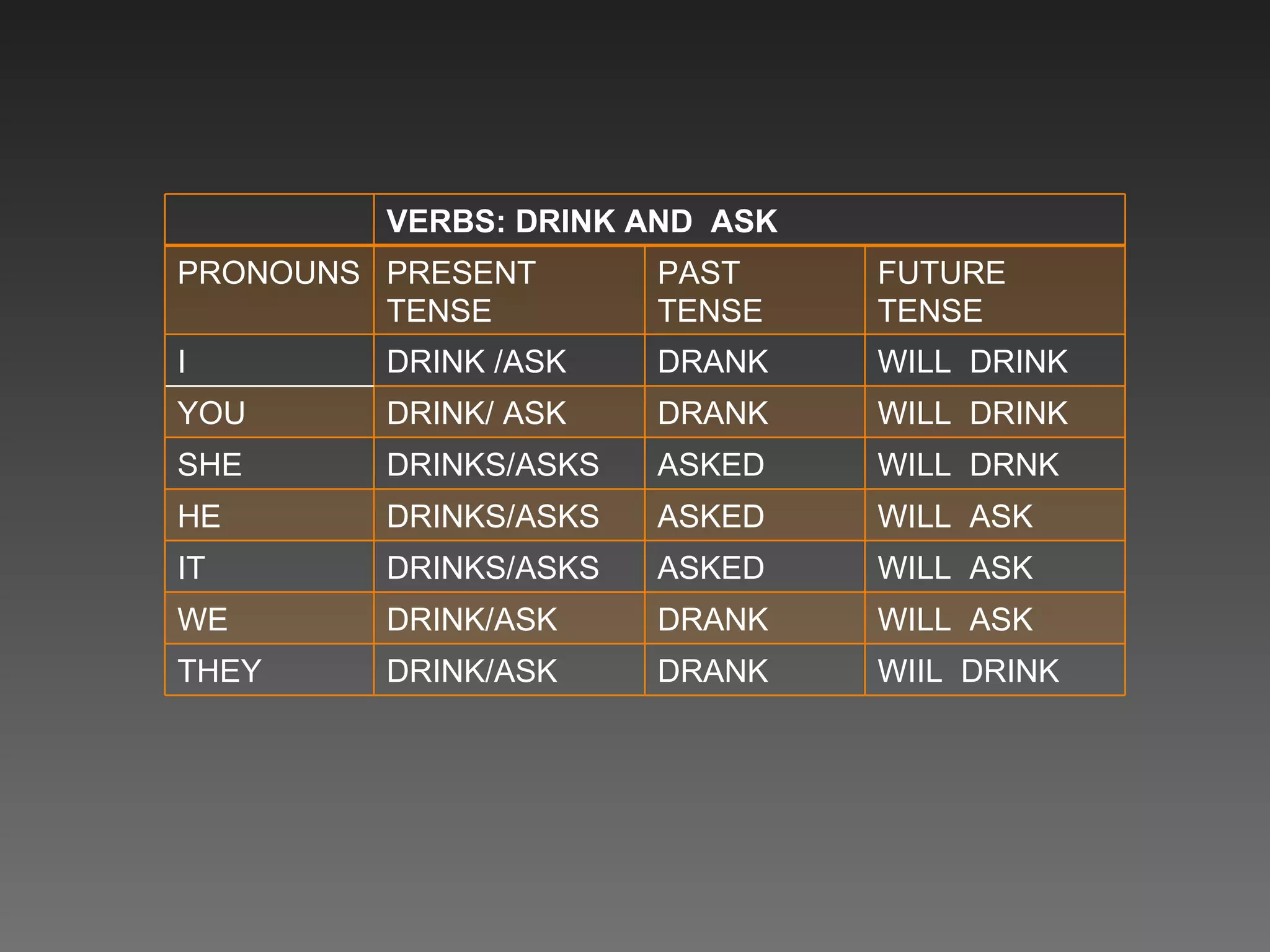
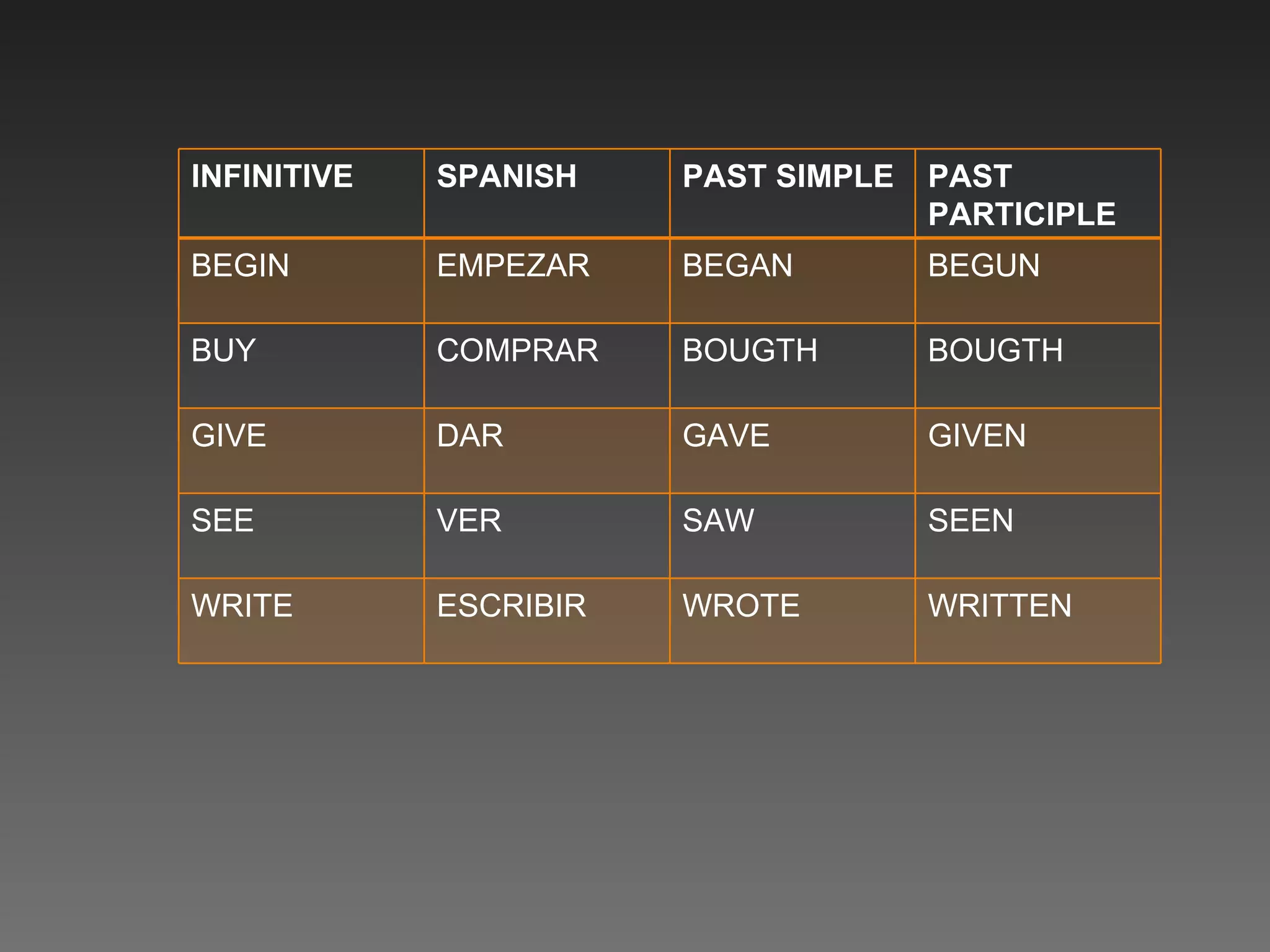
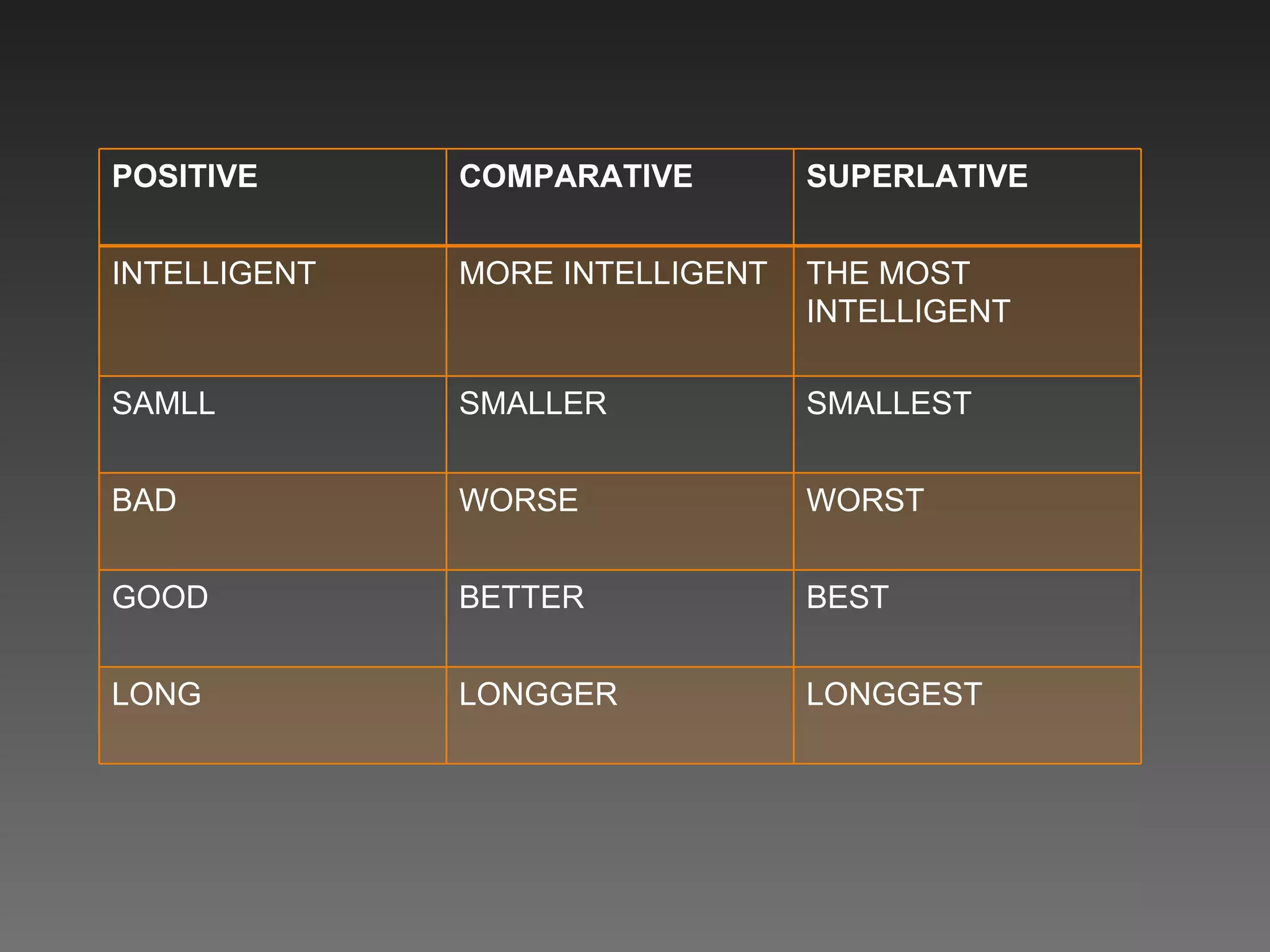
This document provides an introduction and objectives for an interactive English workbook. It covers topics like verb tenses (simple, past, future), regular and irregular verbs, descriptions of families, and the comparative and superlative forms. Exercises are provided to help readers practice these grammar topics. The objectives are to help people easily learn to distinguish between tenses and other concepts and to provide clear explanations through simple exercises.