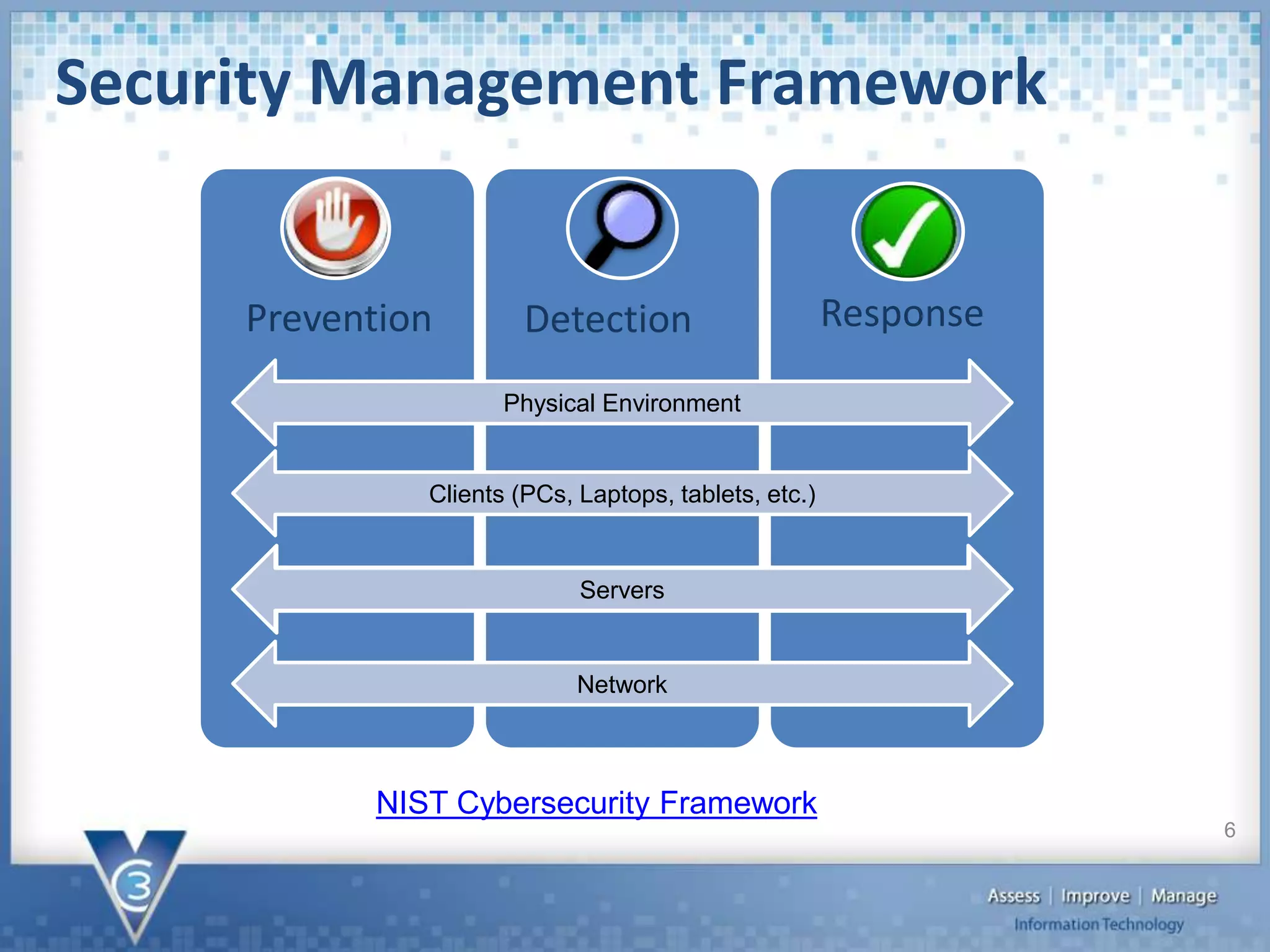
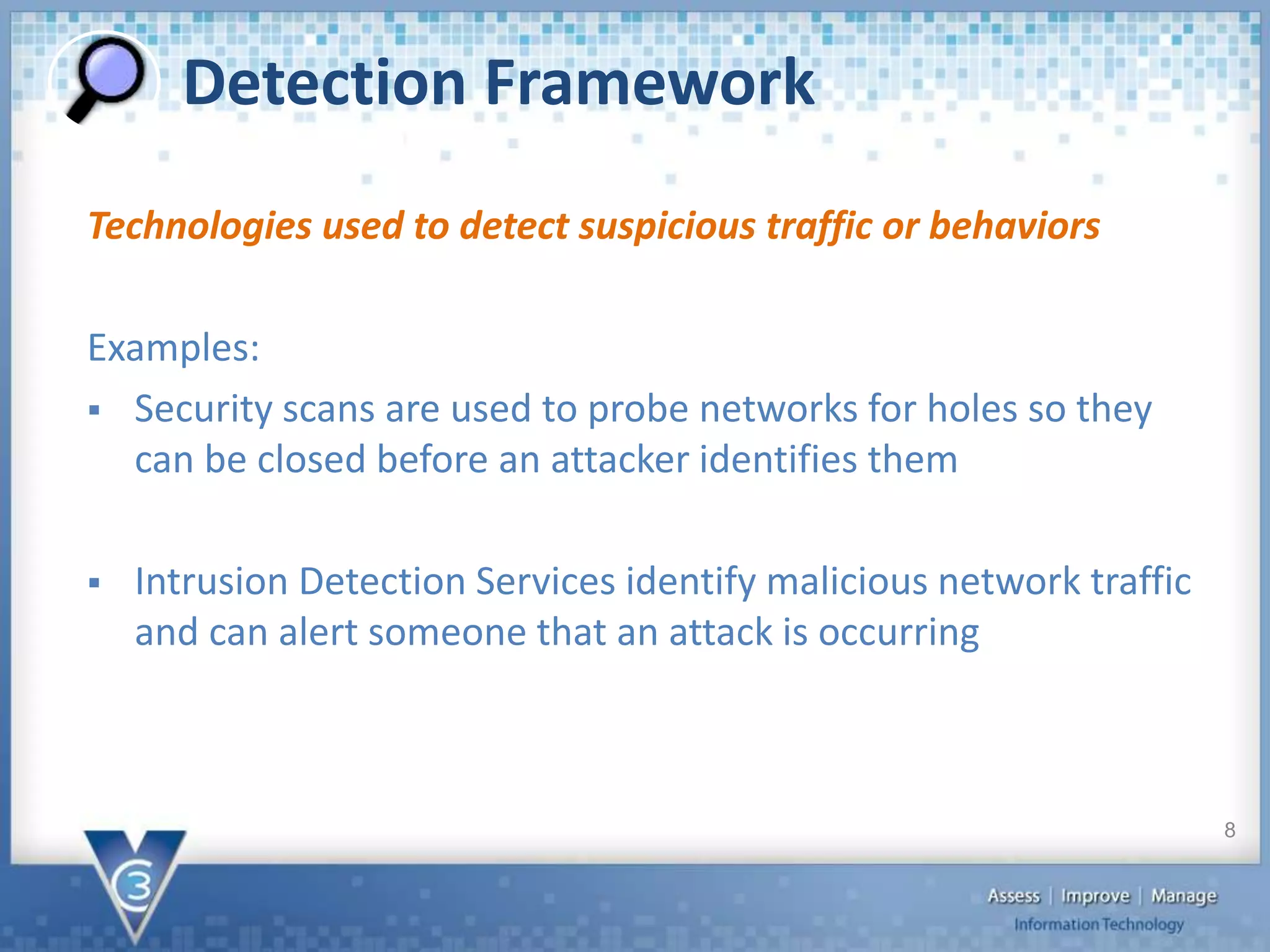
The document discusses the importance of cybersecurity, particularly for local governments, highlighting survey findings that show many are unprepared for breaches. It outlines the framework for managing cybersecurity risks, including prevention, detection, and response strategies, as well as the necessity of protecting both physical assets and data. Additionally, it provides specific steps organizations can take to enhance their cybersecurity posture, including the implementation of tools and policies for prevention and detection.