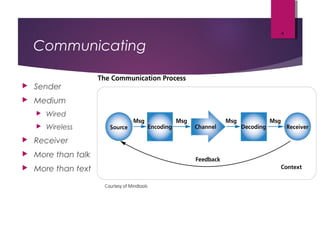
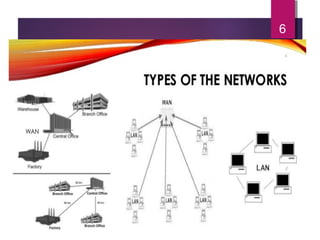
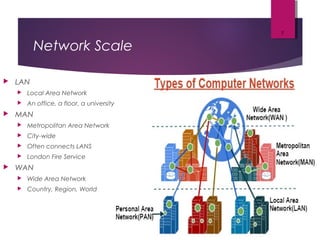
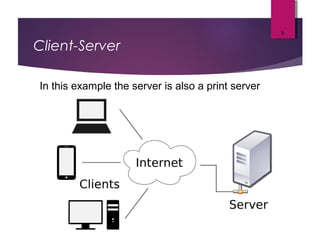
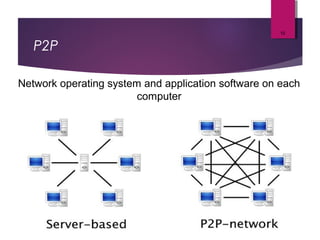
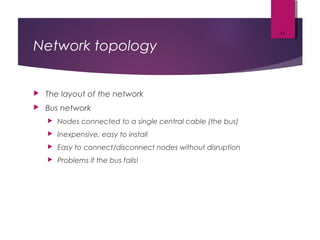
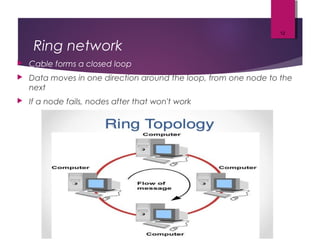
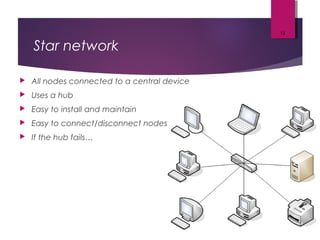
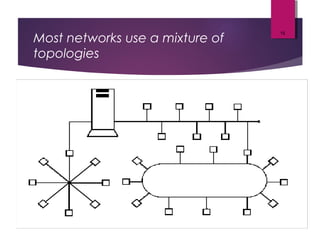
The lecture by Mr. Rajasekar Ramalingam covers key aspects of communication and networks, including types of networks such as LAN, MAN, and WAN, as well as network architectures like client-server and peer-to-peer. It also discusses network topologies including bus, ring, and star, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, communication standards and protocols such as Ethernet and Bluetooth are explained, detailing how they facilitate device communication.