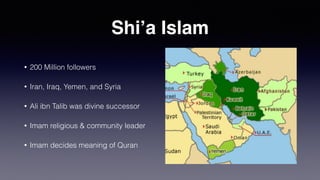
The document discusses evangelism in a pluralistic society. It argues that Christians should practice civil discourse by acknowledging cultural sensitivities, becoming friends with those of other beliefs, openly sharing spiritual experiences, finding connections to the gospel, and asking about openness to learn more while relying on scripture. Civil discourse means respectful discussion of religious beliefs rather than having no beliefs. Most non-Western cultures respect deep personal convictions. The evangelical approach involves acknowledging religious truth claims and that other religions have wisdom while still sharing the gospel message.







































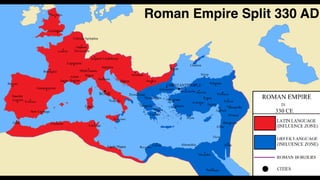
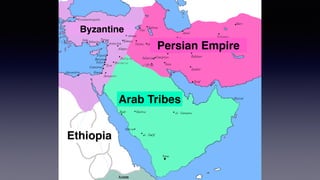
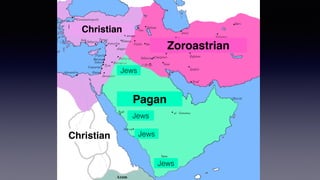
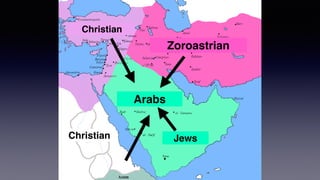

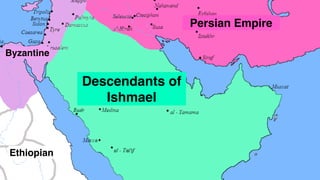











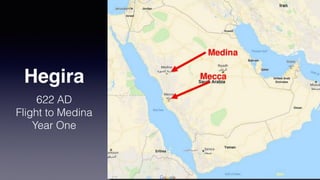















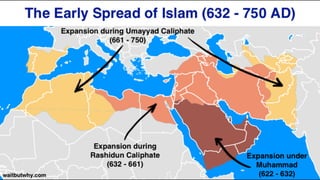




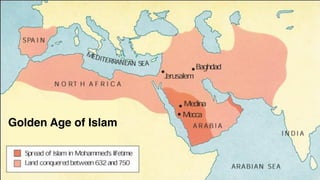












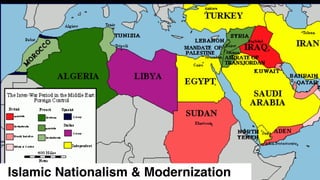

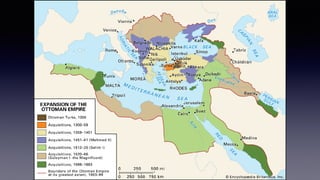
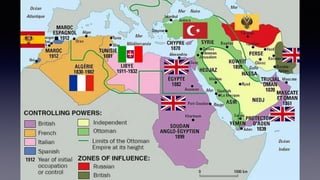
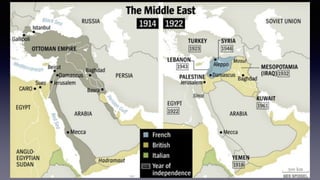















































![1. In the Name of Allah the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful.
2. [All] praise is [due] to Allah, Lord of the worlds -
3. The Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful,
4. Sovereign of the Day of Recompense.
5. It is You we worship and You we ask for help
6. Guide us to the straight path-
7. The path of those upon whom You have bestowed favor, not of those
who have evoked [Your] anger or of those who are astray.
Quran 1:1–7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/int-244topic3islam-221005191752-1a49b0c5/85/INT-244-Topic-3-Islam-152-320.jpg)