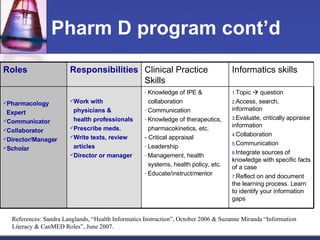
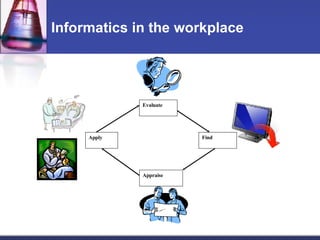
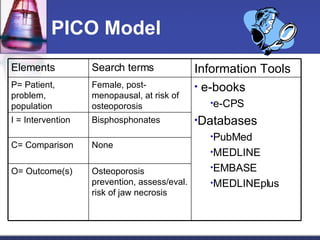
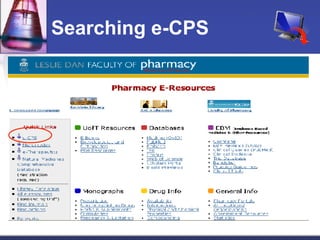
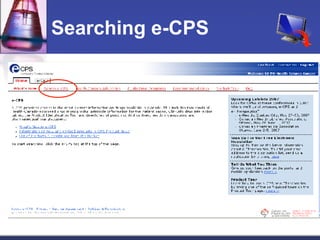
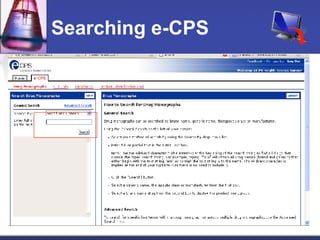
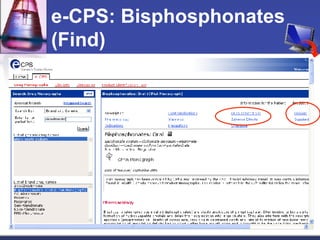
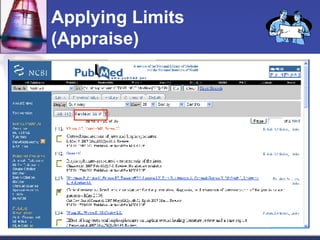
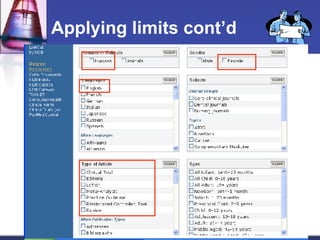
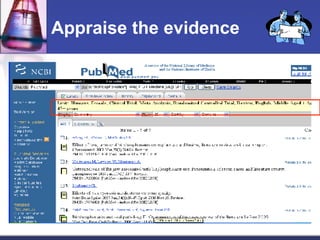
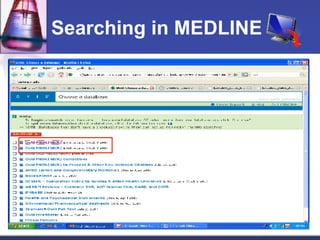
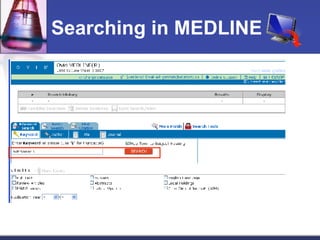
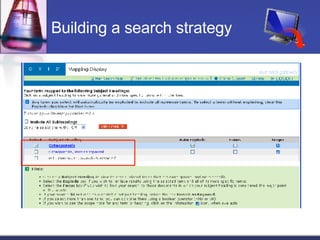
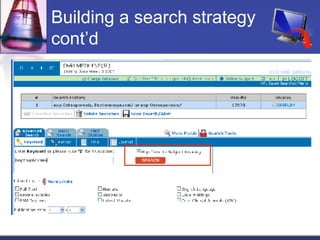
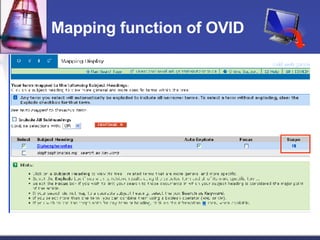
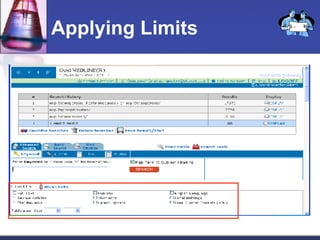
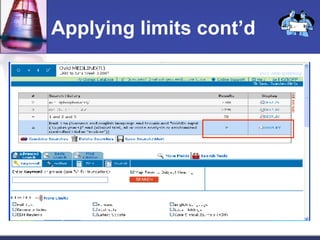
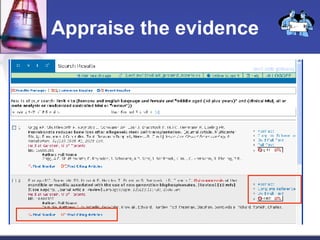
This document provides an overview of informatics for Pharm D students, including defining informatics, the objectives of the Pharm D program, roles and responsibilities, clinical and informatics skills, and using databases like PubMed and MEDLINE to search for information on a case study about the risks of jaw necrosis for a patient taking bisphosphonates to prevent osteoporosis. It demonstrates how to develop a PICO question, search for evidence, apply limits to search results, evaluate the evidence found, and apply it to answer clinical questions.