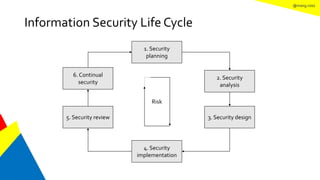
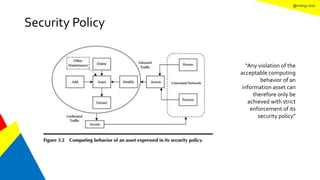
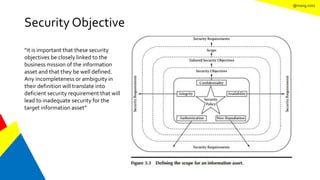
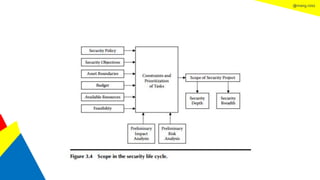
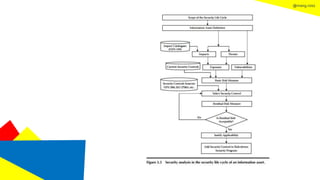
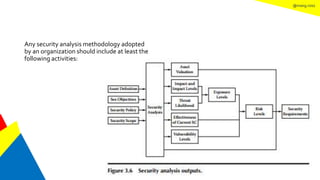
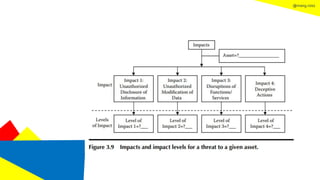
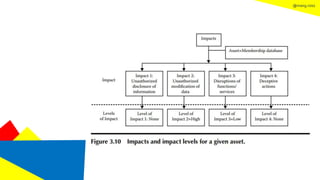
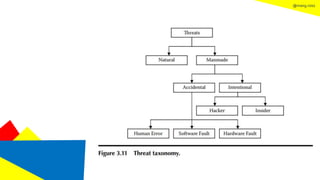
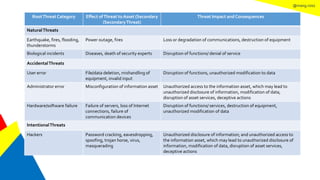
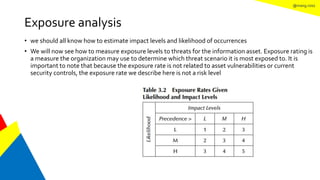
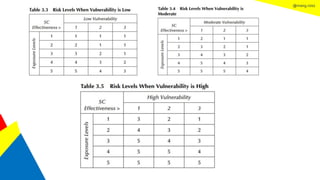
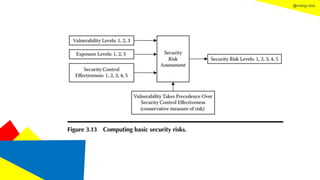
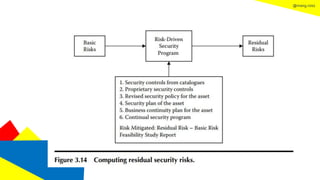
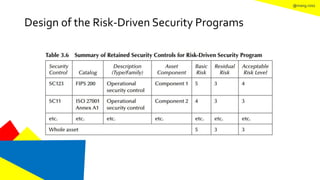
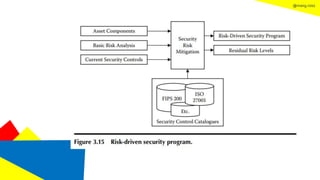
This document discusses the information security life cycle, which includes 6 steps: 1) security planning, 2) security analysis, 3) security design, 4) security implementation, 5) security review, and 6) continual security. It focuses on the first two steps of security planning and security analysis. For security planning, it covers asset definition, security policy, security objectives, and security scope. For security analysis, it describes the key activities of asset analysis, impact analysis, threat analysis, exposure analysis, vulnerability analysis, analyzing existing security controls, and risk analysis to define security requirements.