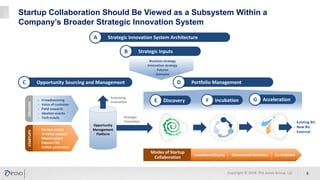
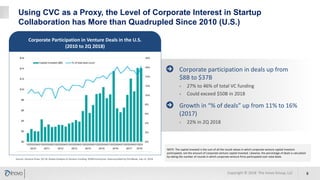
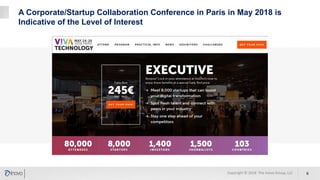
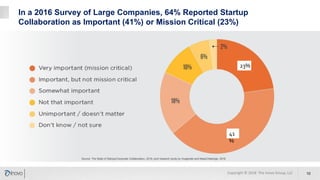
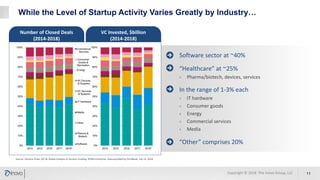
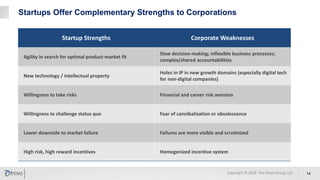
The document discusses the significance of corporate collaboration with startups as a strategy for innovation within larger companies, emphasizing its recent rise in importance and the trends driving this change. It outlines various approaches and challenges involved in such collaborations, highlighting the complementary strengths of startups and the structural difficulties faced by corporations. Inovo offers assistance in designing innovation systems and facilitating specific collaboration initiatives to enhance strategic growth opportunities.