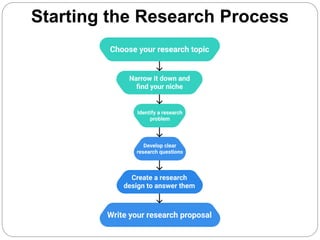
This document discusses designing research topics and titles. It provides steps for developing a research topic, including choosing a broad topic, preliminary research, defining the problem, and refining the research question. Sources of topics and criteria for selecting topics are outlined. Guidelines are presented for creating an effective research title, such as being accurate, concise, and including key variables. Sample research titles are also shown.