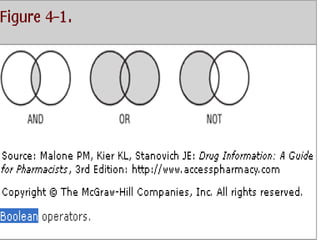
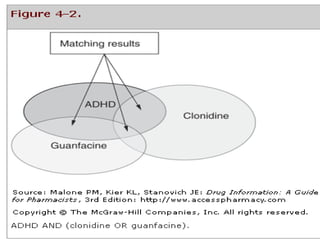
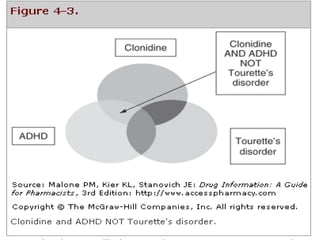
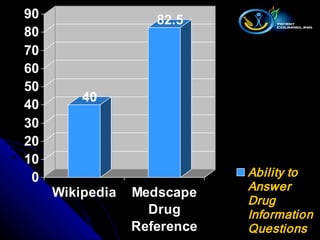
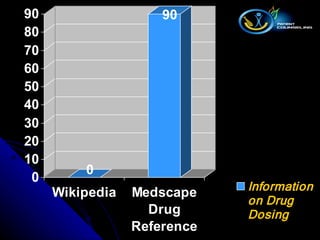
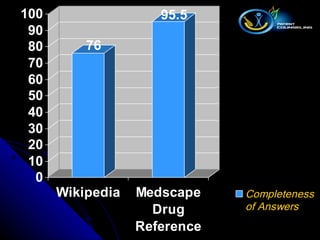
The document outlines the systematic approach pharmacists should take when managing information requests, emphasizing the classification of questions and the importance of using primary, secondary, and tertiary sources for effective information retrieval. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of various types of literature, alongside essential resources for pharmacy practice. Furthermore, it highlights the significance of evaluating the credibility of online information sources, including critical insights about Wikipedia's limitations.