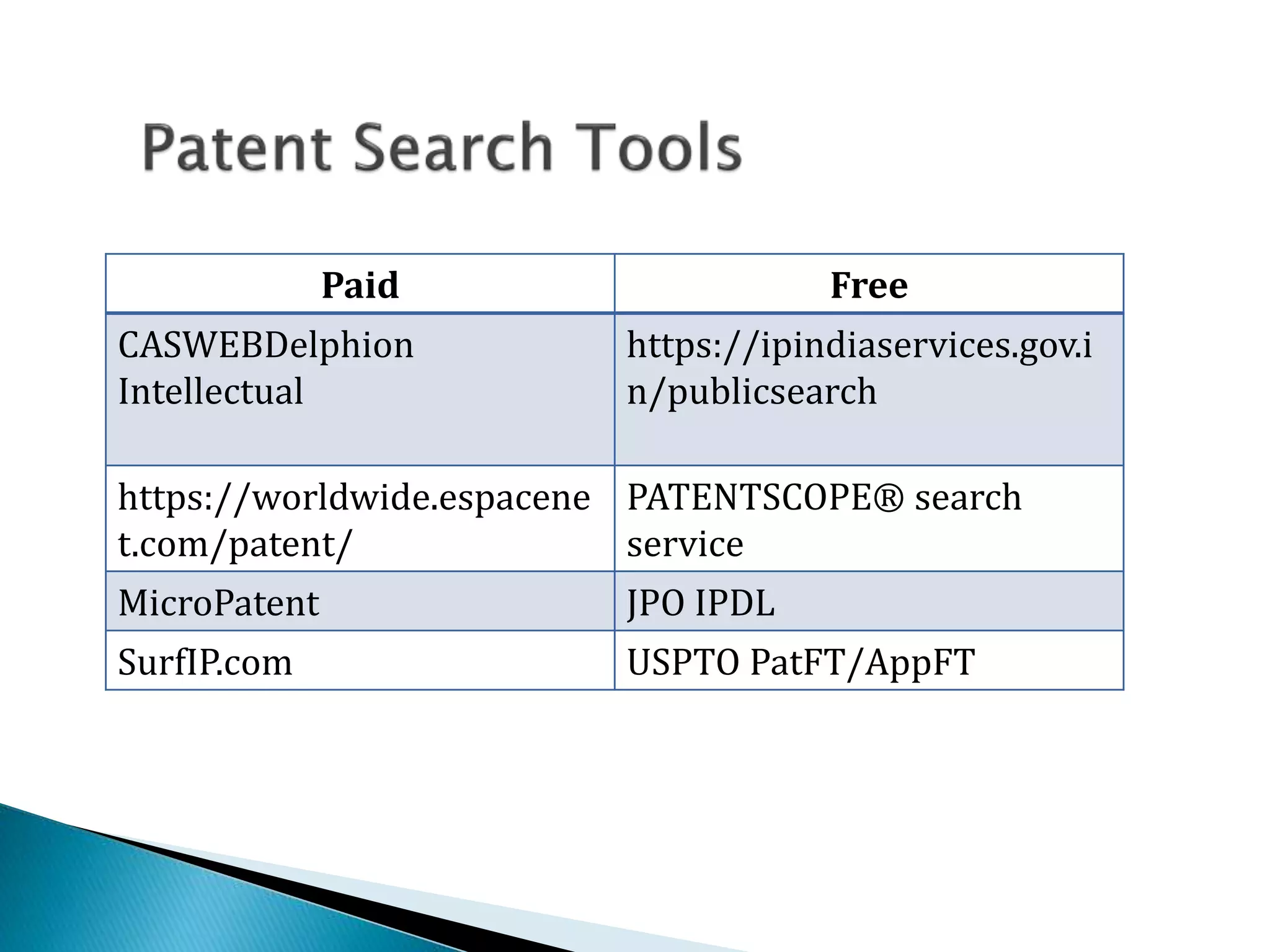
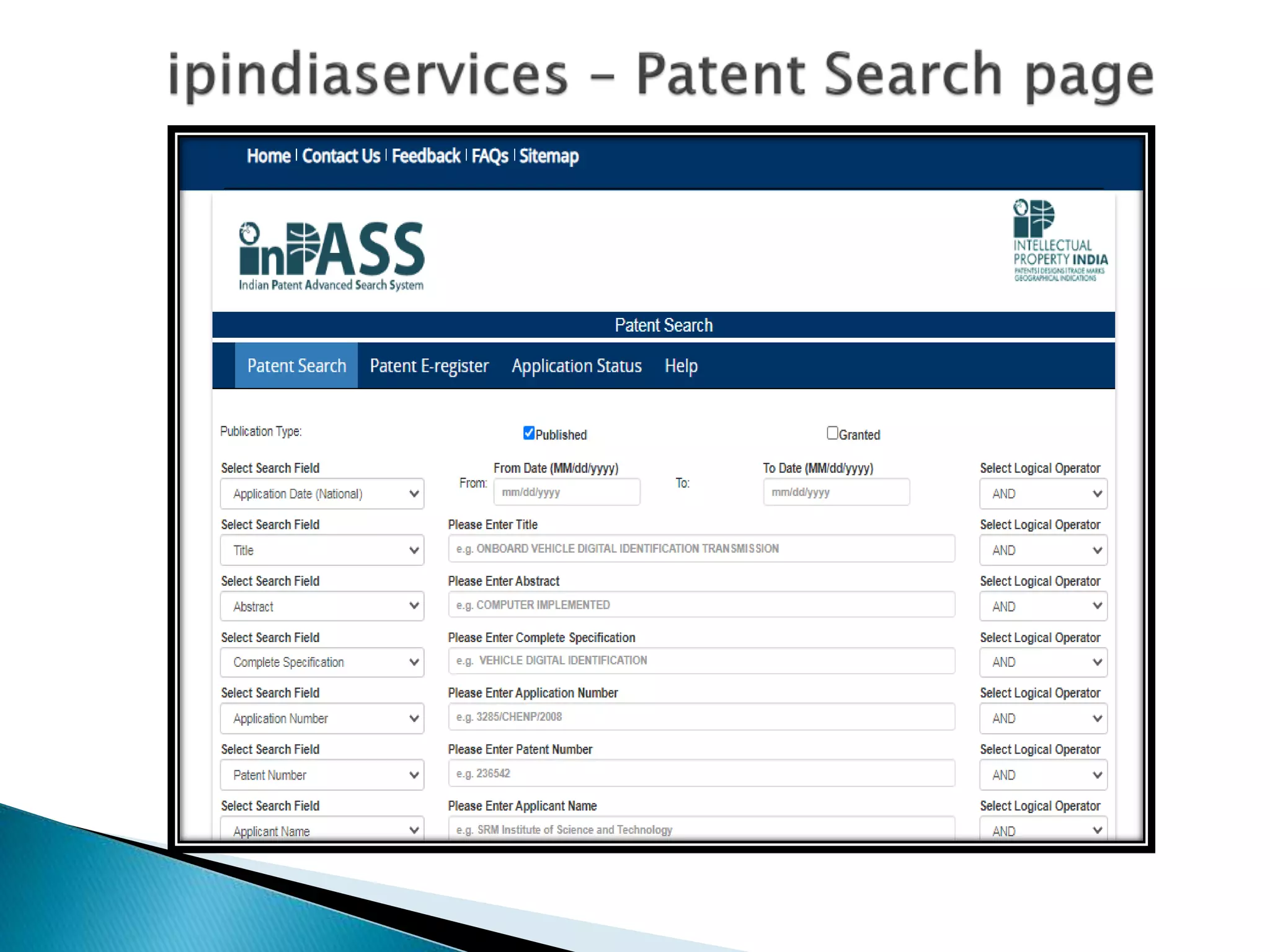
This document discusses intellectual property rights (IPR) and different types of intellectual property. It defines IPR as rights given over creations of the human mind. It describes various types of industrial property including patents, industrial designs, trademarks, trade secrets, and geographical indications. It provides details on relevant acts governing these properties in India and how intellectual property can be registered, protected, and enforced. The purpose of IPR is to encourage innovation by allowing people to profit from their creations.