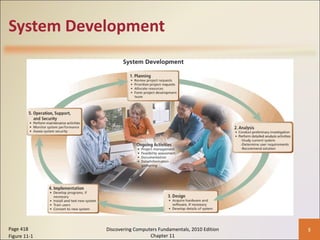
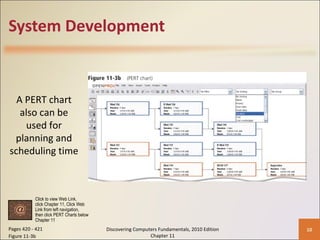
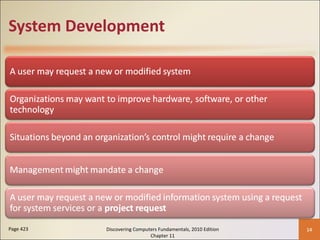
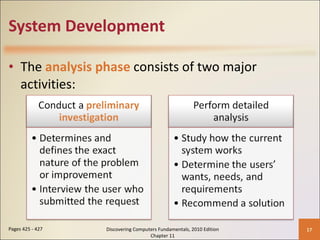
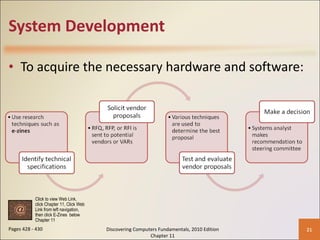
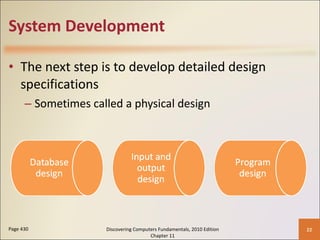
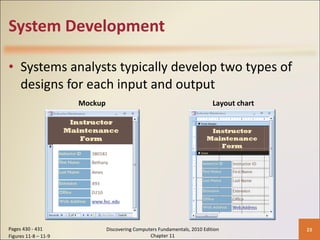
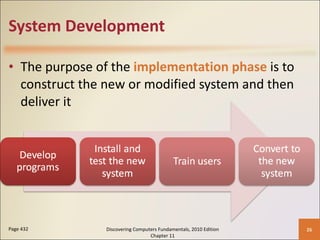
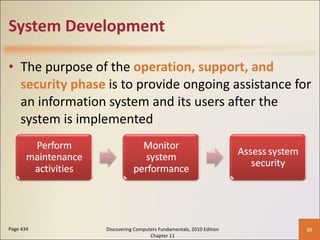
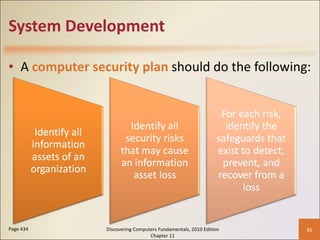
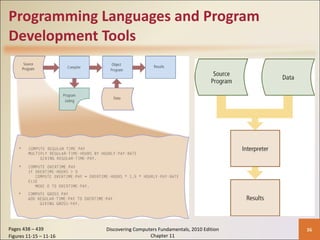
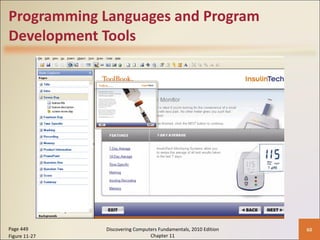
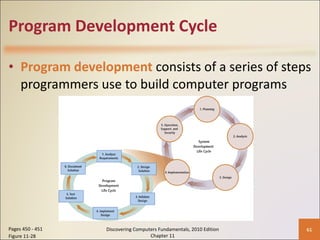
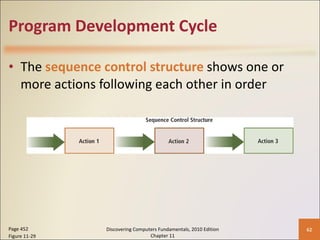
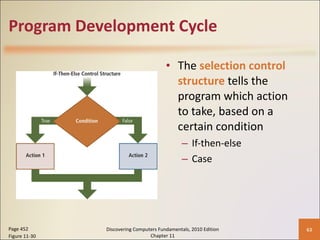
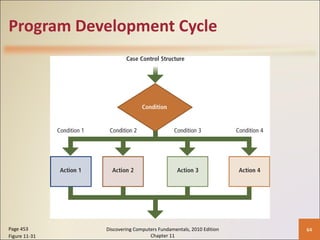
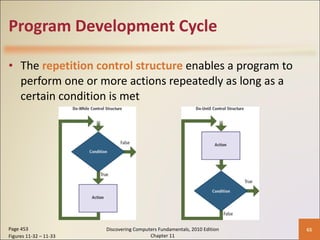
Chapter 11 of 'Discovering Computers Fundamentals, 2010 Edition' discusses system development, outlining guidelines, project management tools like Gantt and PERT charts, and the phases of project management including planning, analysis, design, implementation, and operation. It highlights the importance of programming languages, with insights into procedural, object-oriented, and fourth-generation languages, as well as tools for program development and web technologies. The chapter also covers the program development cycle and control structures used in programming.