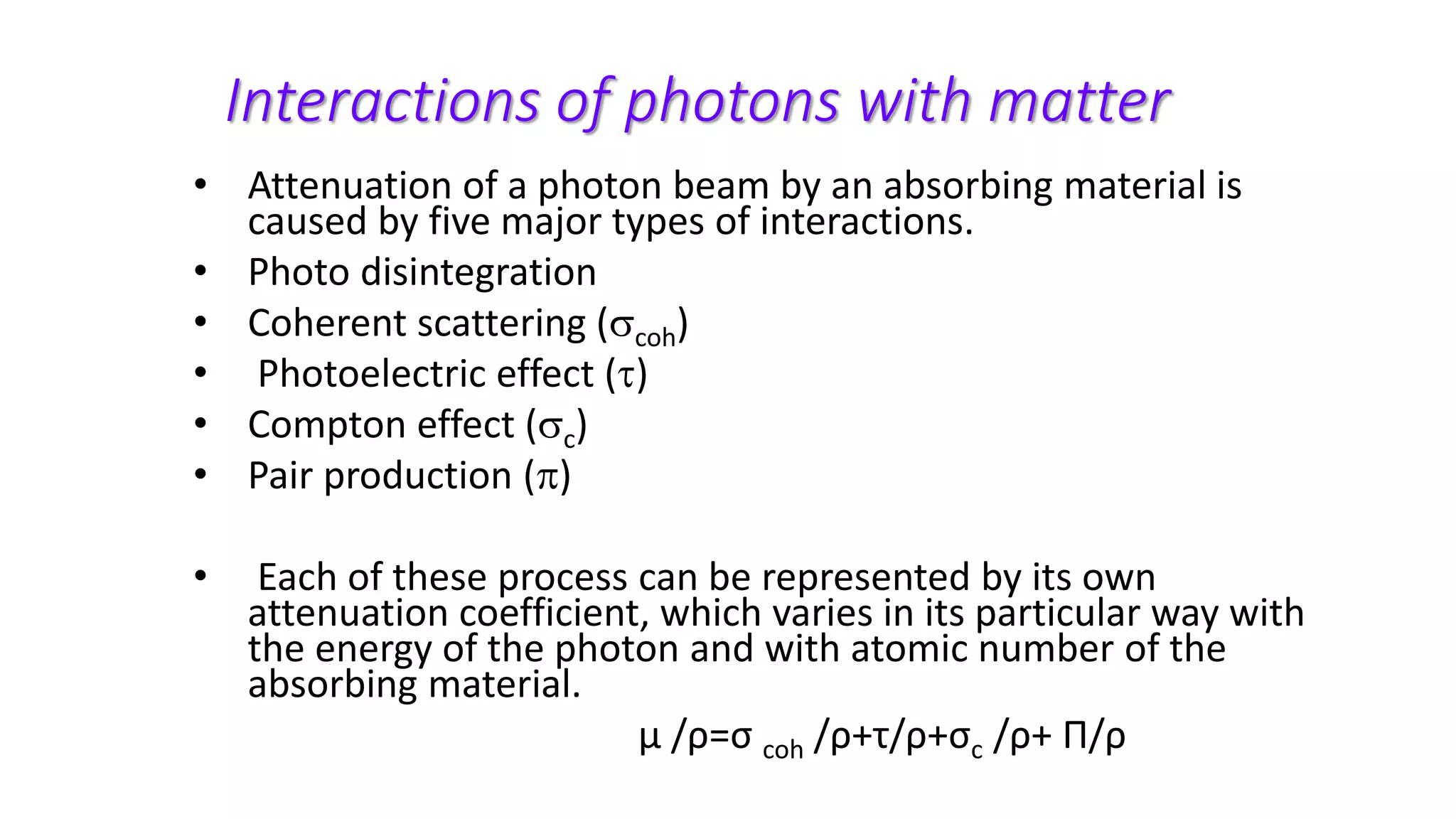
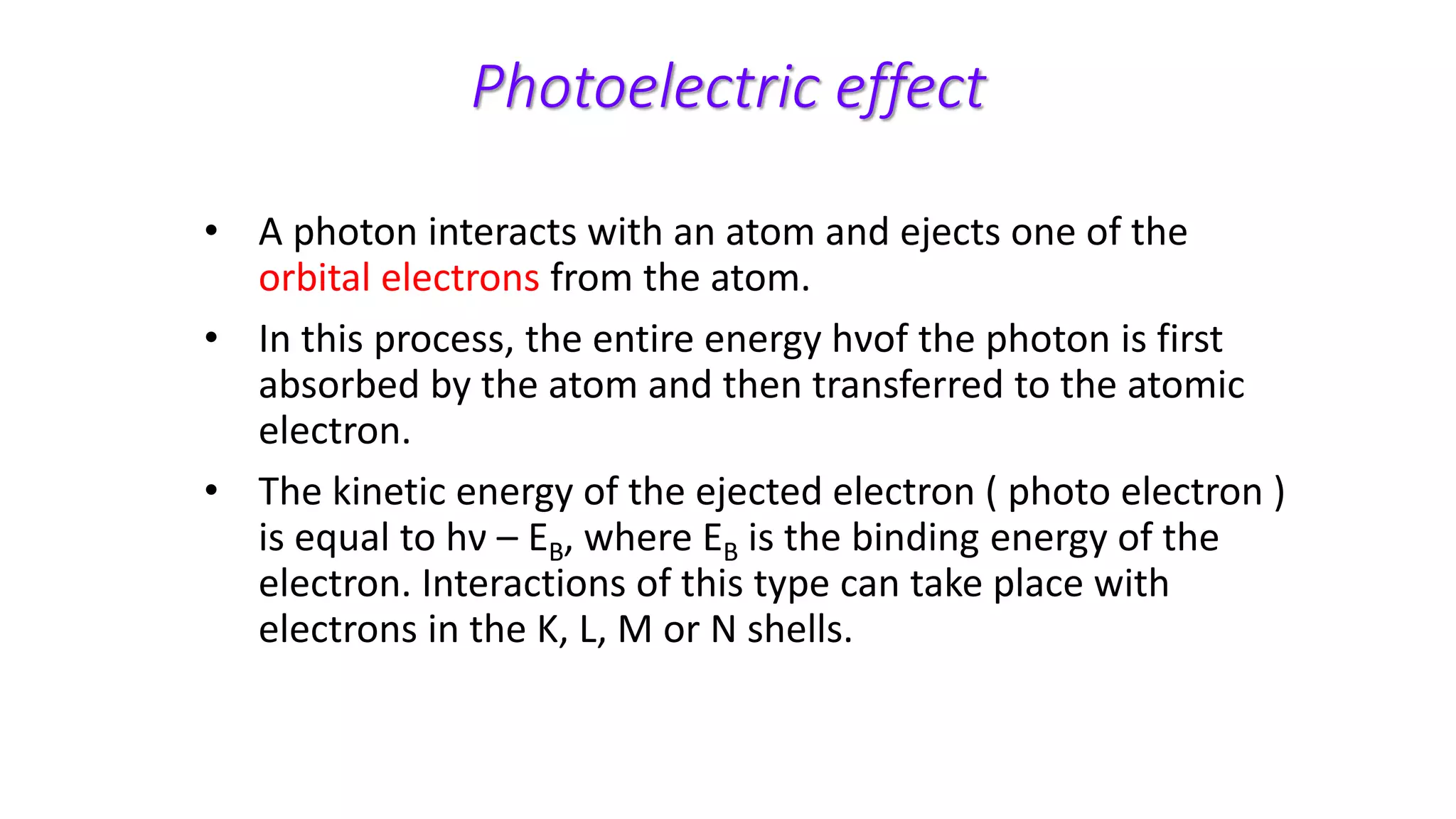
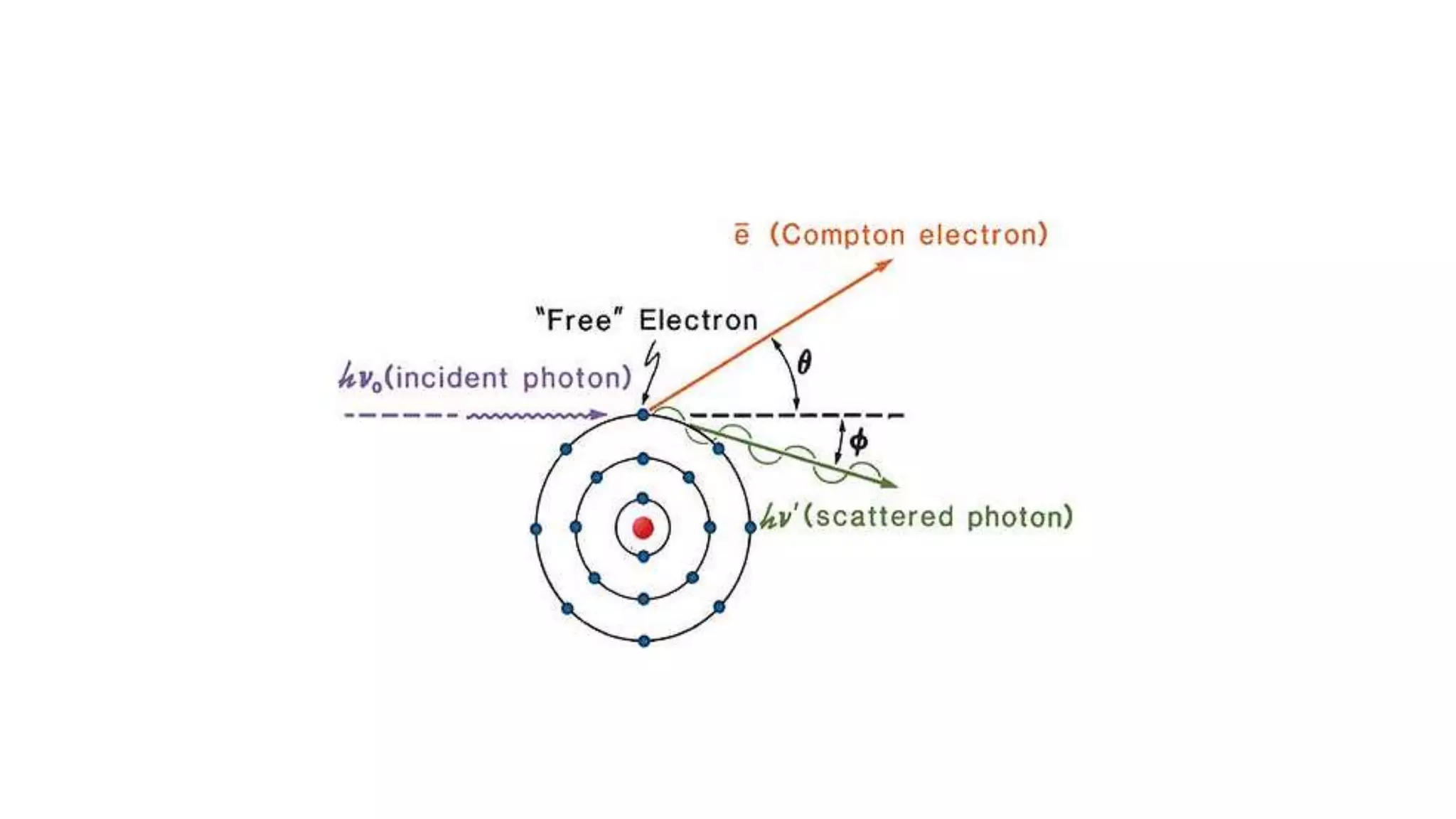
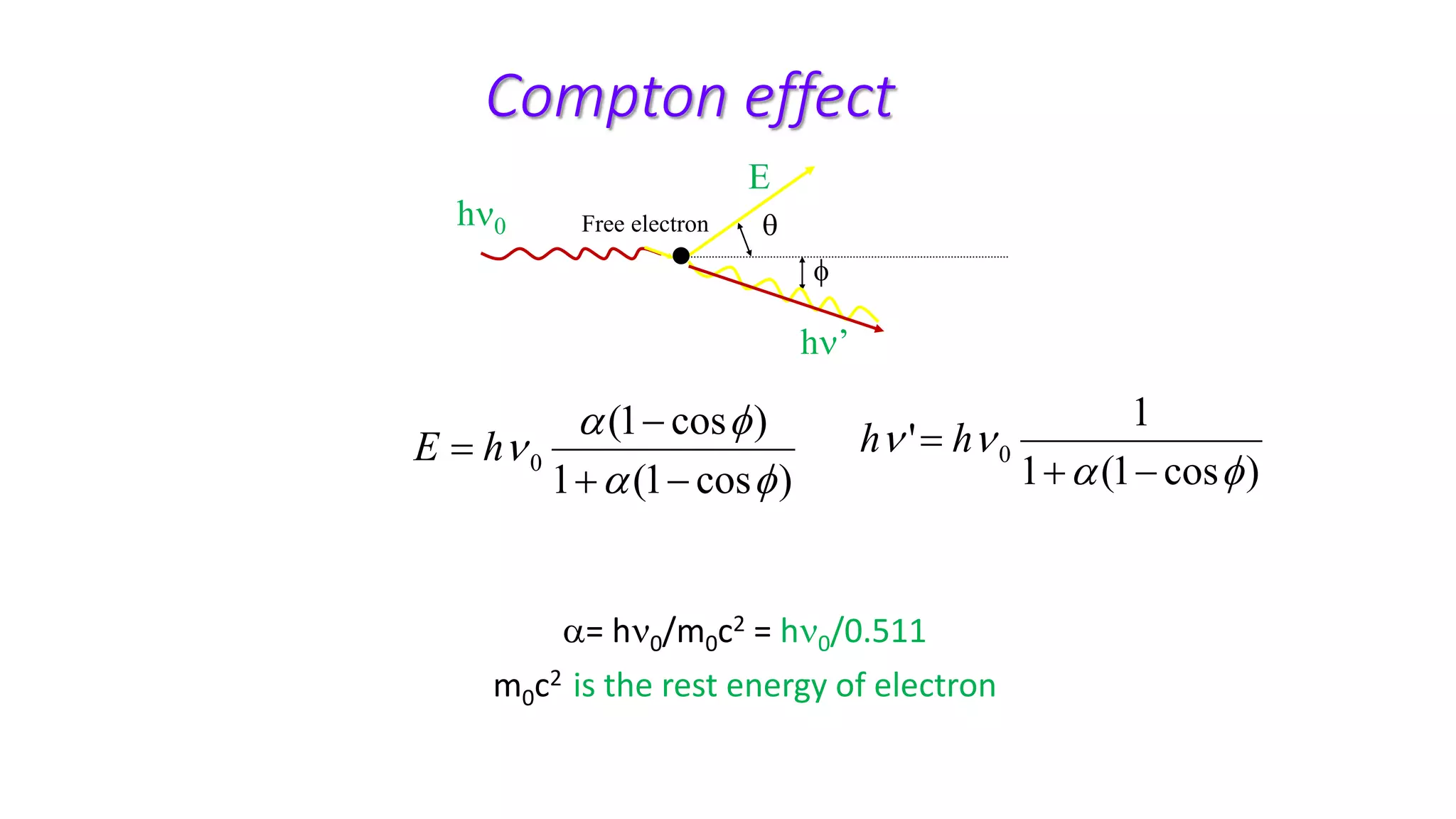
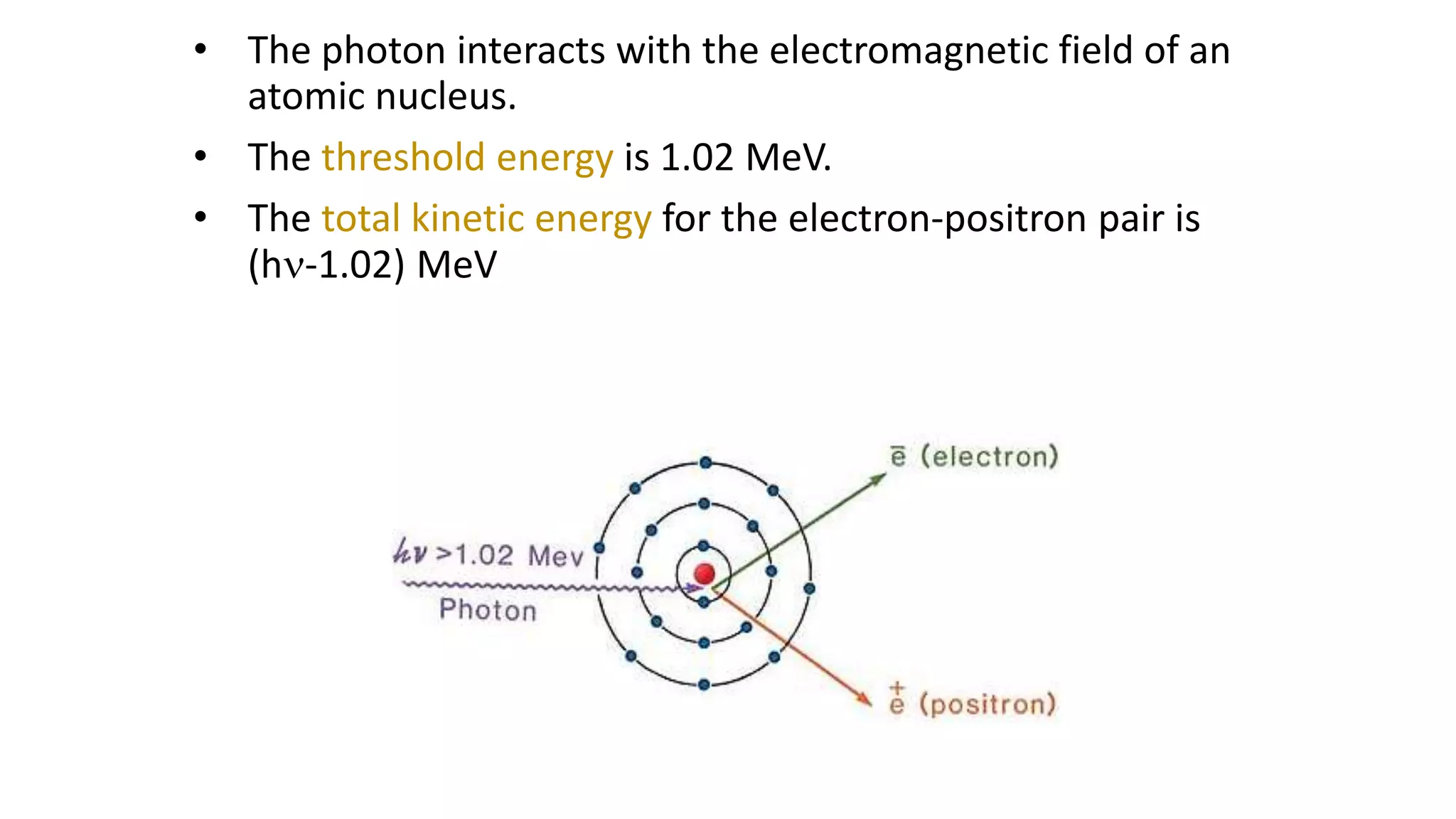
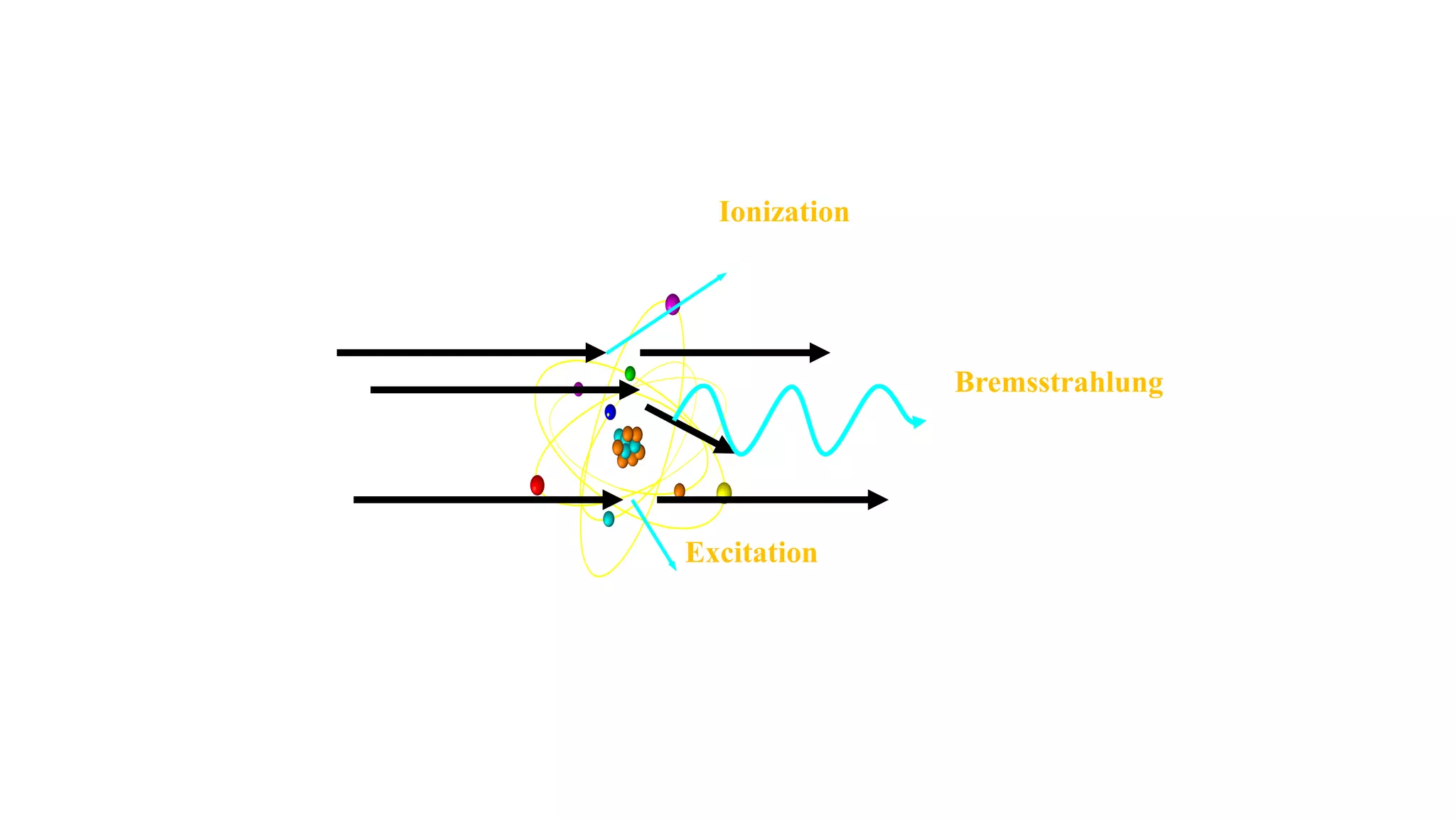
Ionizing radiation can ionize matter directly through charged particles like electrons and protons or indirectly through neutral particles like photons and neutrons. Directly ionizing particles have sufficient kinetic energy to ionize through collisions, while indirectly ionizing particles release directly ionizing secondary particles when interacting with matter. Photons can be attenuated by interactions like the photoelectric effect, Compton scattering, and pair production, with the dominant interaction depending on photon energy. Charged particles interact through Coulomb forces, losing energy through ionization and bremsstrahlung. Neutrons interact primarily through collisions, transferring energy efficiently to heavier nuclei.