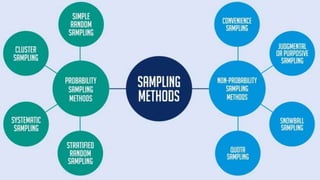
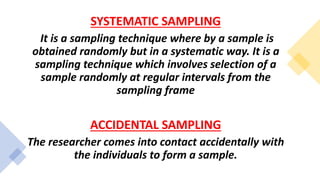
Instrumentation refers to the process of developing, testing, and using measurement devices called instruments. Good research instruments are valid, reliable, gather relevant data, test hypotheses, and contain clear instructions. Sample handling describes how samples are transported and processed in the lab, with some samples only reliable for a short time. Samples are used in research to make inferences about populations in a practical and cost-effective way. Common sampling techniques include random, systematic, stratified, snowball, and accidental sampling. The sampling error occurs when using a sample instead of the whole population to estimate unknown population parameters.