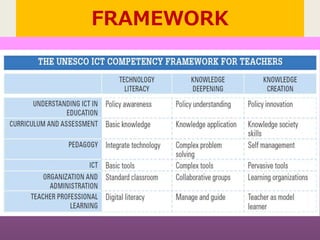
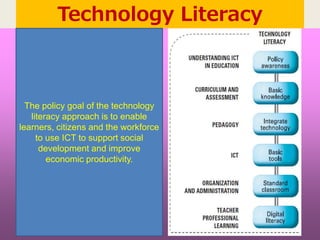
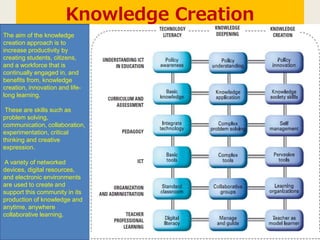
This document discusses UNESCO's ICT Competency Framework for Teachers (ICT-CFT). It notes that life and society are changing rapidly with new technologies, and education must change as well by integrating ICT. The framework aims to develop teachers' competencies in three areas: technology literacy to use ICT effectively, knowledge deepening to apply knowledge to real problems, and knowledge creation to engage in lifelong learning and innovation. It argues this will help education achieve social and economic goals by preparing students for a knowledge-based society and economy. The framework is part of UNESCO's efforts to promote education reform, reduce poverty, and improve lives through linking education, ICT, and economic growth.