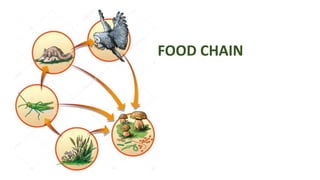
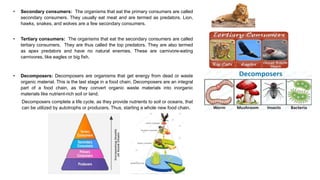
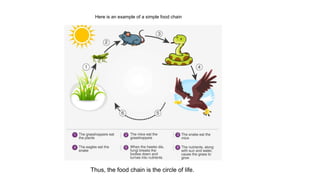
A food chain refers to the transfer of energy from one organism to another as each organism eats and is eaten. It typically involves producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and decomposers. Producers, like plants, get their energy from the sun. Primary consumers eat producers, secondary consumers eat primary consumers, and tertiary consumers are apex predators that eat secondary consumers. Decomposers break down dead organisms and waste to recycle nutrients back into the system.