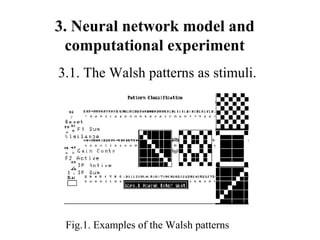
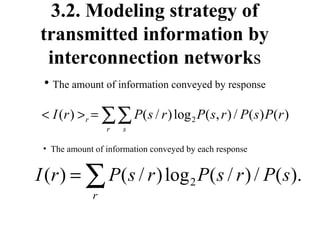
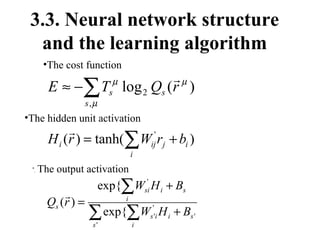
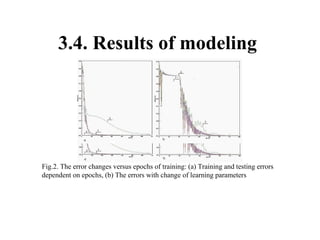
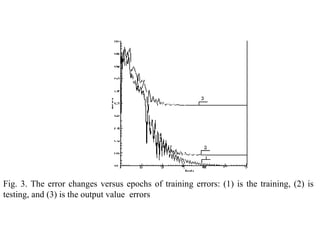
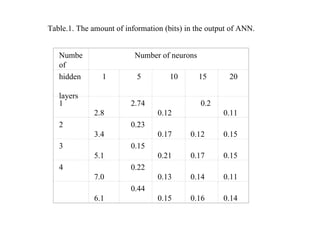
The document discusses using neural networks and information theory to model how information is conveyed in the brain. It presents a neural network model that was trained on Walsh patterns as stimuli to test how much information could be encoded and decoded. Computational experiments showed the model was able to code and decode information by implementing an artificial neural network, though more research is still needed to apply this to practical communication systems.