1) Intellectual property refers to creations of the human mind like ideas, inventions, and artistic works, and intellectual property rights give the creators control over the use of their works.
2) Intellectual property rights are important as they reward original efforts, stimulate innovation and creativity, prevent duplication of work, provide commercial value in research, and prevent exploitation.
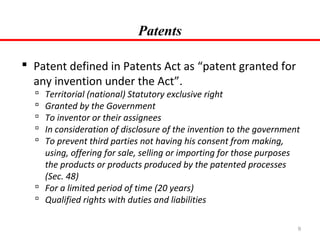
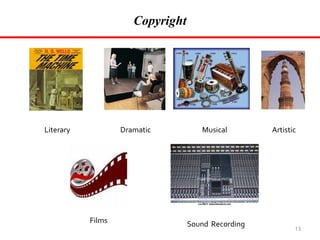
3) The main forms of intellectual property rights discussed are patents, which protect inventions; copyrights, which protect original creative works; trademarks, which protect brands and logos; and industrial designs, trade secrets, geographical indications, integrated circuits, and plant variety protections.