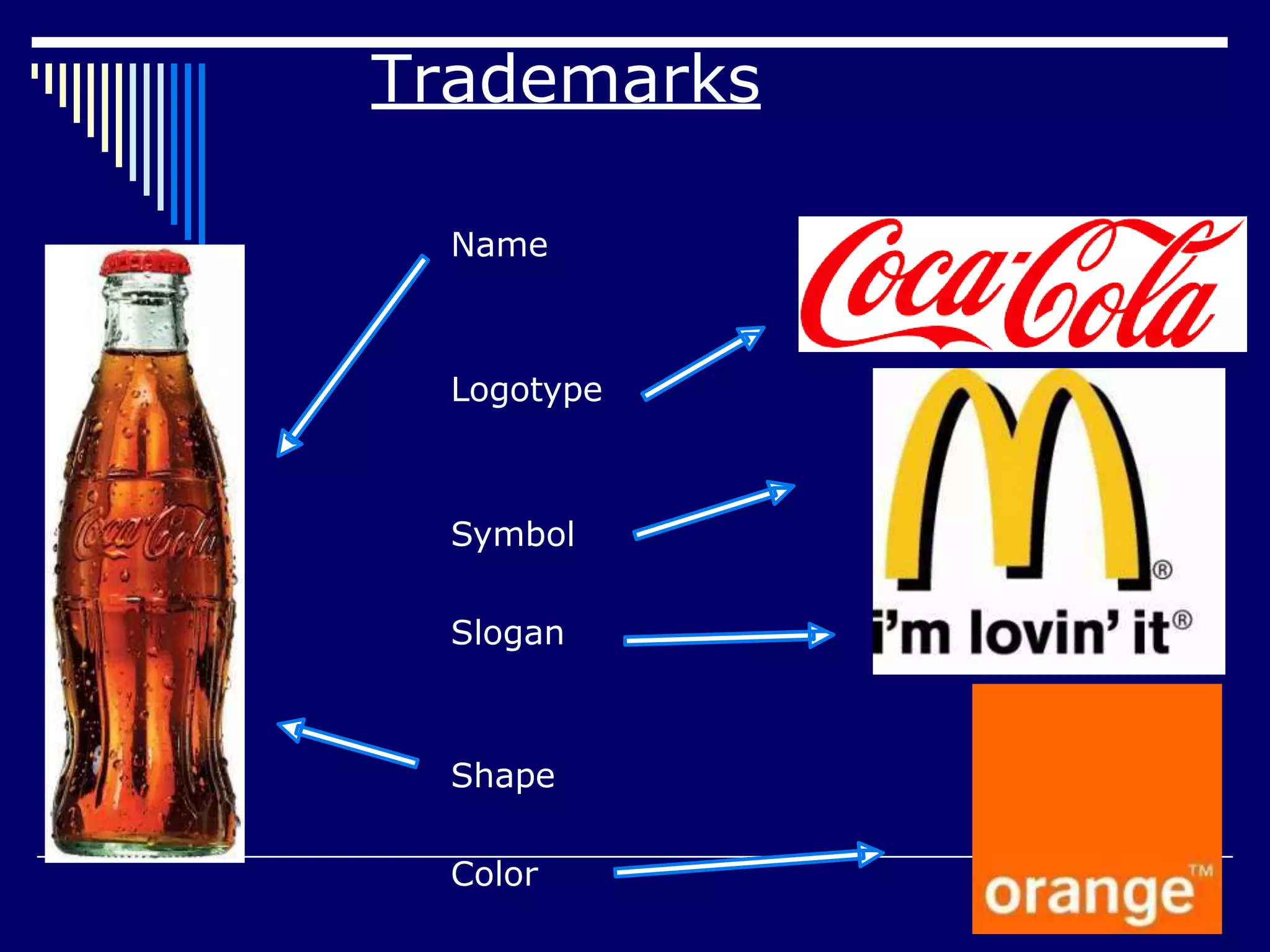
The document discusses various aspects of intellectual property legislation. It begins by introducing WIPO, the World Intellectual Property Organization, which was established in 1967 and promotes intellectual property protection worldwide from its headquarters in Geneva. The document then defines intellectual property as ownership of an idea or design by its creator, and gives exclusive rights to that creation. It outlines the main types of intellectual property protections: patents, copyrights, trademarks, industrial design, geographical indications, and trade secrets. For each type, it provides details on applicable laws, duration of protection, registration processes, and examples. Overall, the document provides a comprehensive overview of intellectual property concepts and the legislation governing different forms of intellectual property rights.








![Patents
• It is covered under the Act called the Patents Act,
1970 [Amended by Patents Act, 2005]
• It is a monopoly right granted to a person, who invented a
new product or process of making an article, for 20years
under the Indian Patens Act, 1970,
• It can be renewed after expiration of period.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intellectualpropertyrights-200219055019/75/Intellectual-property-rights-9-2048.jpg)