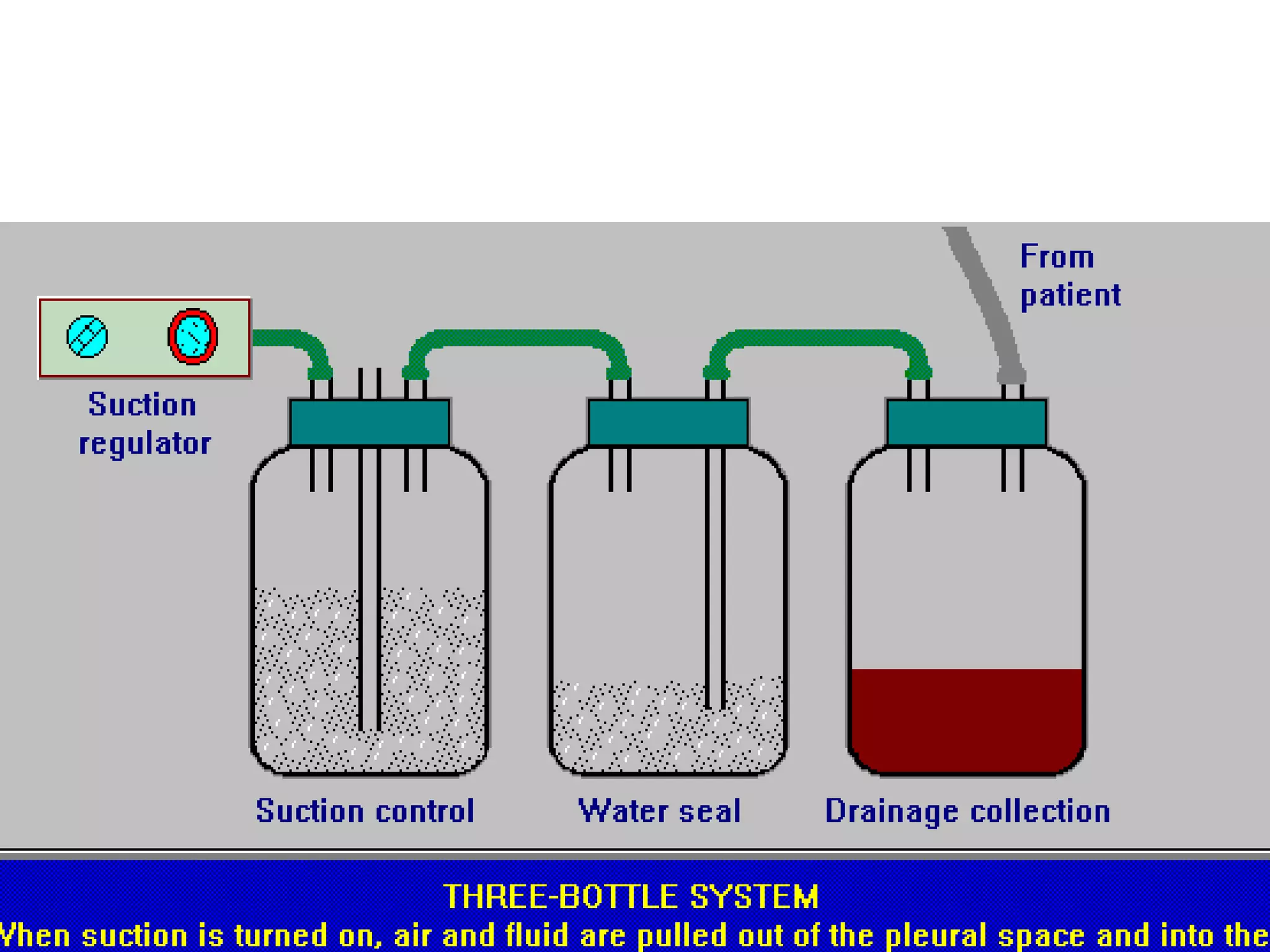
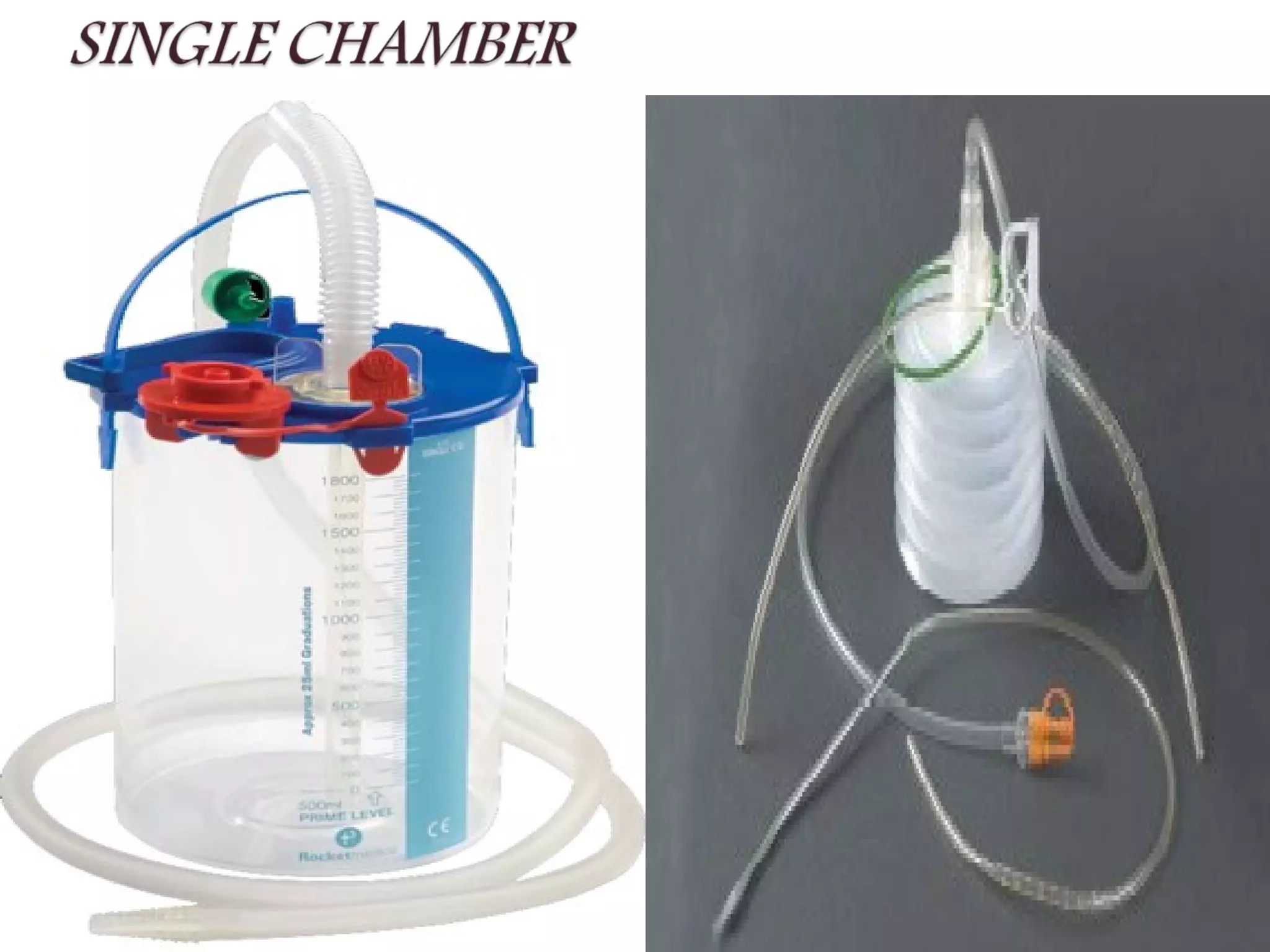
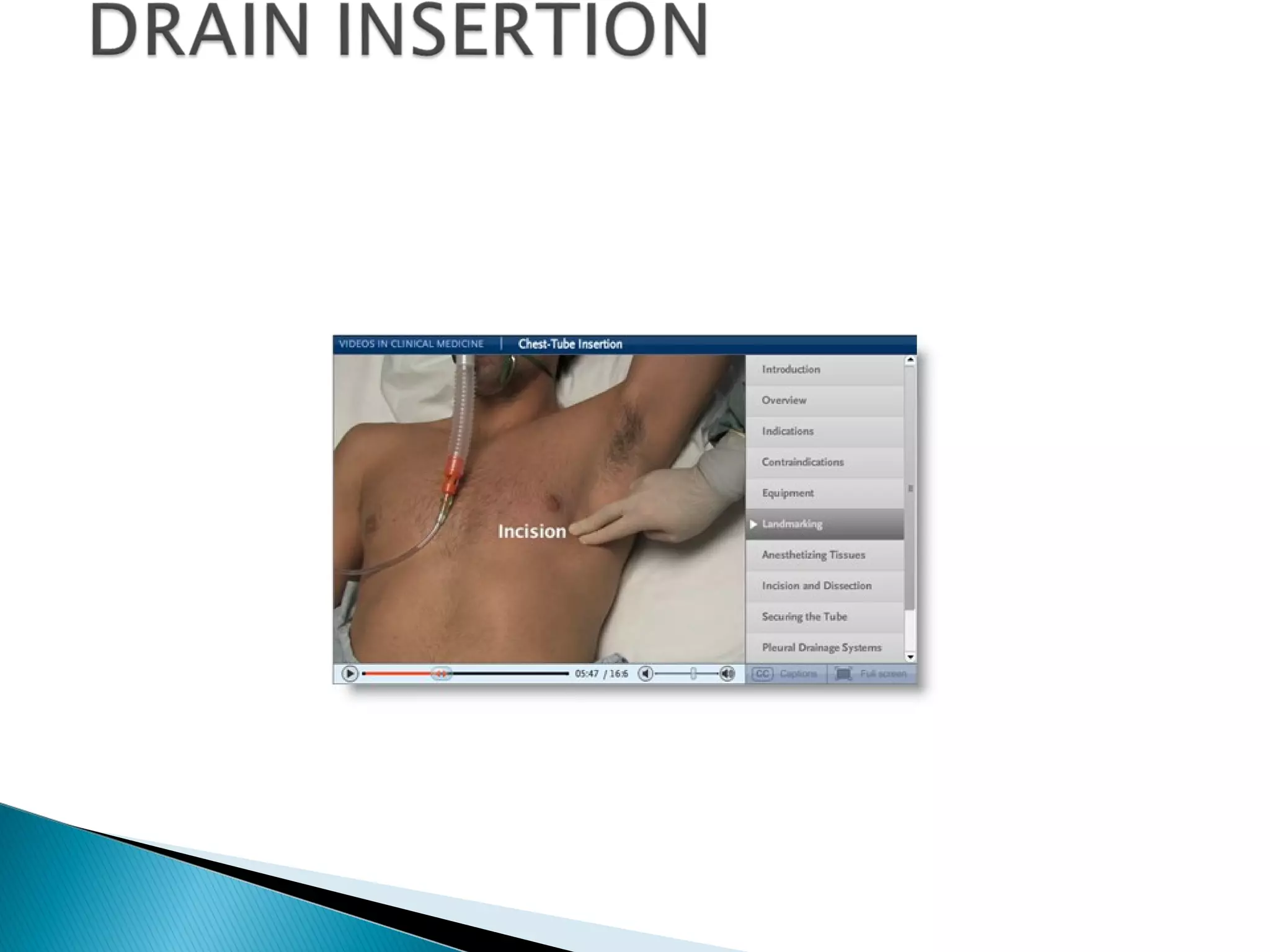
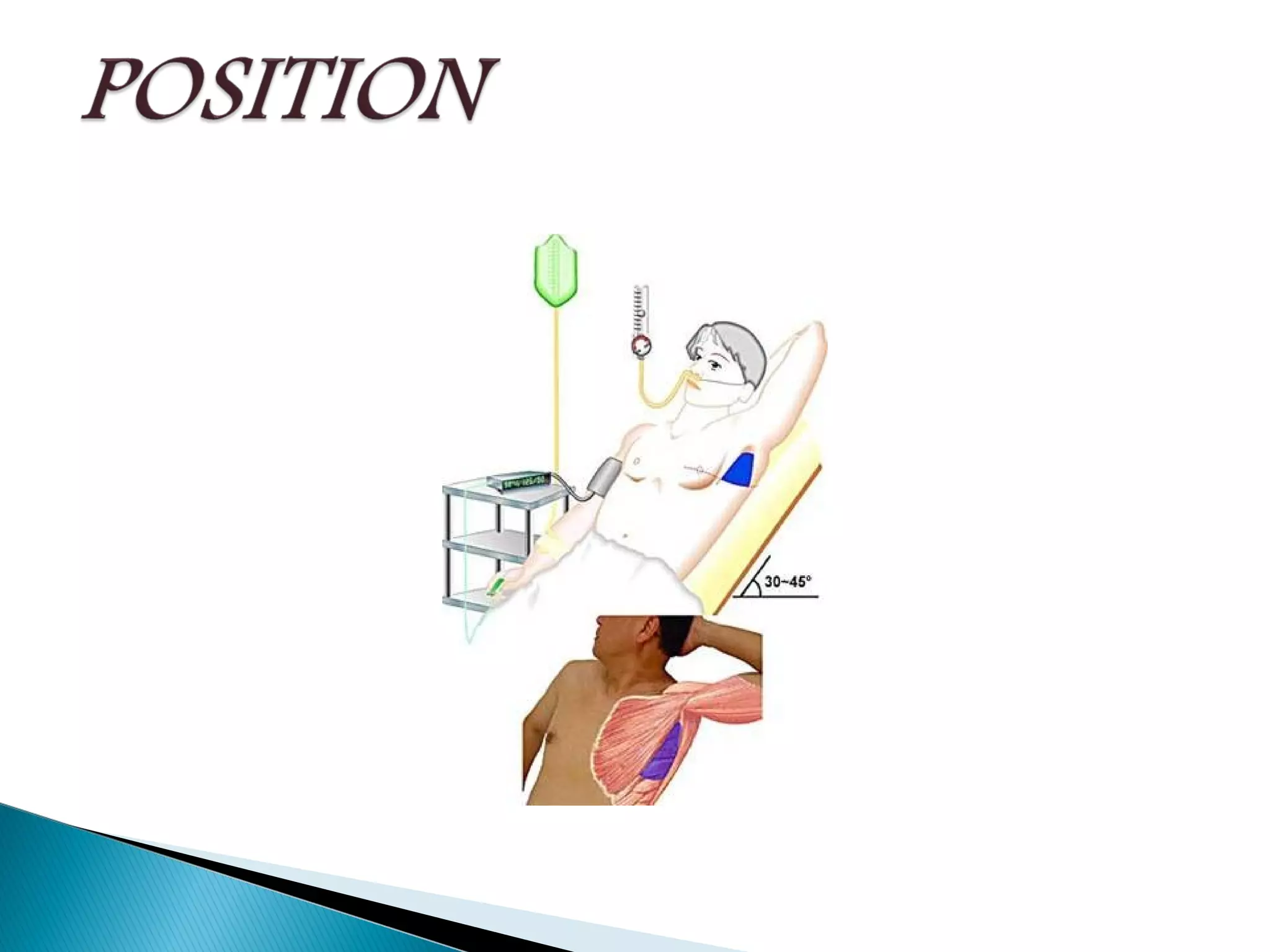
The document discusses chest tubes, which are flexible plastic tubes inserted through the chest wall into the pleural space or mediastinum to drain fluid or air. Chest tubes are used to overcome the accumulation of air or fluid in the pleural cavity that can impair ventilation. The pleural membranes have an important role in ensuring the lungs are expanded, so any disruption or changes in the pleural space will compromise ventilation. The document provides information on chest tube sizes for adults and children, indications for chest tube insertion, postoperative care and monitoring, potential complications, and common problems that may occur.