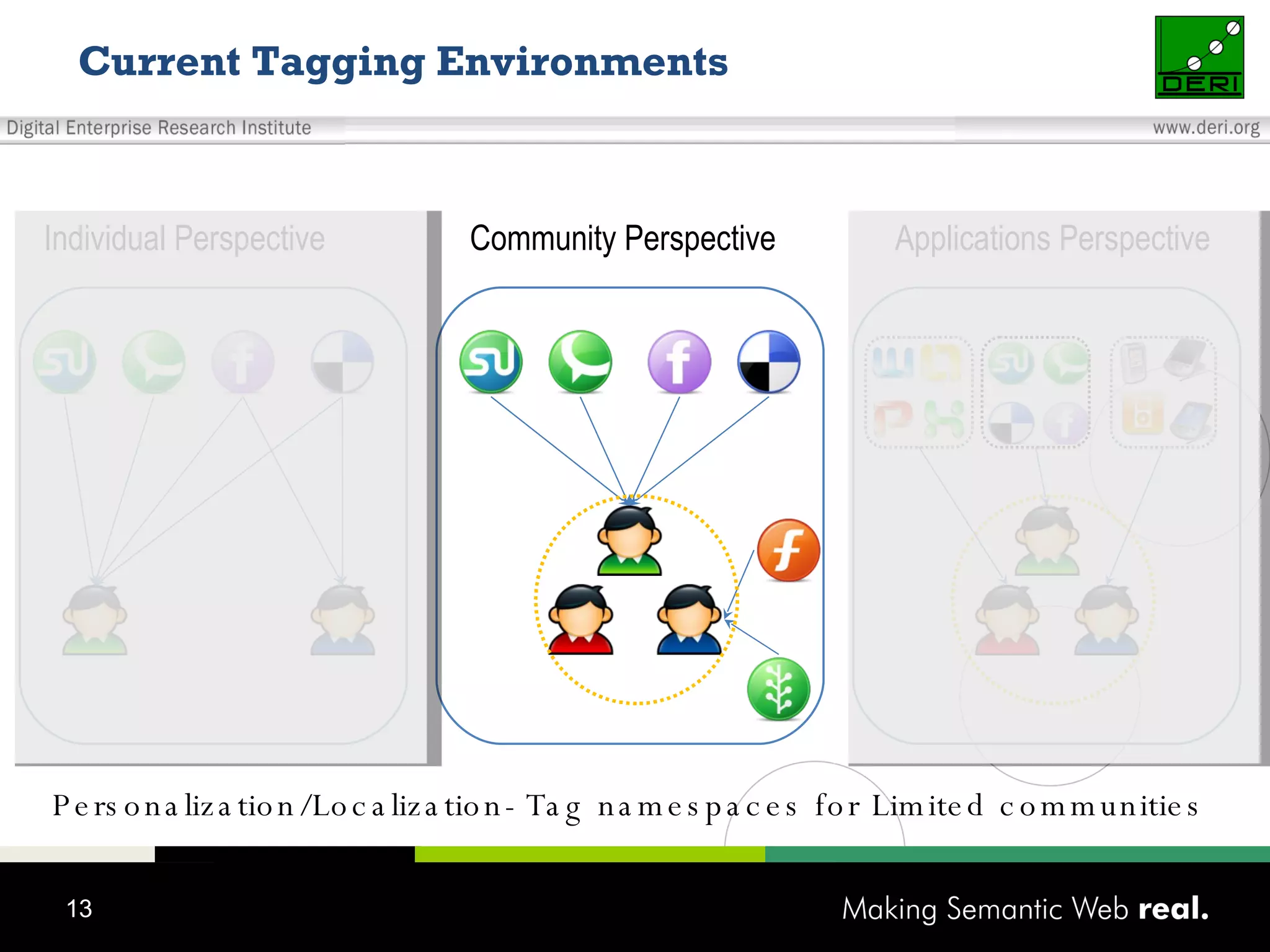
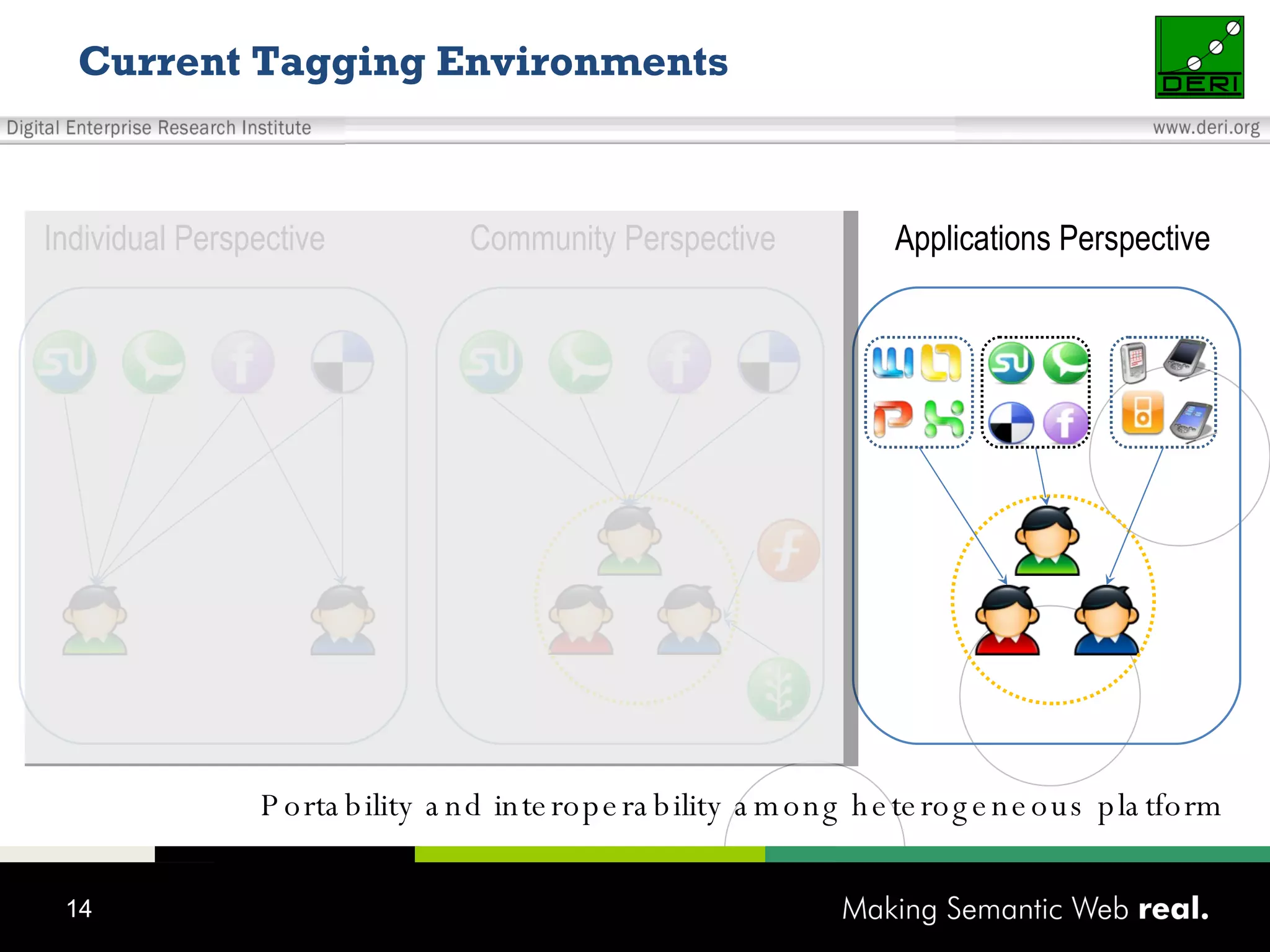
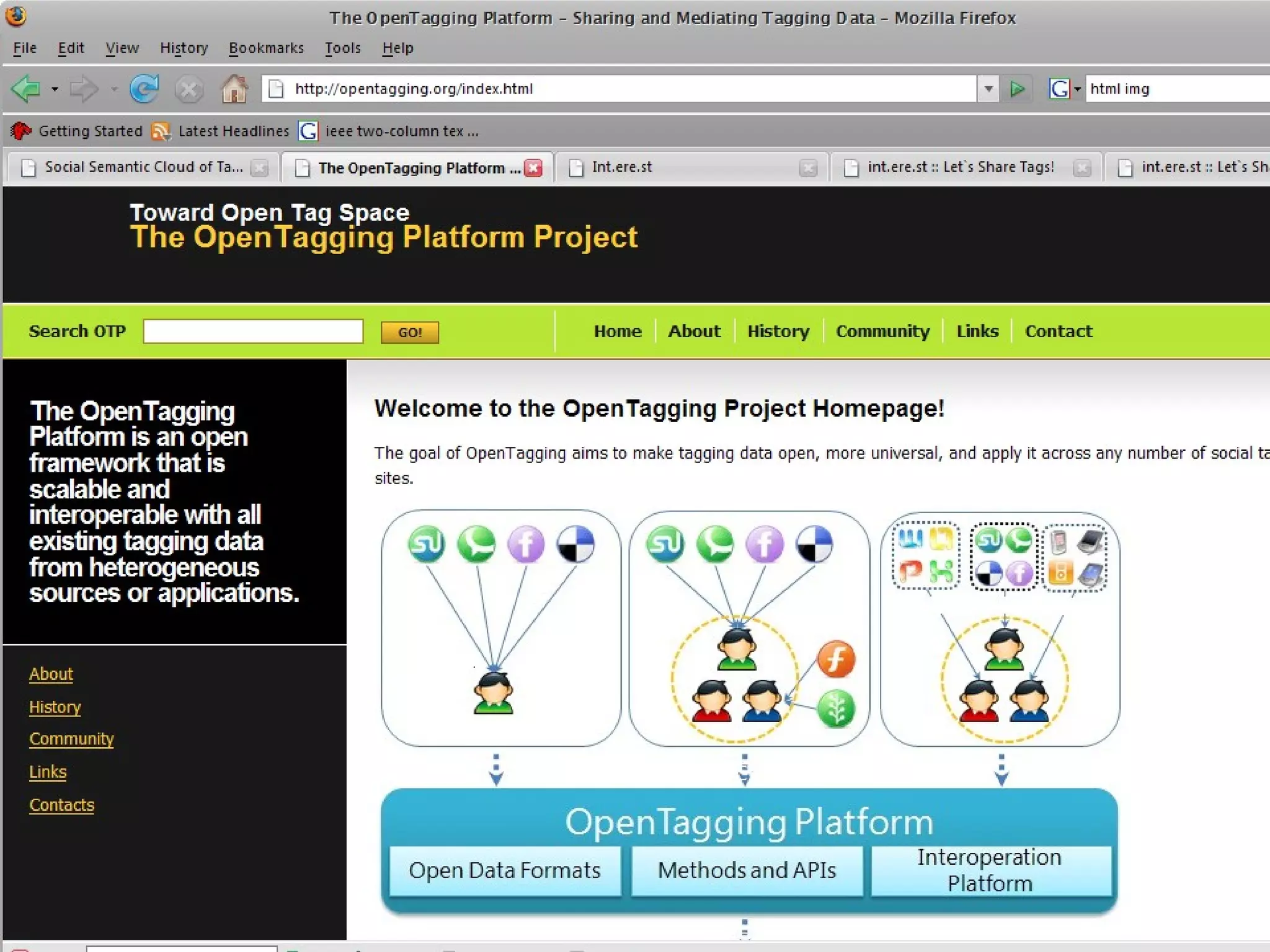
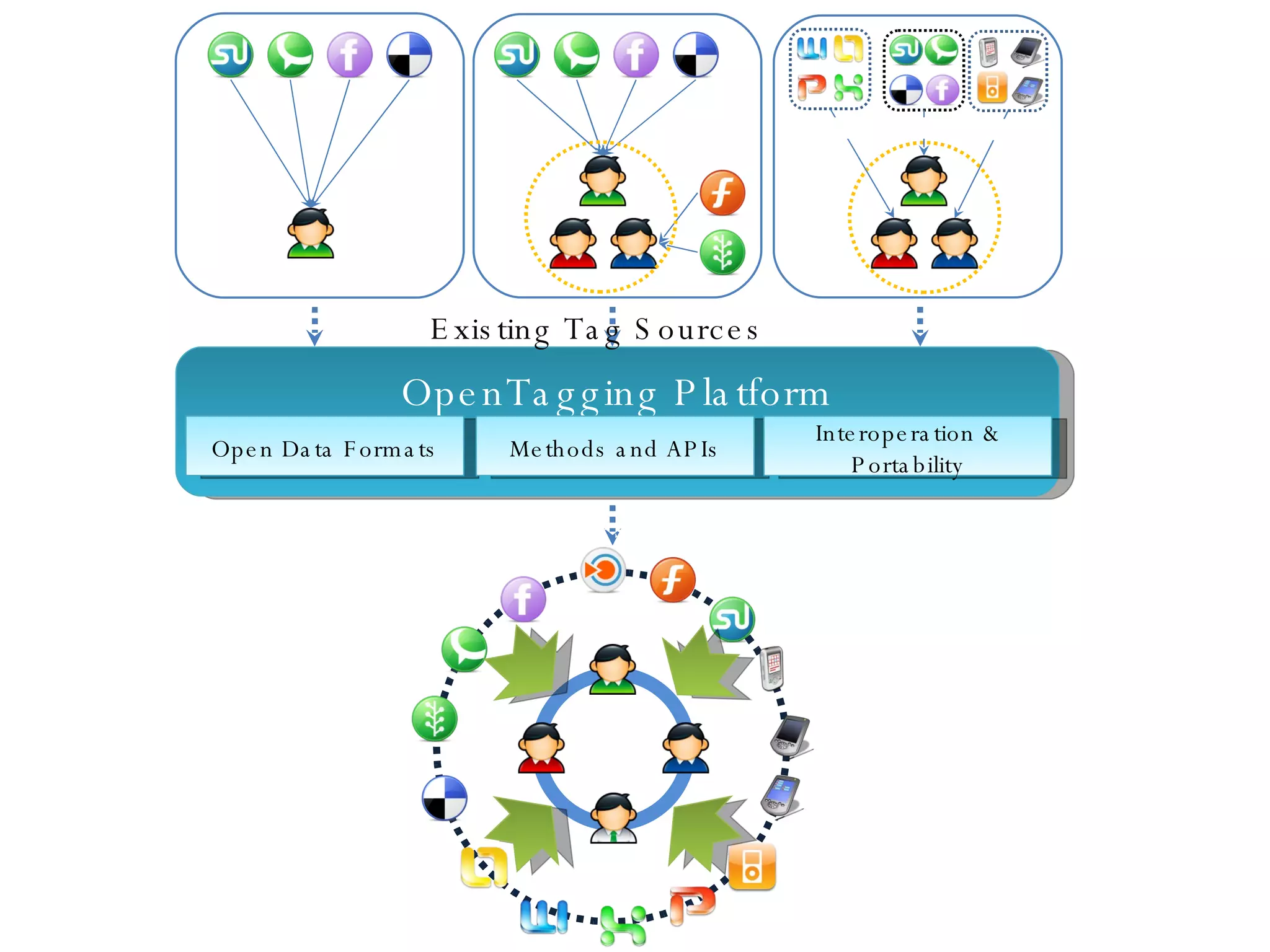
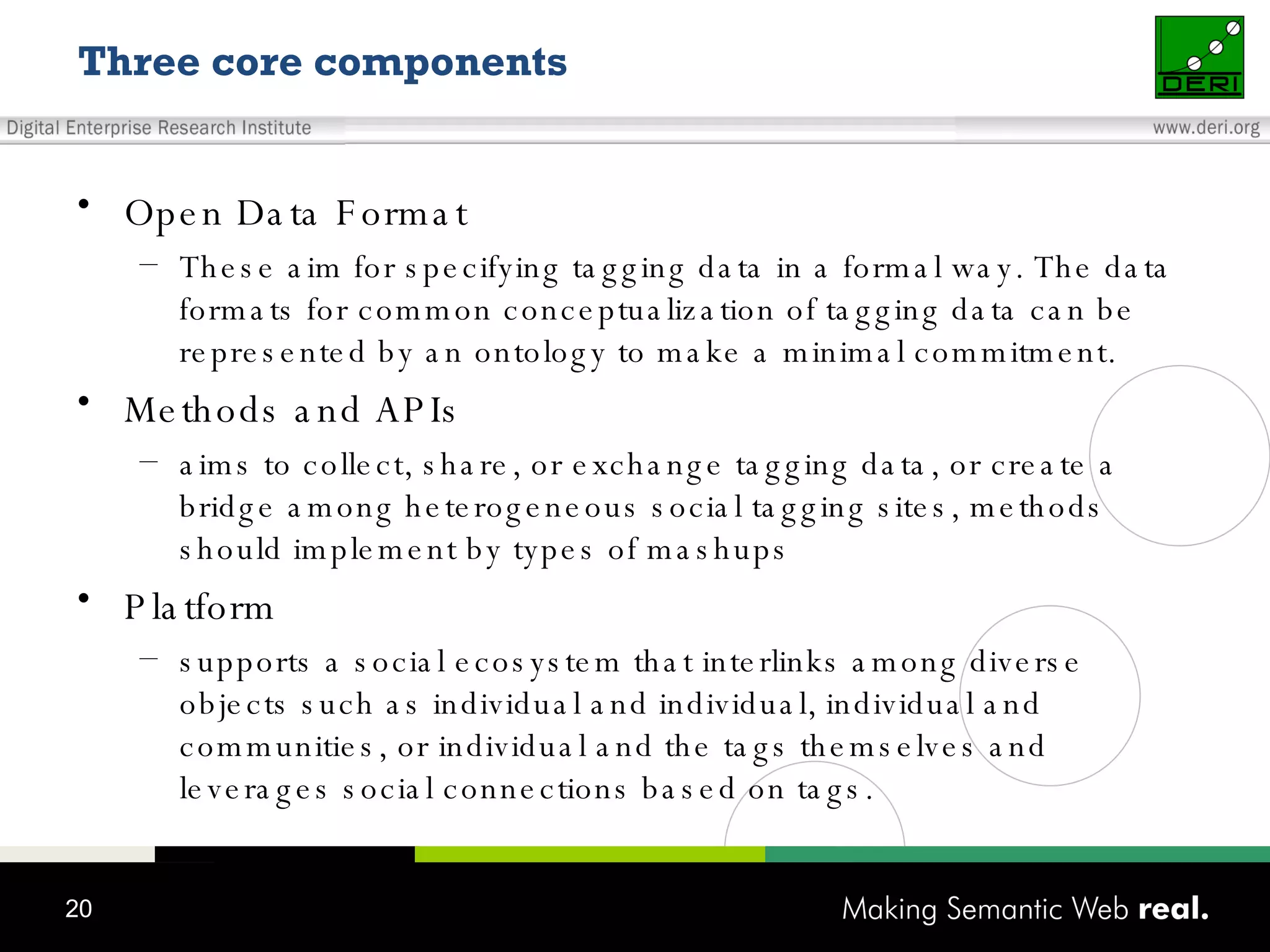
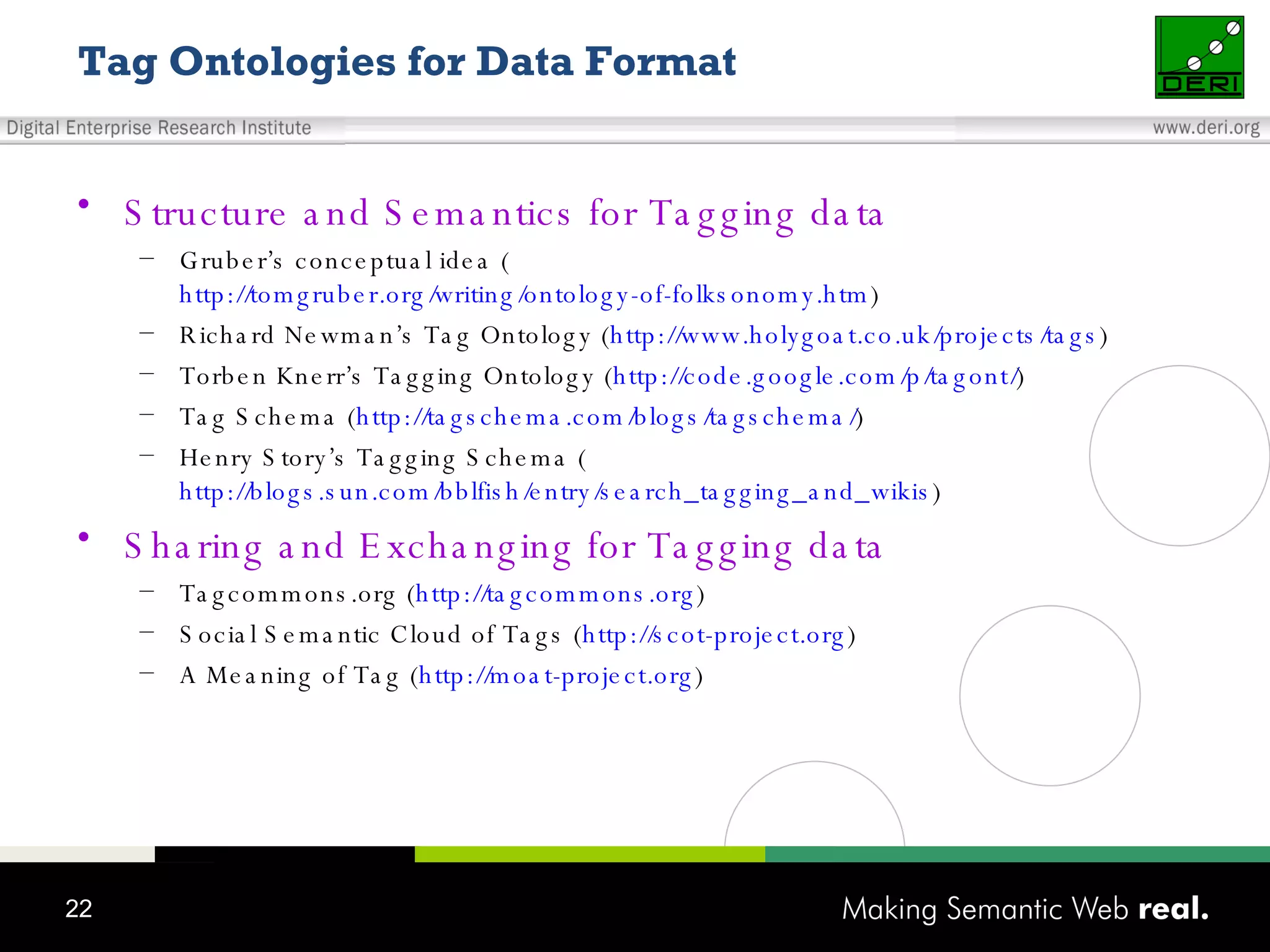
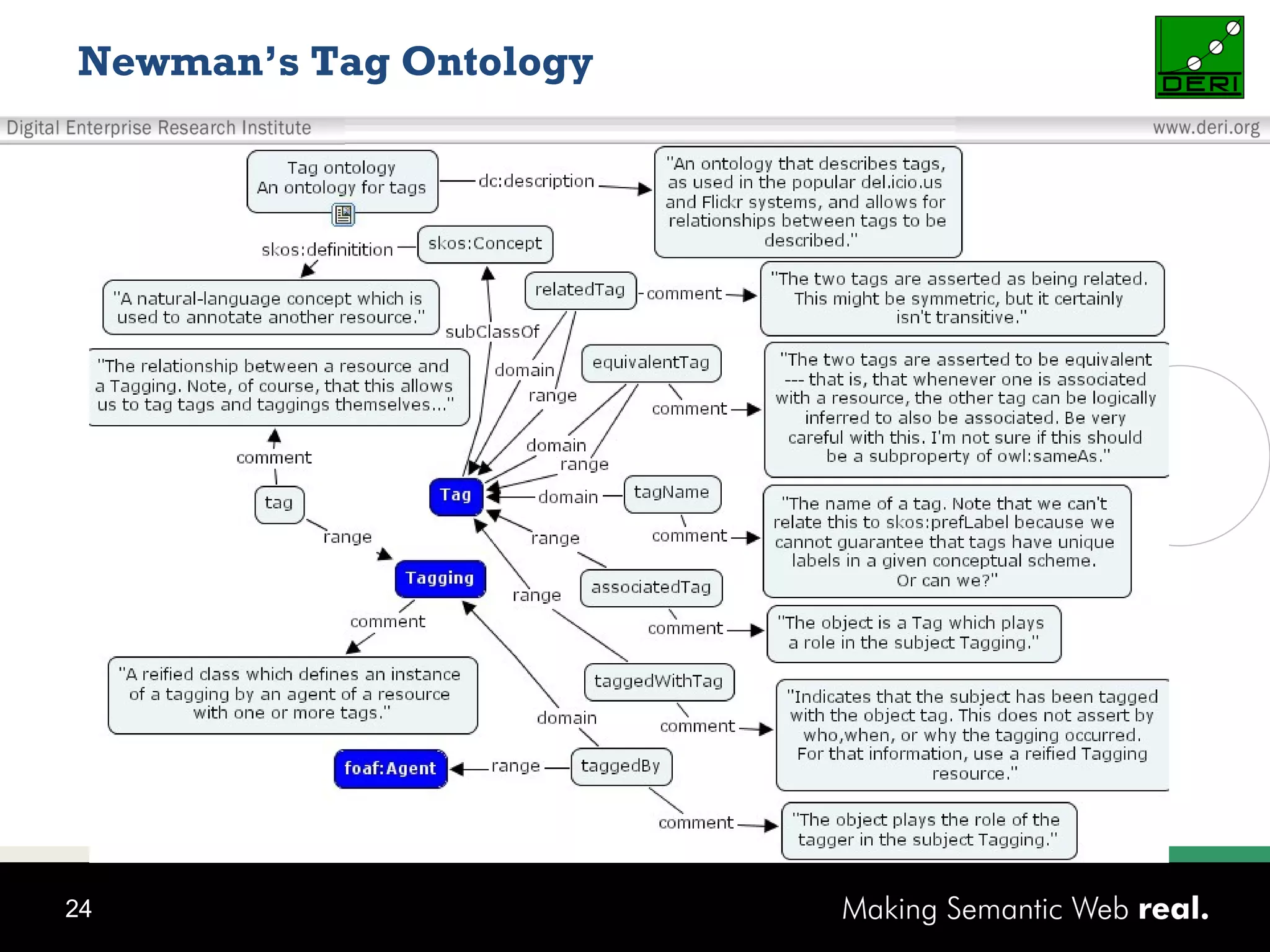
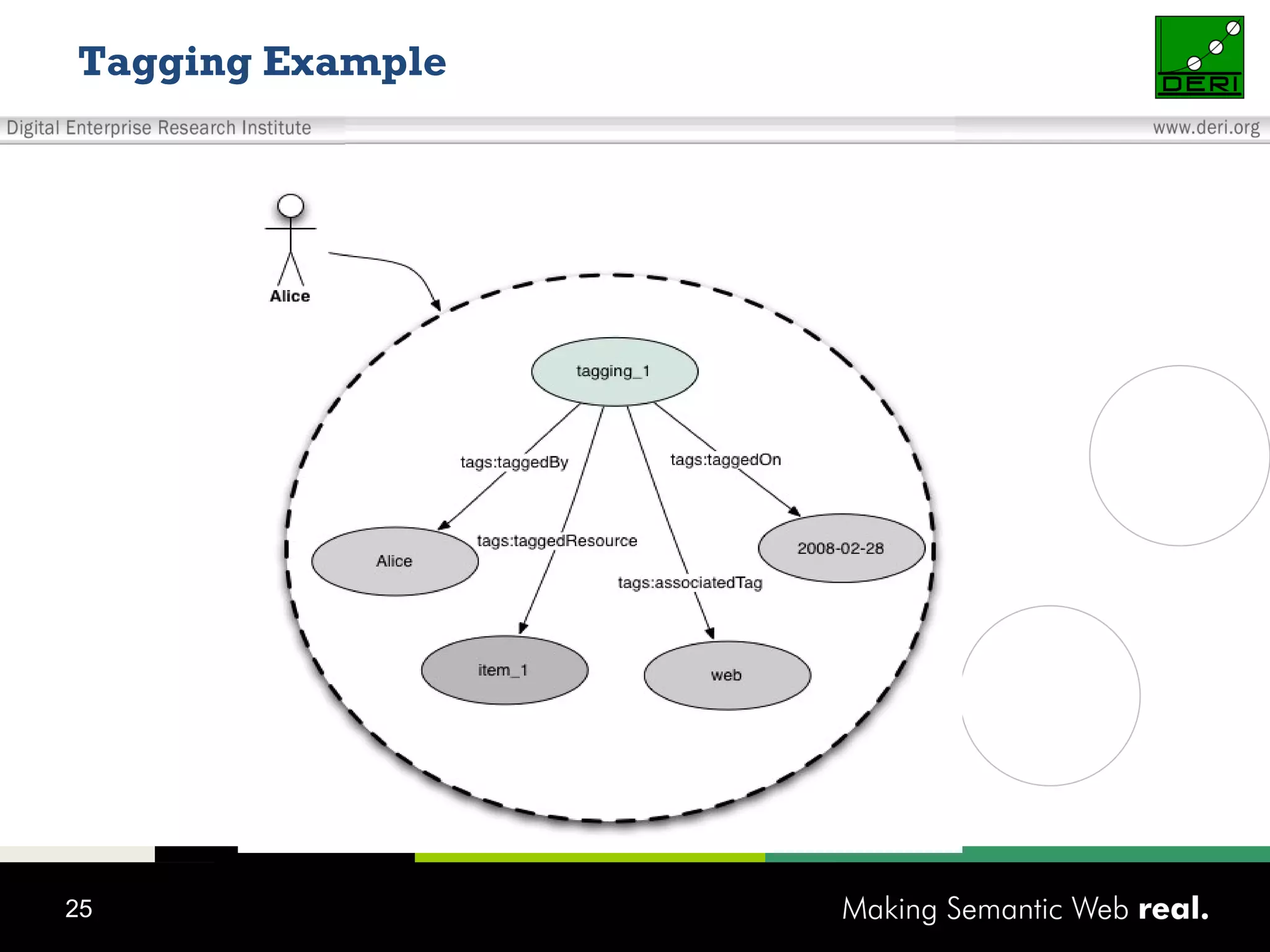
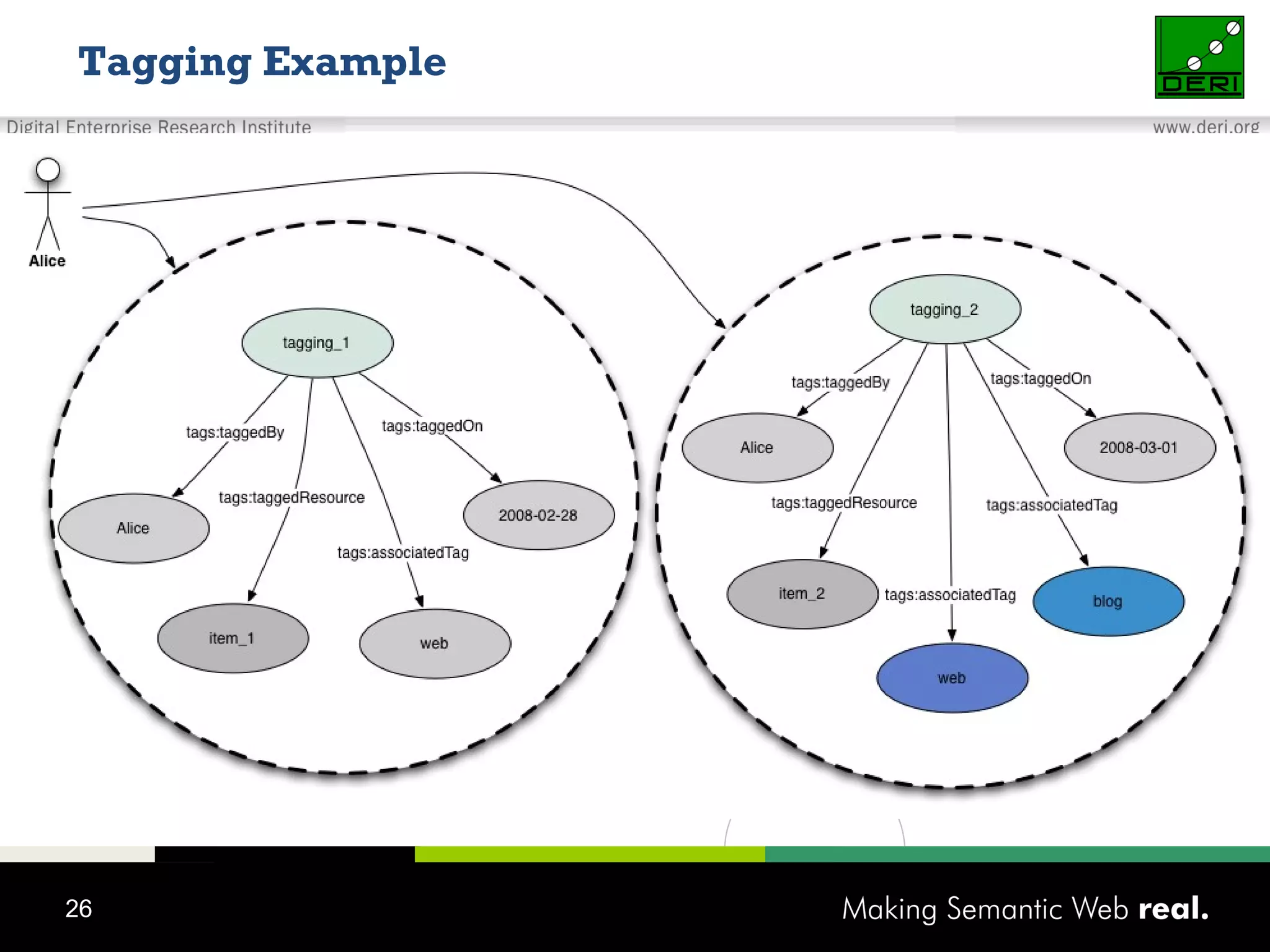
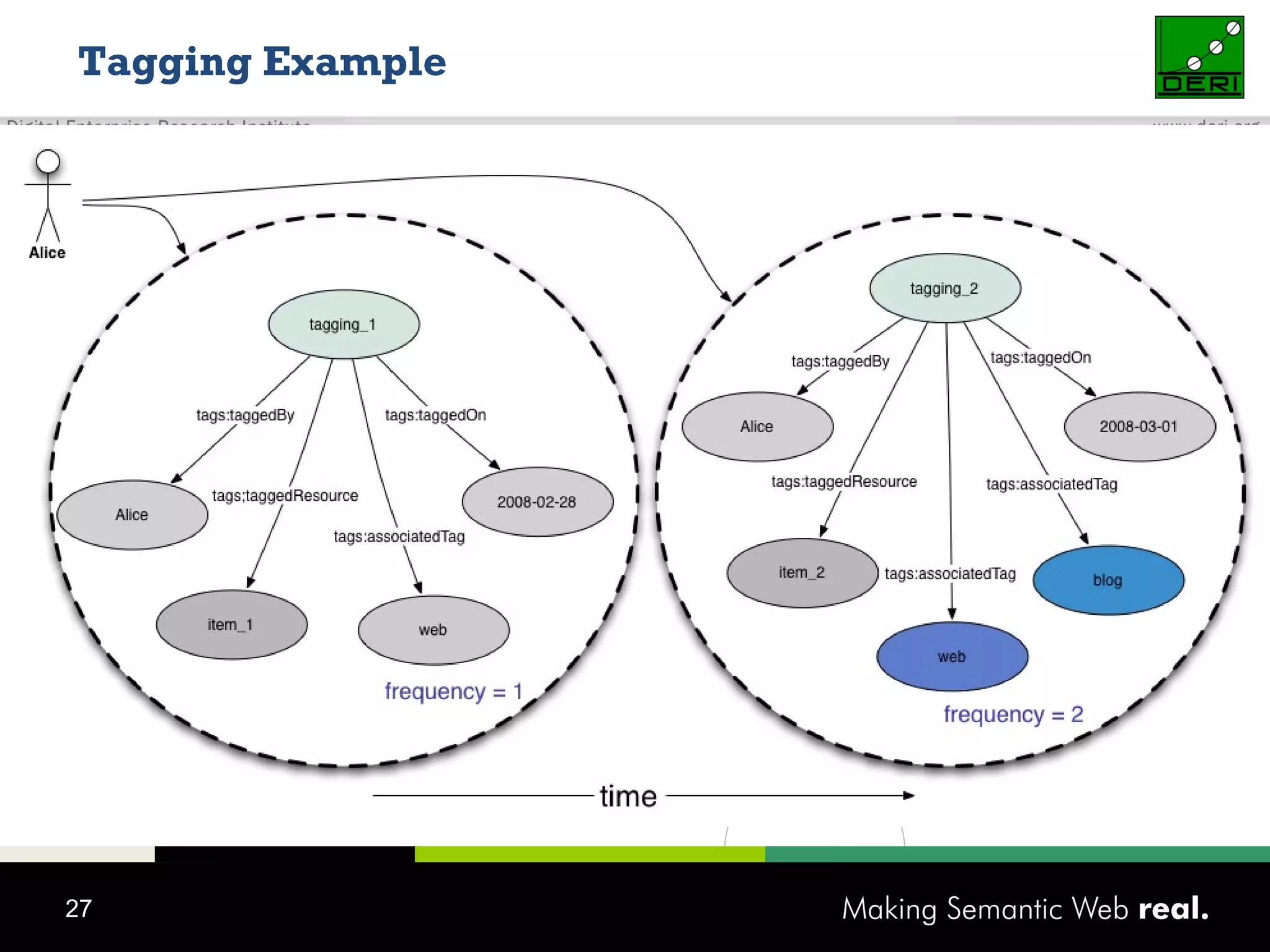
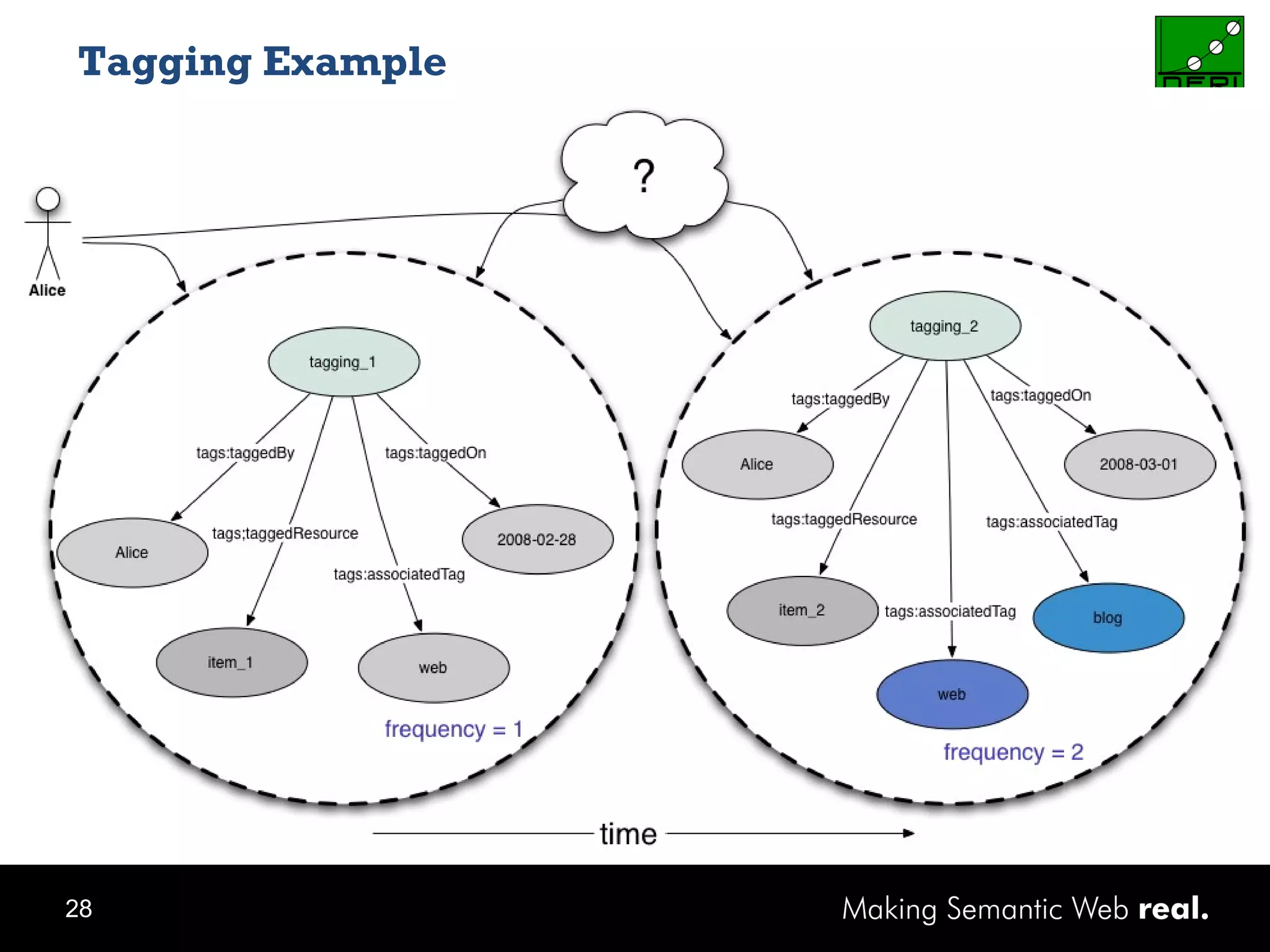
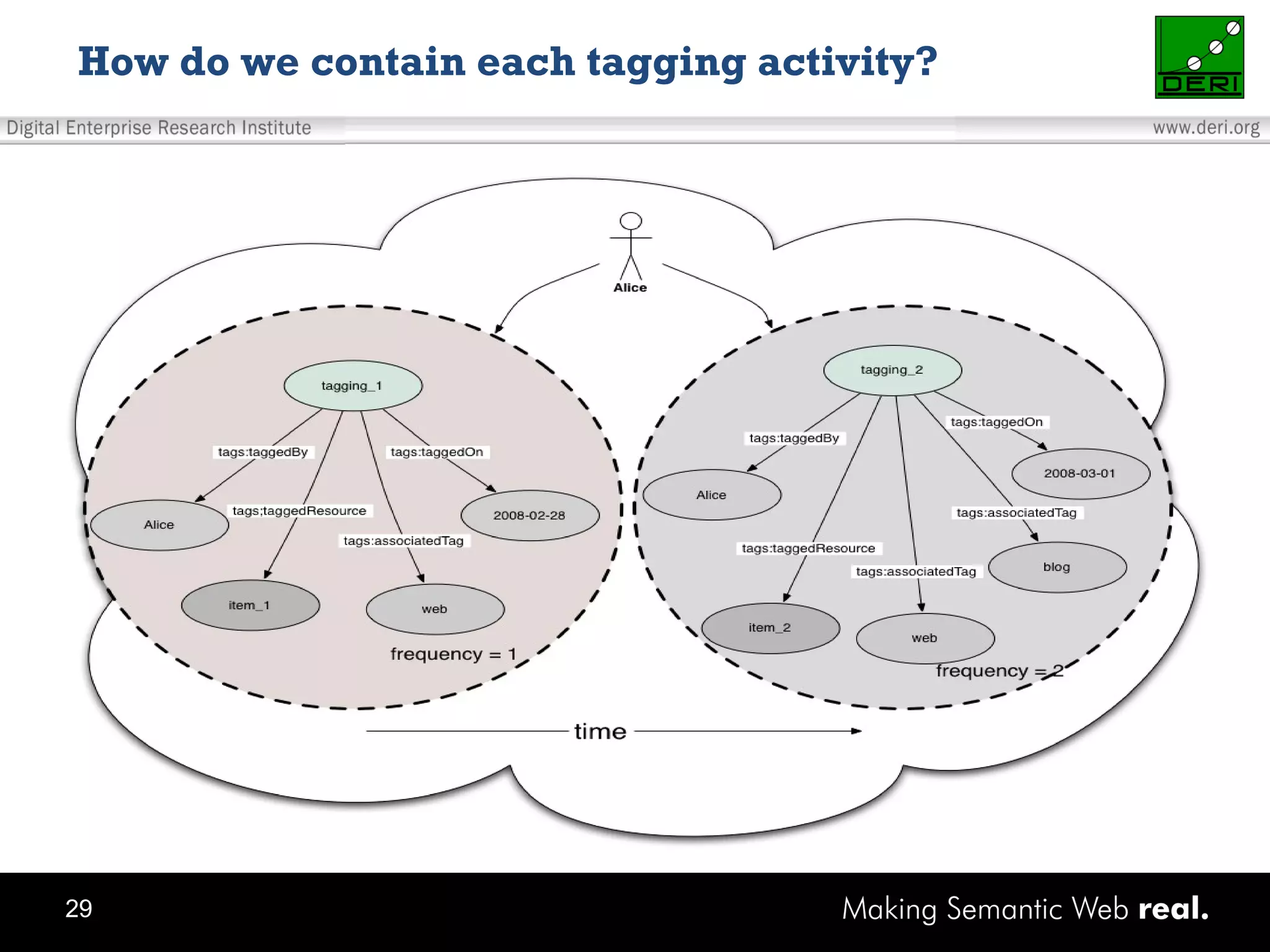
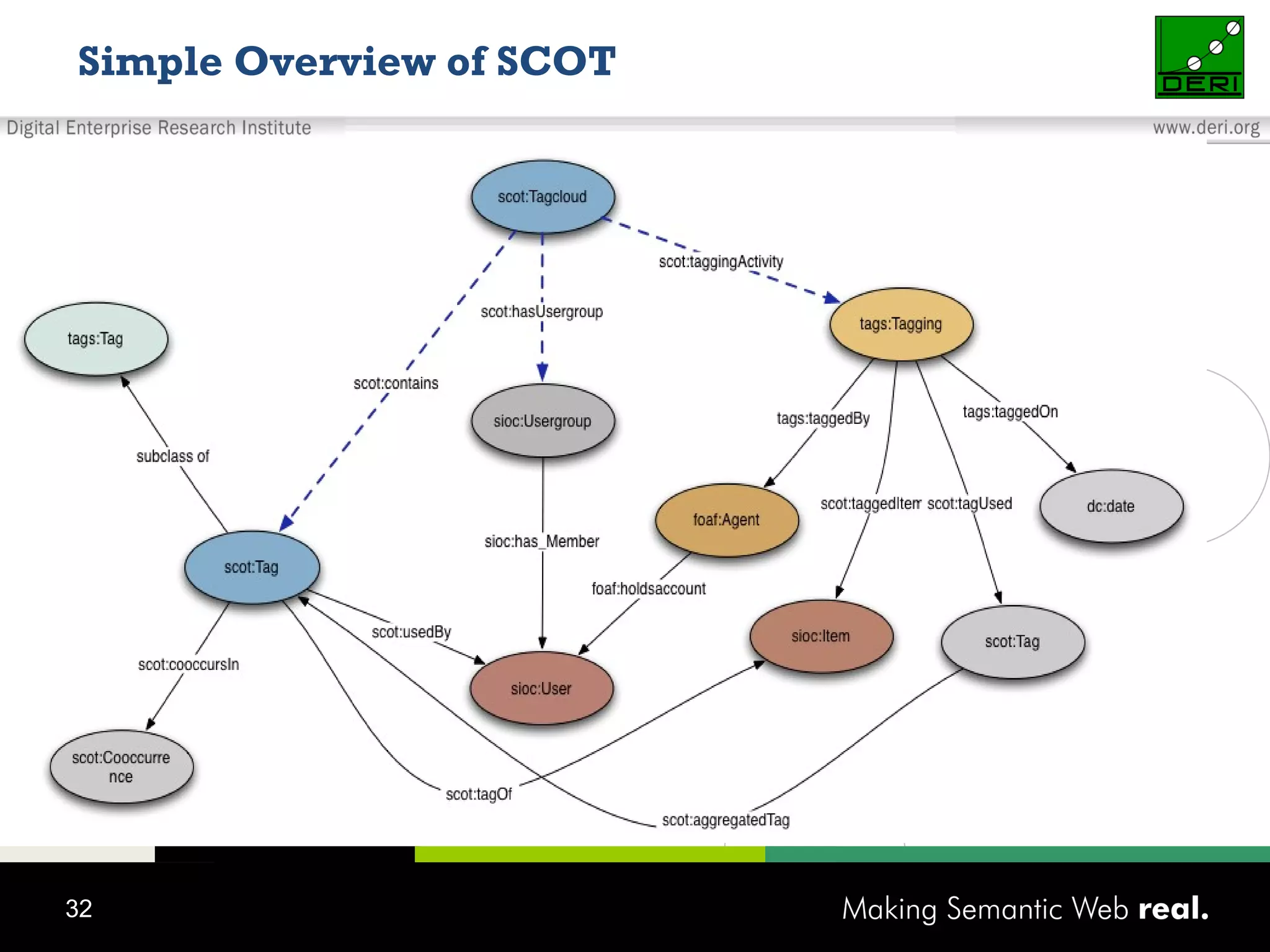
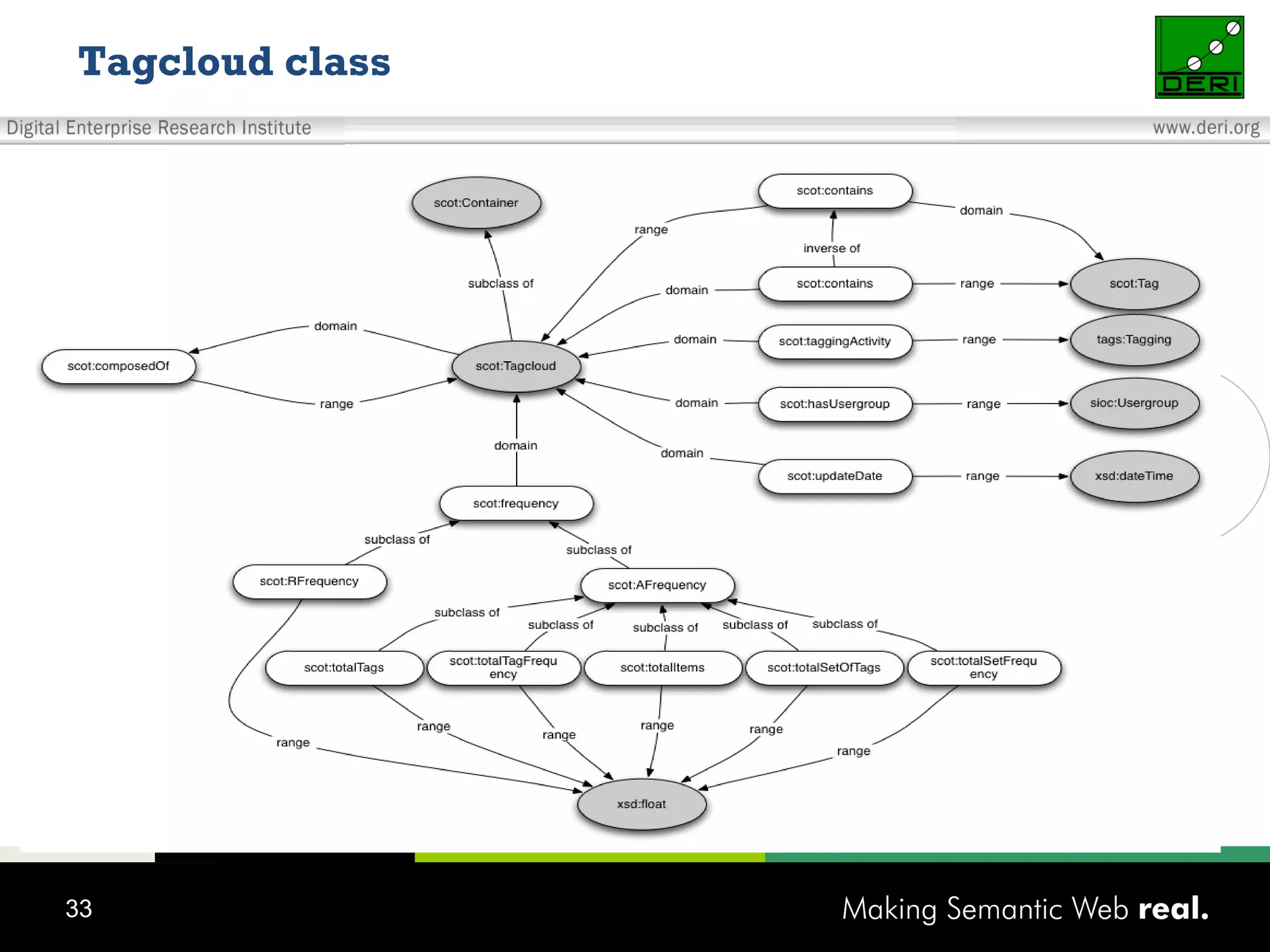
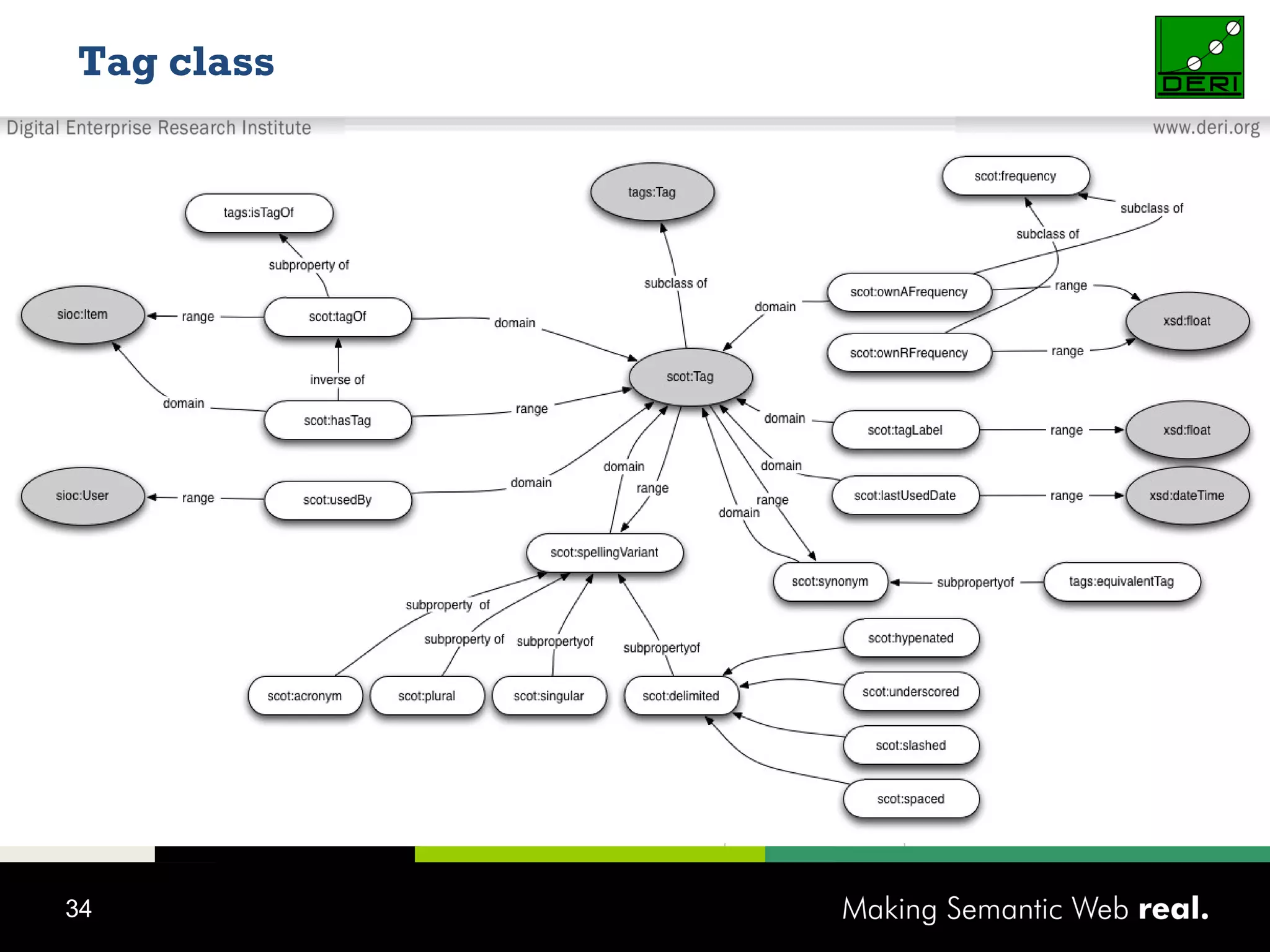
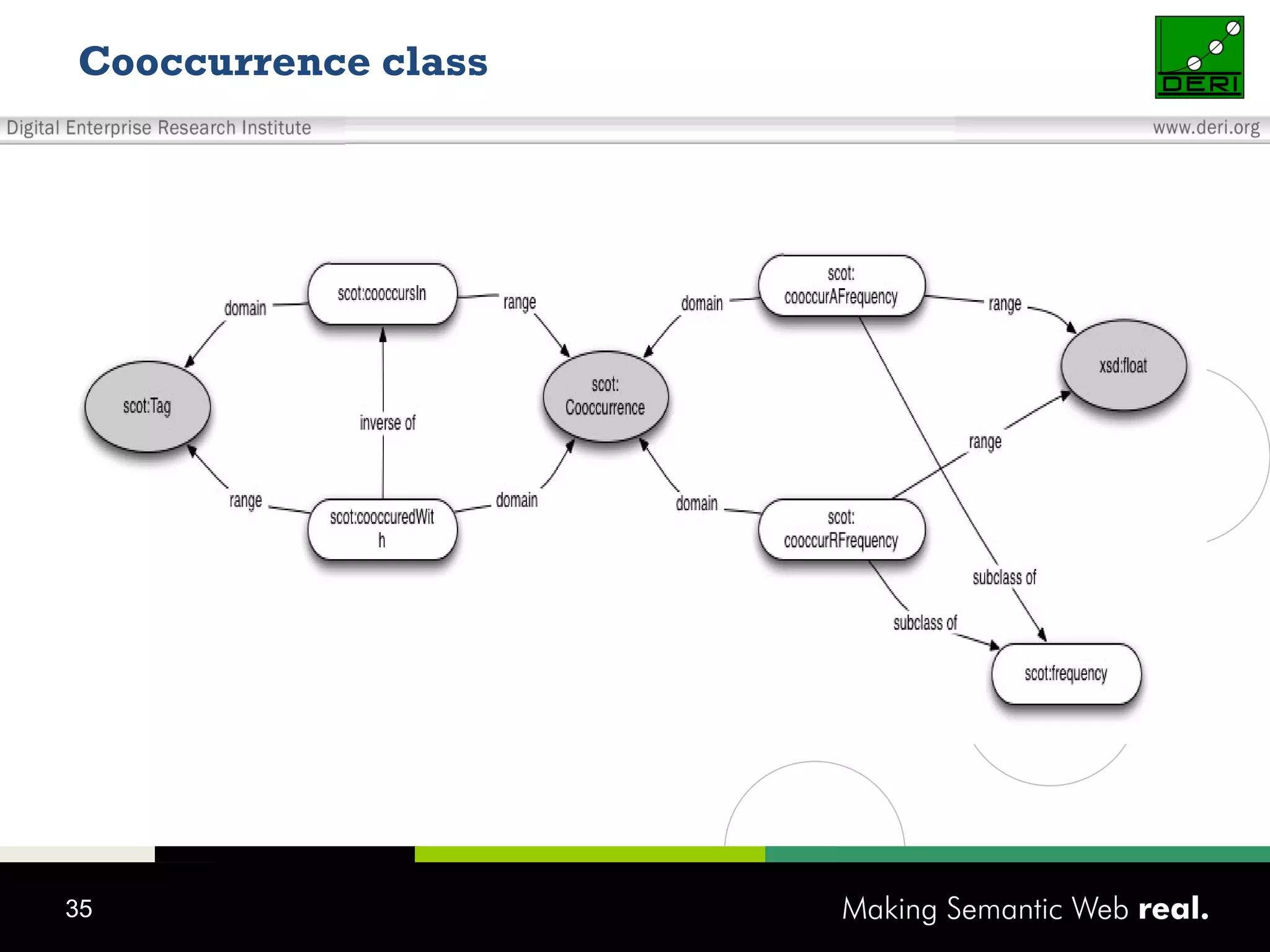
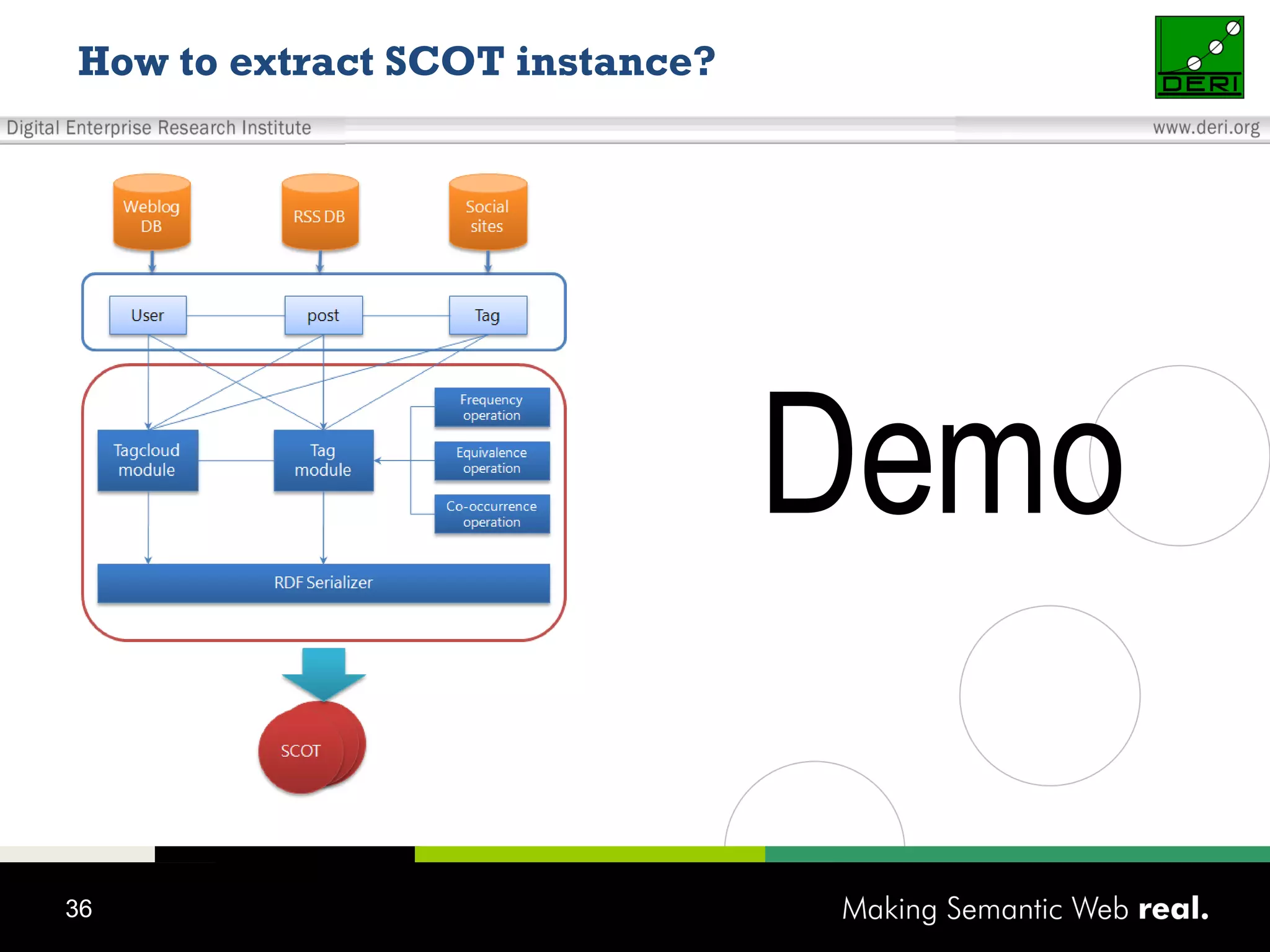
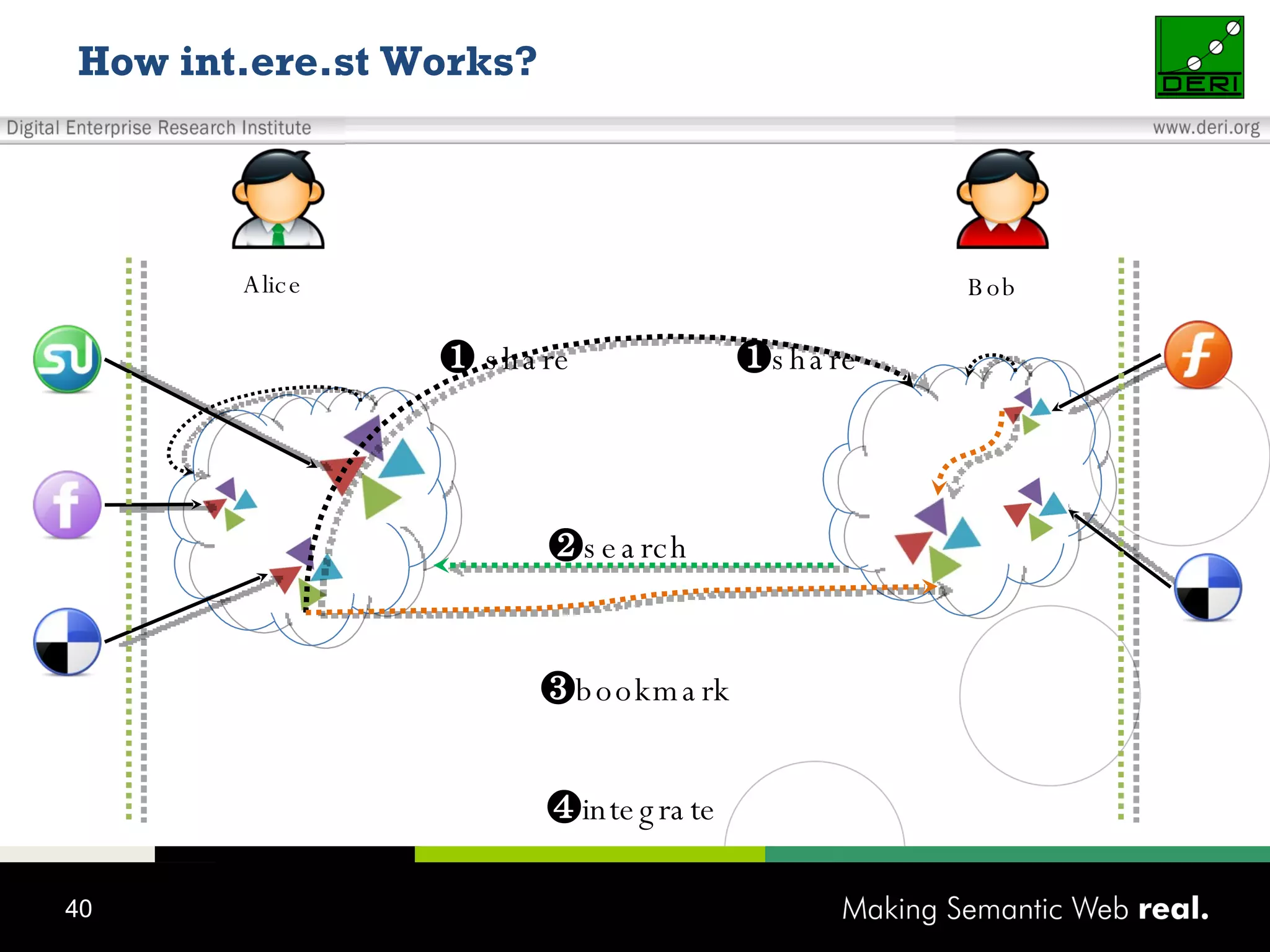
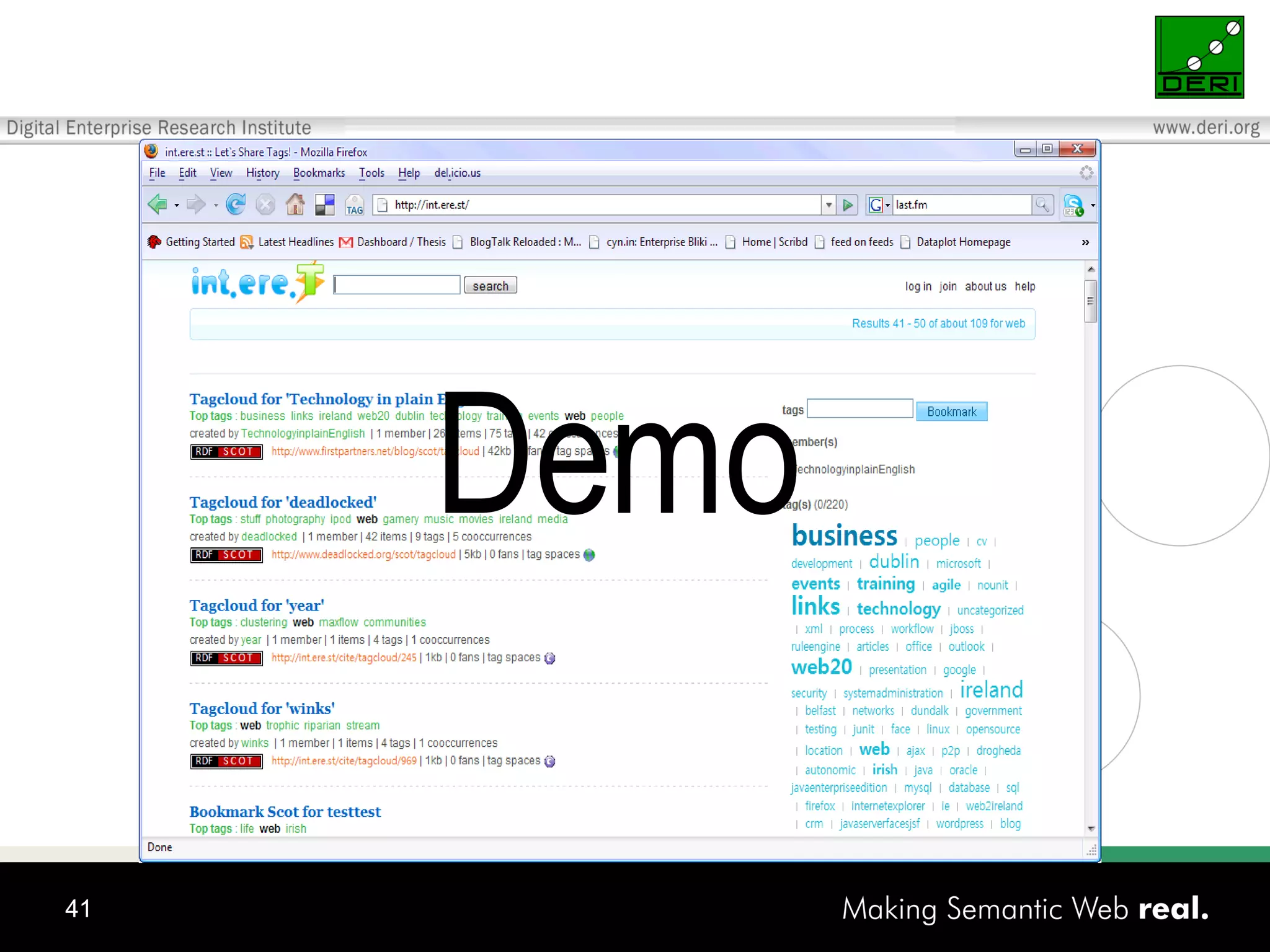
This document discusses the need for sharing tags across different systems and platforms. It proposes using SCOT (Social Semantic Cloud of Tags), an ontology for representing tagging data, and the OpenTagging platform for enabling interoperability among tags from different sources. The OpenTagging platform uses SCOT's data model and provides APIs to retrieve, search, and integrate tagging data from various social tagging applications and services in a unified manner. This allows tags to be portable and shared across different users, communities and sources.