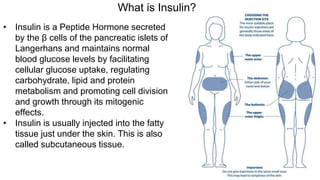
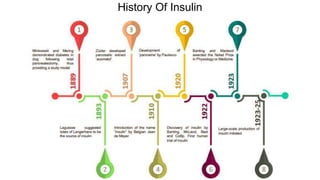
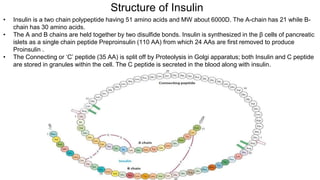
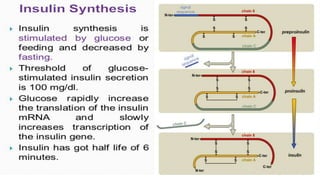
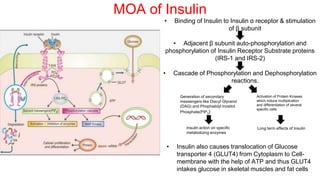
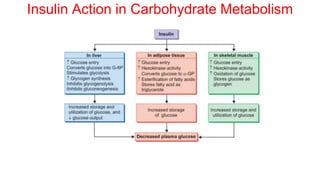
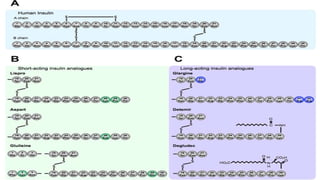
Insulin is a peptide hormone that regulates blood glucose levels. The history of insulin includes its discovery and purification from animal sources as well as the development of recombinant DNA technology to produce human insulin. Insulin is synthesized as a single chain peptide that is cleaved into separate A and B chains which are linked by disulfide bonds. Insulin binds to cell surface receptors to facilitate glucose uptake and regulate metabolism. Various insulin formulations were developed with different onset, peak, and duration of action. Insulin analogues were created using genetic engineering to more closely mimic the body's natural insulin secretion and allow better matching of insulin dose to meals. Insulin is used to treat diabetes mellitus.