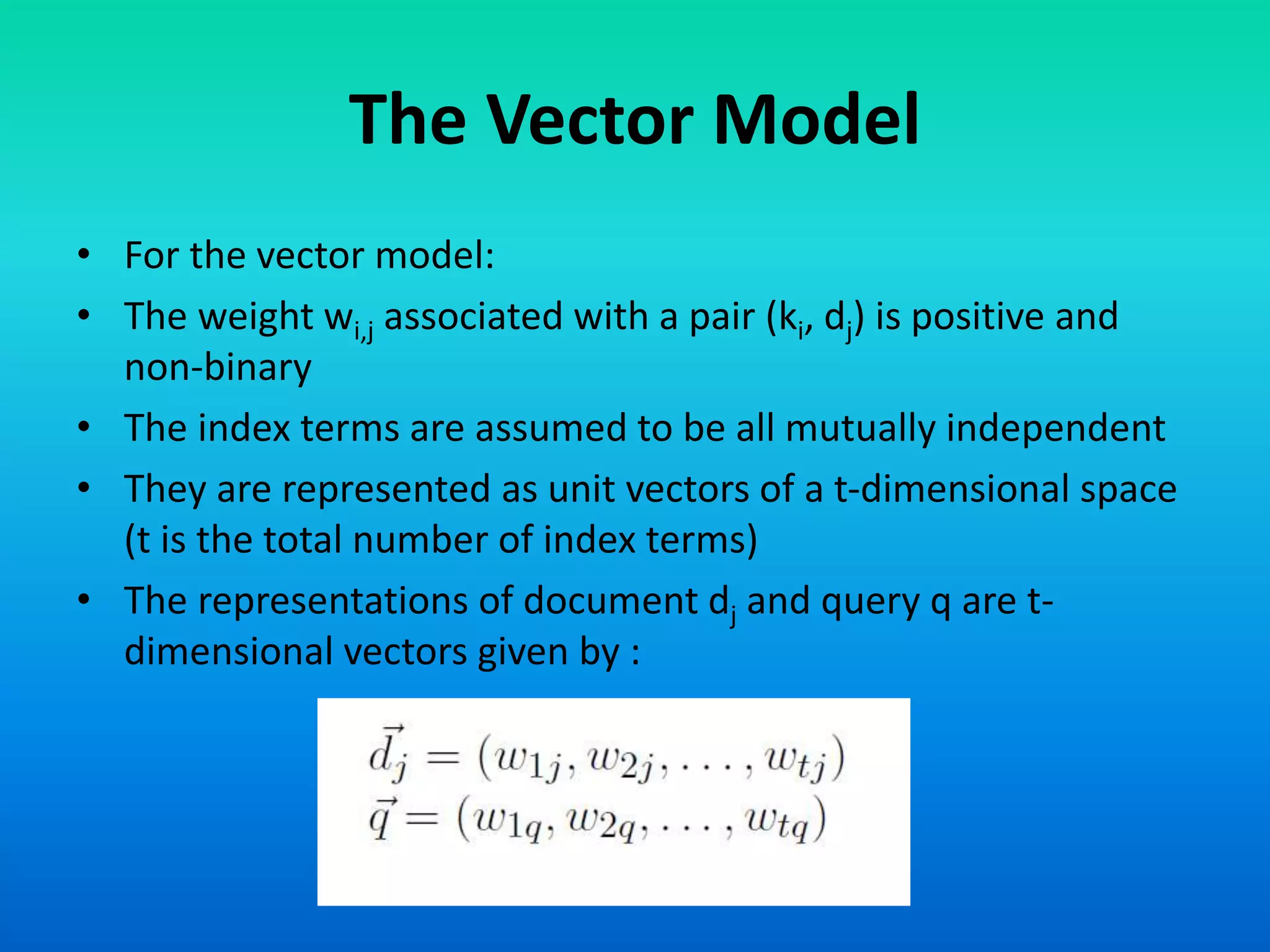
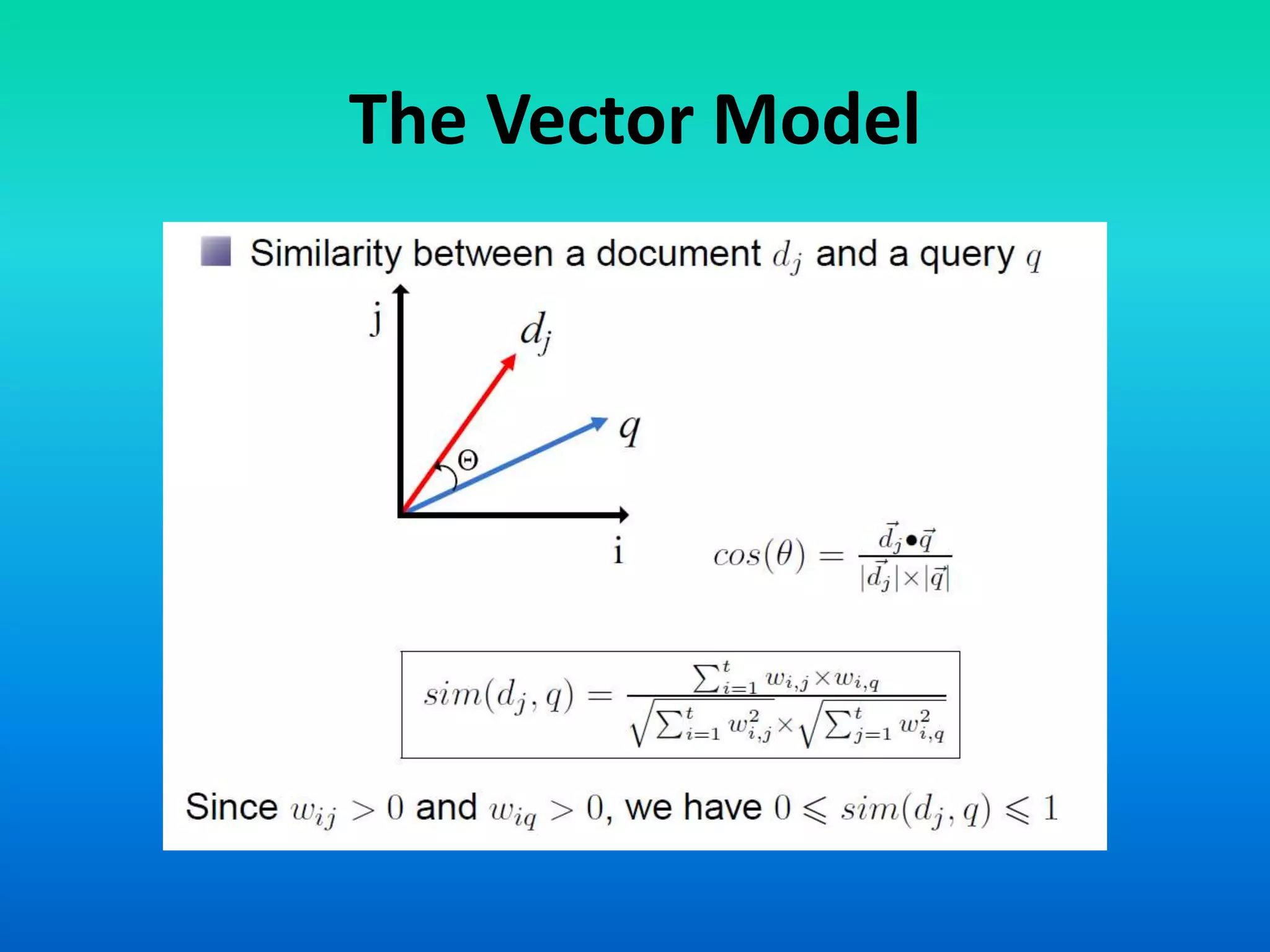
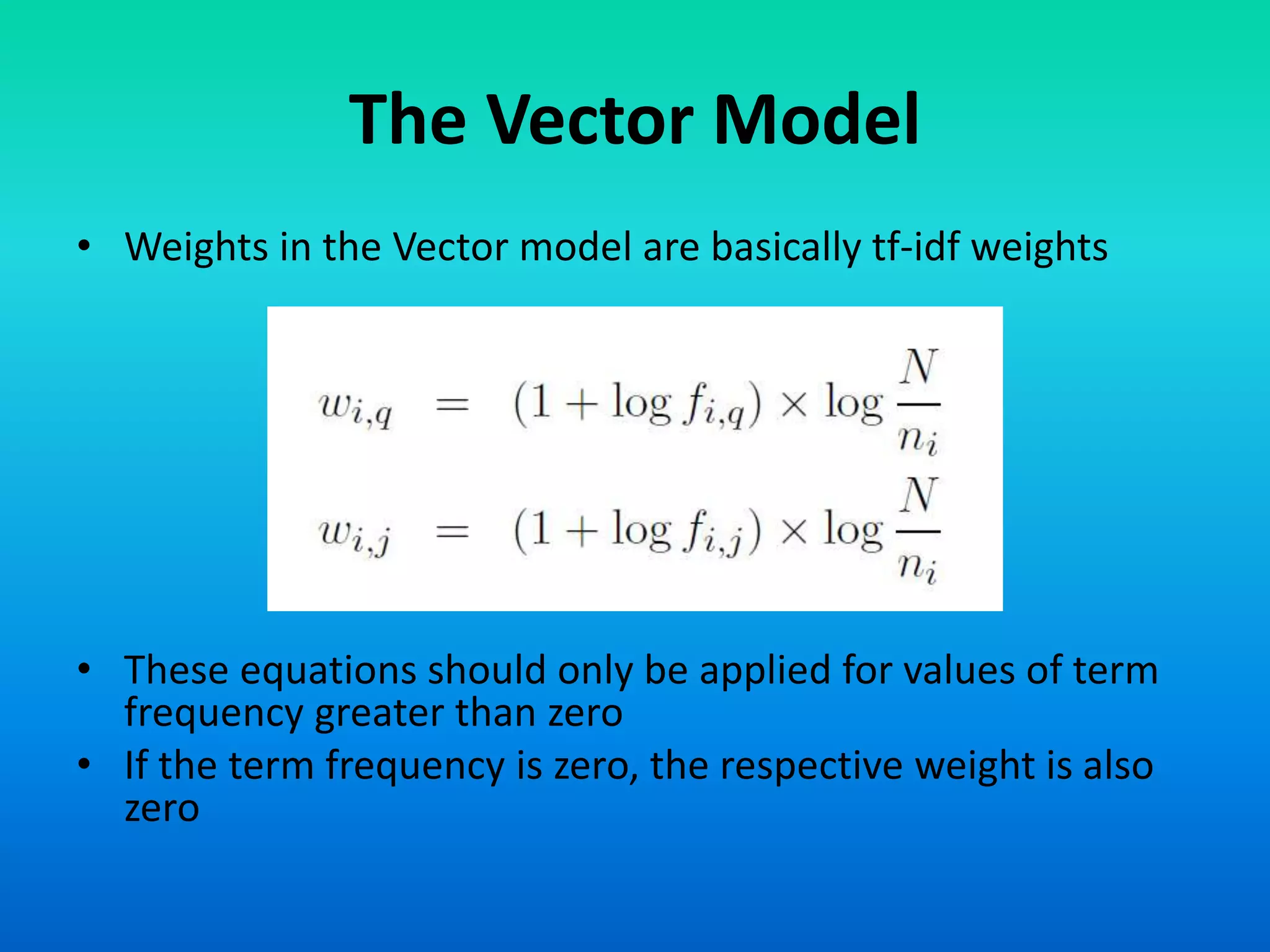
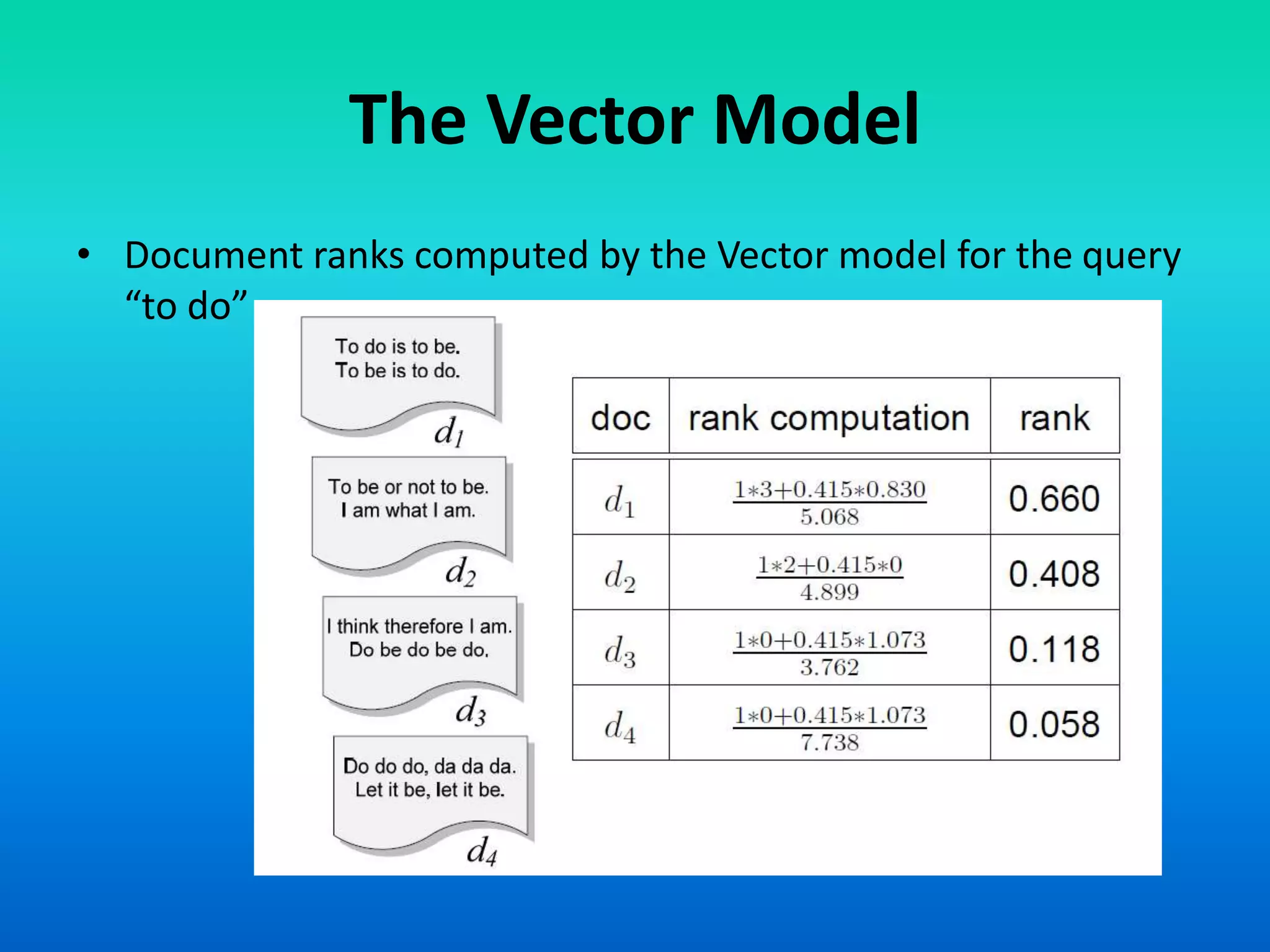
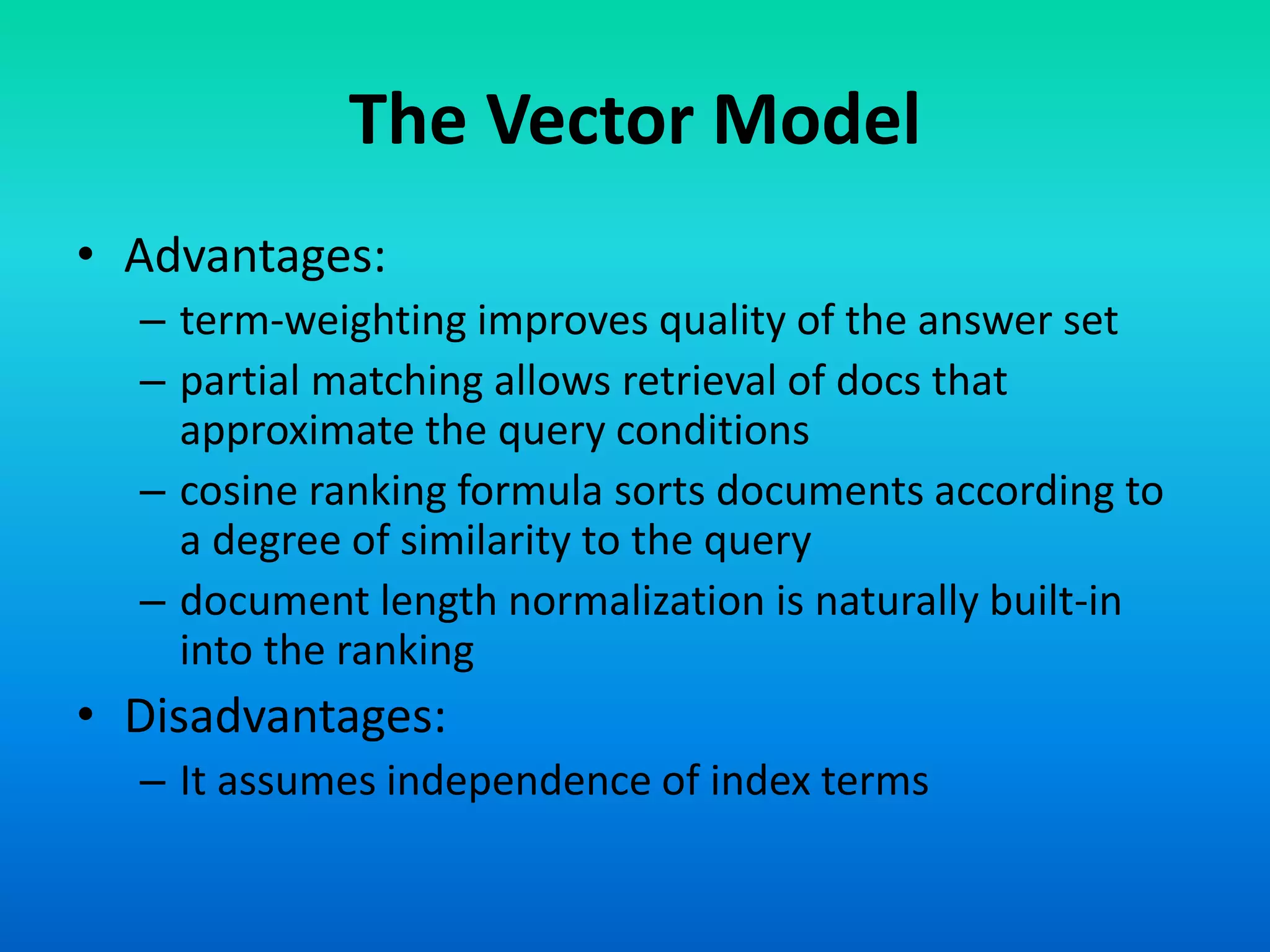
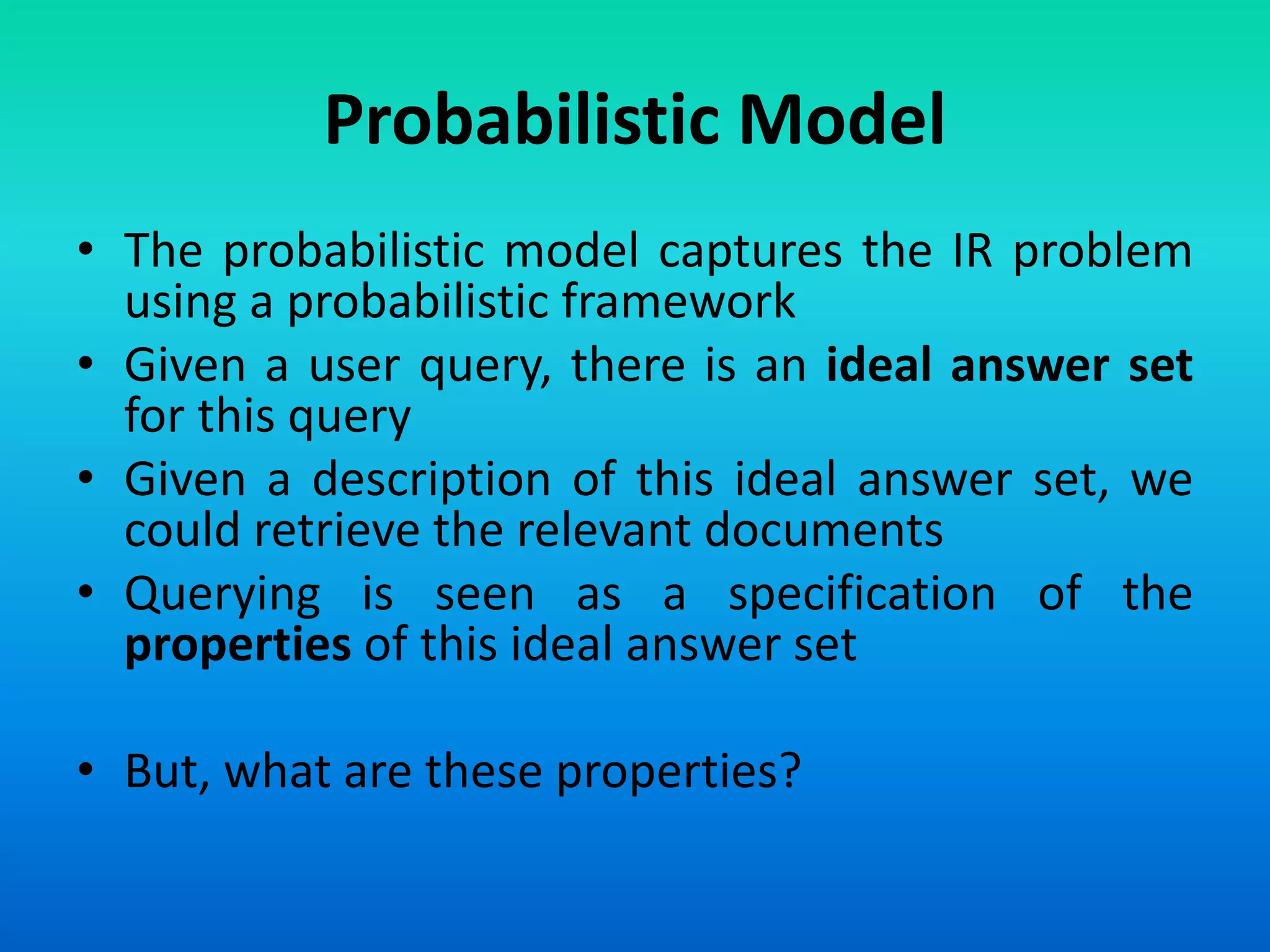
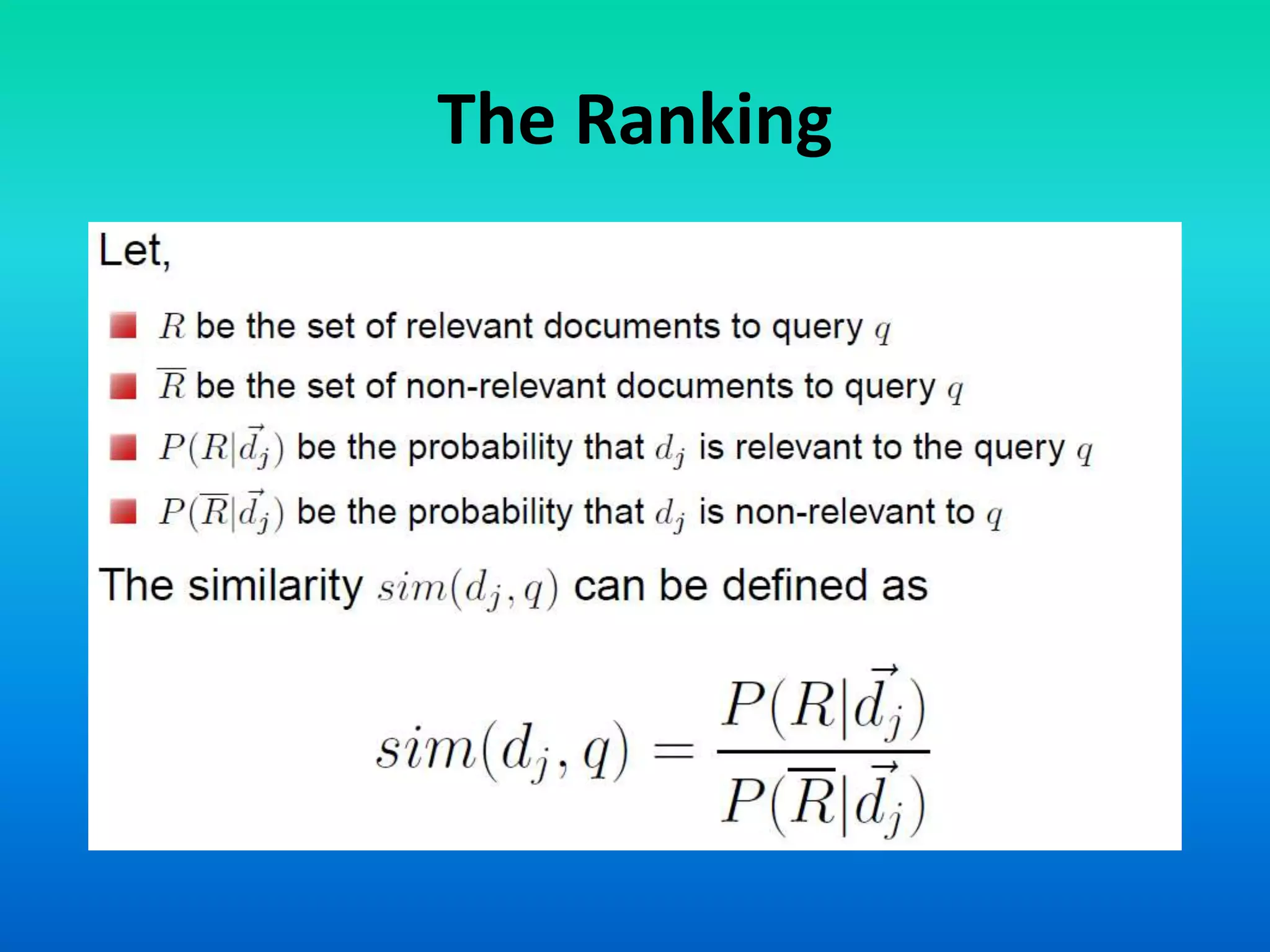
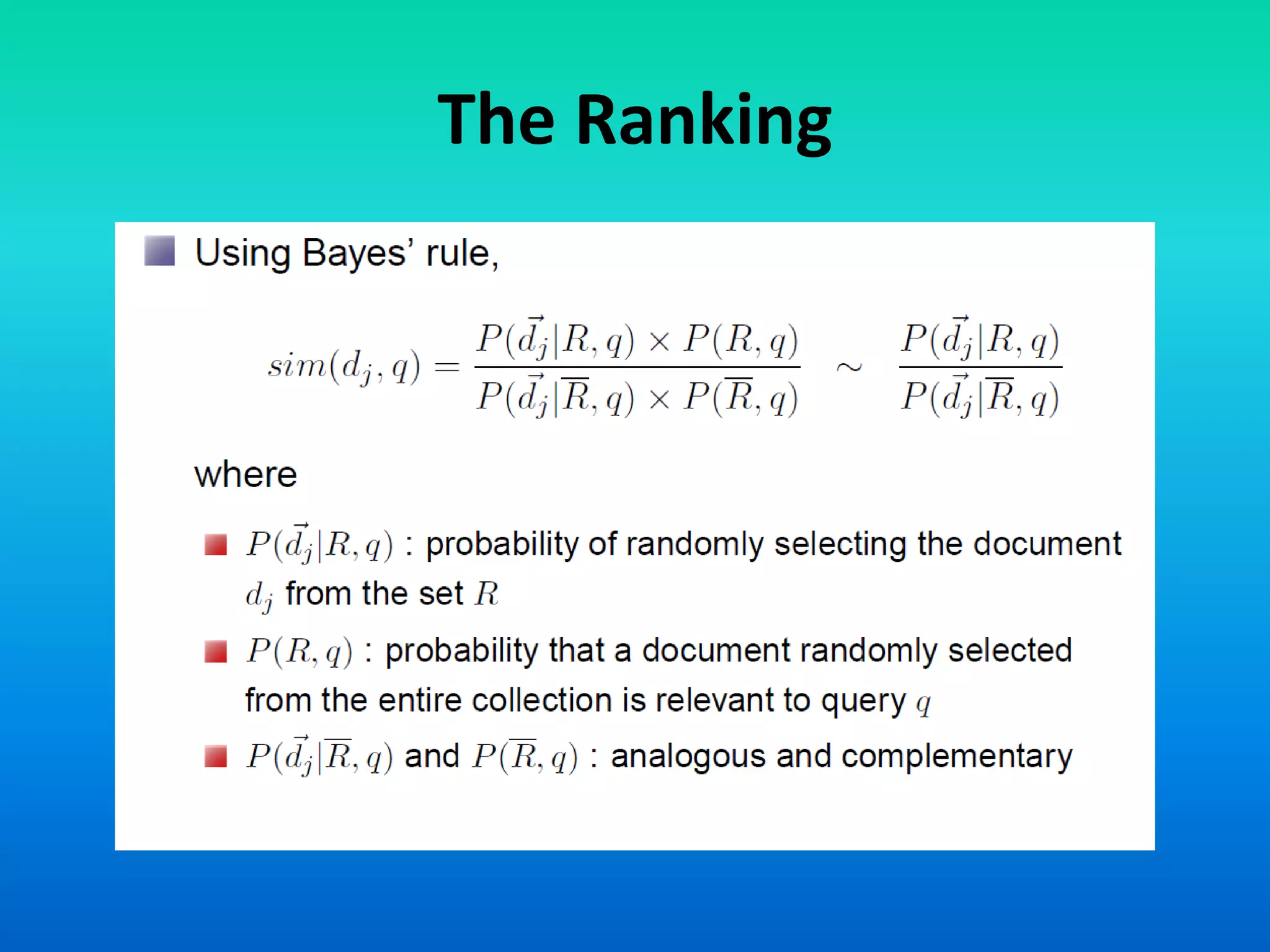
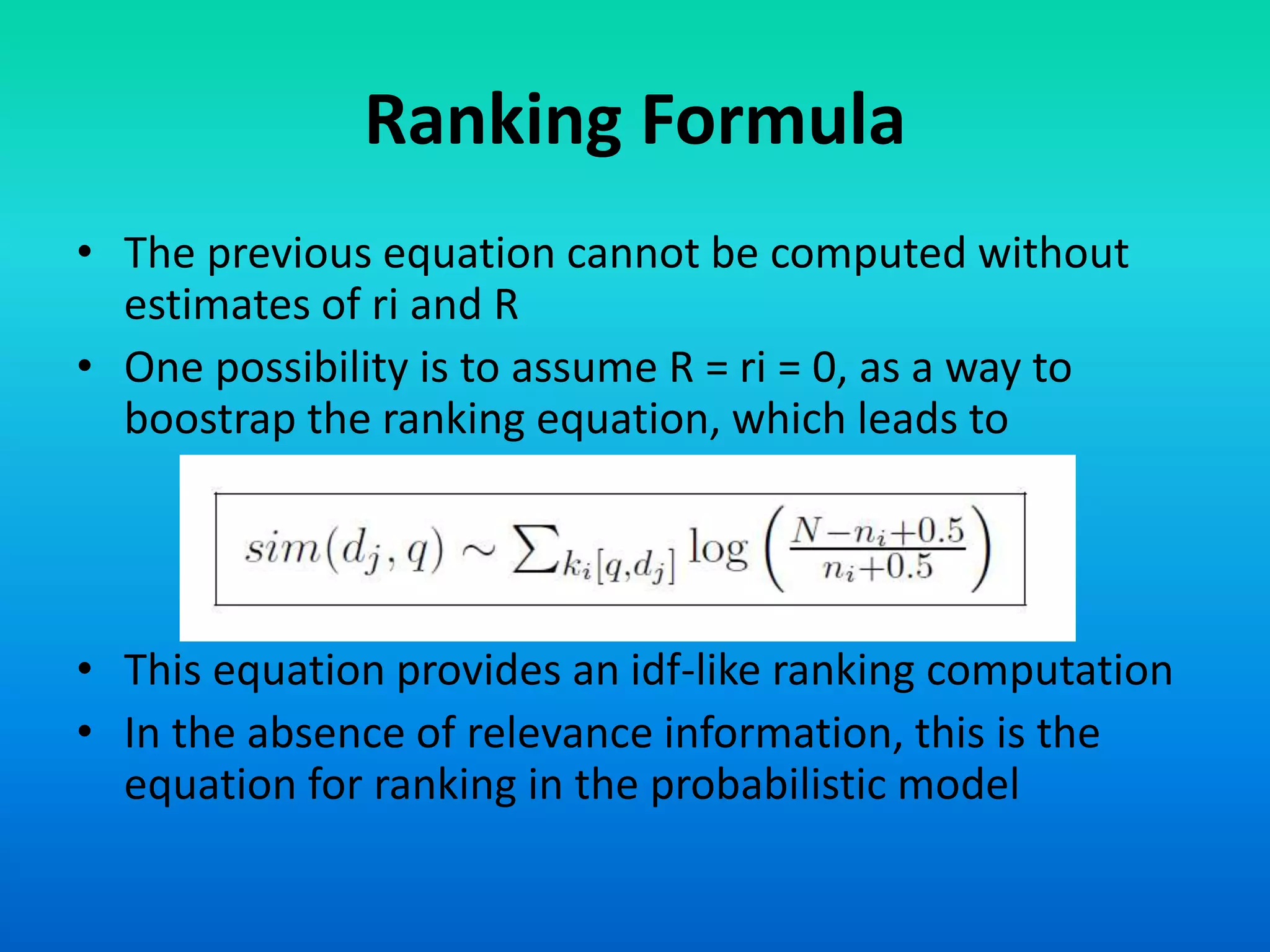
The document discusses two models of information retrieval: the vector model and the probabilistic model. The vector model uses non-binary weights to determine similarity between queries and documents, improving the quality of search results through partial matching, while the probabilistic model attempts to estimate the relevance probability of documents based on query characteristics. Each model has its advantages and disadvantages, such as the vector model's dependency assumption and the probabilistic model's need for initial relevance estimates.