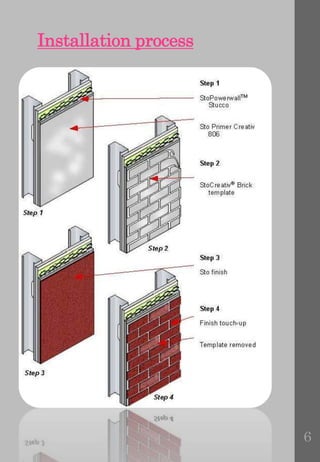
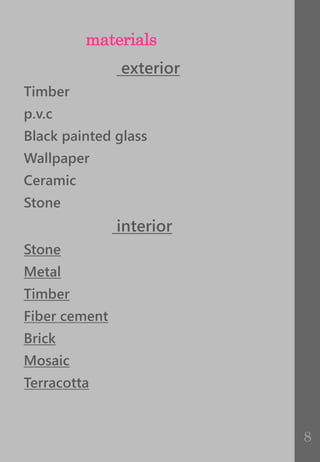
Cladding provides an outer protective layer for buildings and serves several key functions. It encloses the building structure, protects it from weather elements, and allows for dry construction methods. Cladding systems aim to impose minimal additional weight on the building frame while enhancing architectural appearance. To fulfill these objectives, cladding must demonstrate strength and stability under self-weight and wind loads, compatibility with the building frame to accommodate movements, weather resistance, durability, thermal insulation, fire resistance, sound insulation, and aesthetics. Common cladding materials include timber, PVC, glass, stone, and various interior options like stone, metal, and fiber cement.