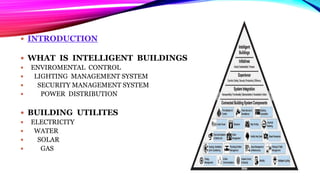
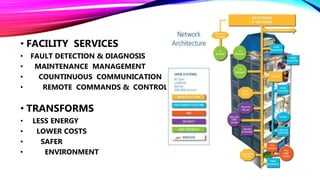
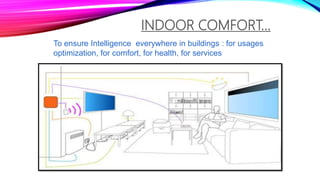
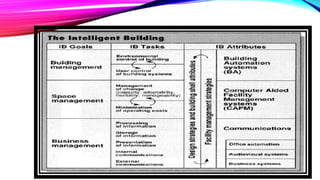
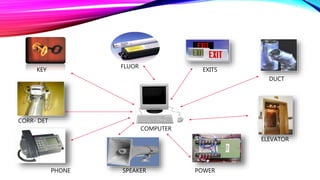
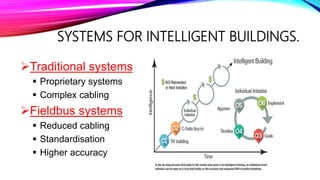
An intelligent building incorporates information systems that support information flow, allow business automation, and enable flexible, simple, and economical monitoring and management. It integrates various building systems like energy management, lighting, security, and communications. The objectives of intelligent buildings are energy management and indoor comfort through features like flexibility, distributed memory, and sensors. Future trends include facilitating global communication networks and innovation in smart buildings and smart cities.