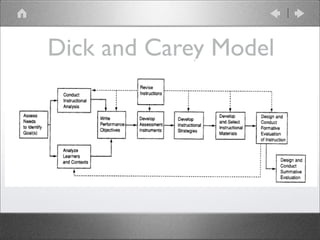
The Dick and Carey Systems Approach Model is a behaviorist approach to instructional design consisting of 10 components across 6 phases: design, analysis, development, formative assessment, revision, and summative evaluation. The first two phases involve assessing learner needs to identify goals, then conducting an instructional analysis to determine entry skills and conditions for learning. Next, performance objectives are written describing what learners will do. Assessments are developed, an instructional strategy is planned, and materials are prepared. During formative assessment, instruction is evaluated for effectiveness and revised as needed before summative evaluation of outcomes.