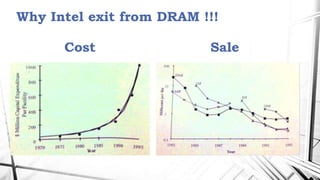
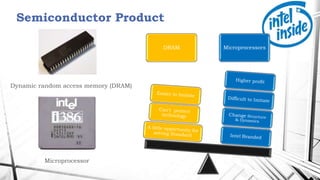
1. Founded in 1968, Intel Corporation began as a microprocessor company and later entered the DRAM business in the 1980s. However, Intel exited from DRAM production in the 1990s due to high costs and increasing competition from Japanese manufacturers.
2. Intel adapted to changes in the semiconductor industry and the rise of personal computers and the Internet. Under Andy Grove's leadership, Intel shifted its focus to microprocessors and worked closely with customers and suppliers.
3. Factors contributing to Intel's success included large investments in research and development, manufacturing technology, and developing relationships within the semiconductor industry cluster in Silicon Valley. Upgrading technology and gaining competitive advantages through proprietary standards also helped Intel sustain its leadership in microprocessors