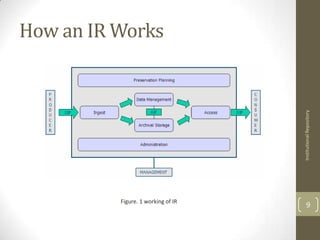
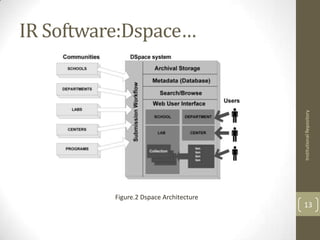
Institutional repositories are digital collections that preserve and provide access to a university's research output. They allow for long-term preservation of works and open access to scholarly articles, data, and other materials. Content is ingested through a submission process, preserved in a bitstream format, and disseminated through search and browsing. Institutional repositories differ from traditional databases in their use of bitstream storage and workflows. Common repository software includes DSpace and EPrints, which provide features like metadata collection, document archiving, and usage statistics. However, challenges exist in gaining contributor support and addressing intellectual property issues.