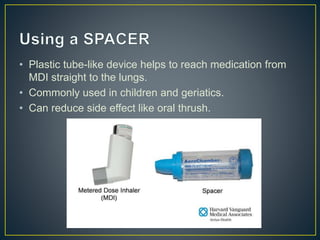
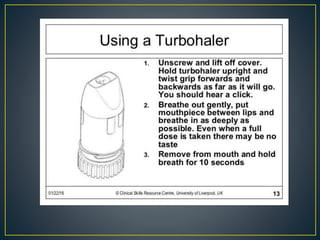
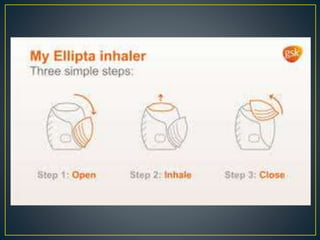
The document outlines various asthma medications, including relievers such as salbutamol and anticholinergics like ipratropium, as well as preventers including corticosteroids and leukotriene modifiers. It details different inhaler types, their usage, and their respective advantages and disadvantages, such as the need for coordination and potential side effects like oral thrush. Proper inhaler technique and maintenance practices are emphasized to ensure effective medication delivery and reduce adverse effects.