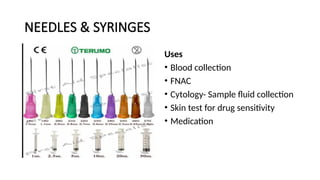
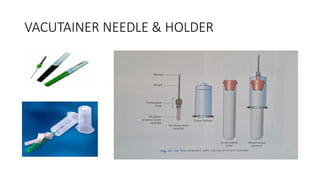
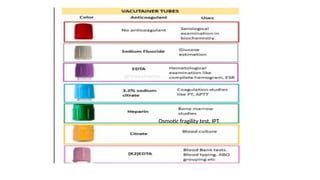
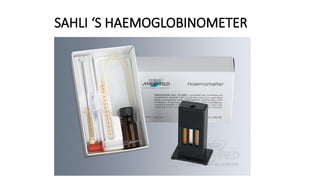
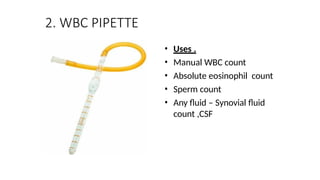
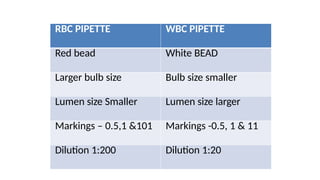
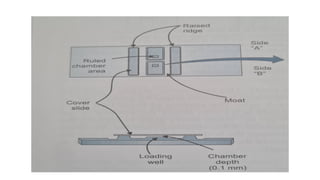
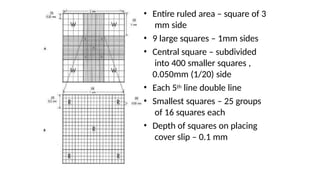
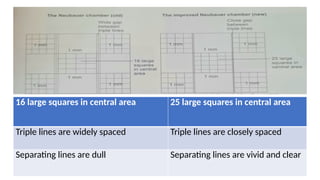
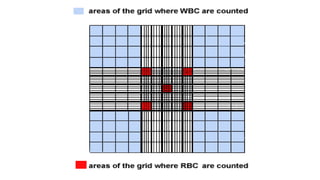
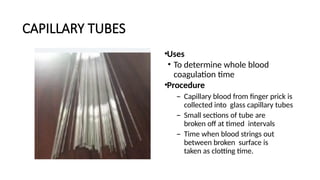
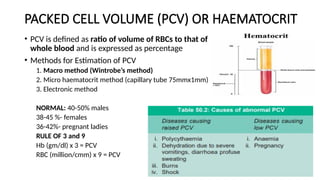
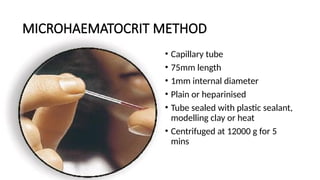
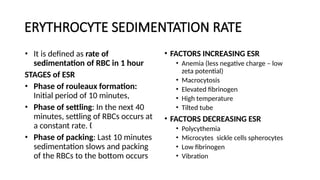
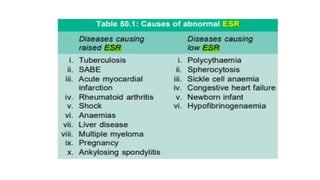
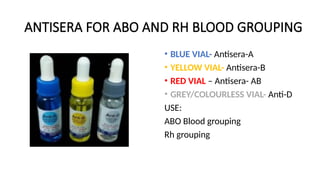
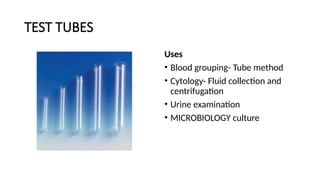
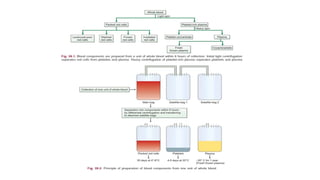
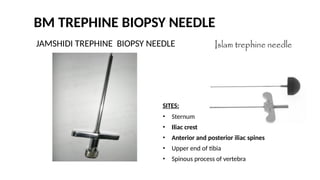
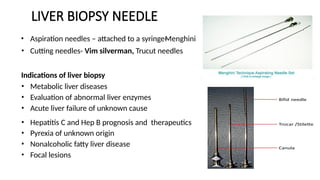
The document details various hematology instruments and their uses, including lancets, needles, pipettes, and specialized tubes for blood collection and analysis. It also outlines methods for tests such as hemoglobin measurement, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and packed cell volume estimation, including their procedures and normal values. Additionally, it describes the construction and applications of blood bags, aspiration needles, and specific laboratory equipment for analyzing bodily fluids.