Embed presentation





















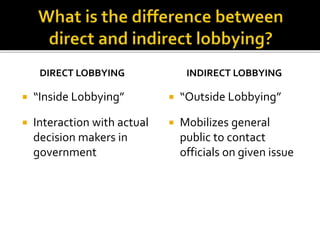
This document discusses interest groups and their activities. It defines interest groups as groups of citizens who share common interests and try to influence policy. It describes different types of interest groups and their purposes, which include representation, participation, education, and agenda building. The document also discusses factors that motivate group formation, such as common problems or threats. It provides examples of influential interest group leaders and the types of benefits groups provide their members, such as material, solidary, and expressive benefits. Finally, it outlines different lobbying strategies used by interest groups, including direct and indirect lobbying.





















