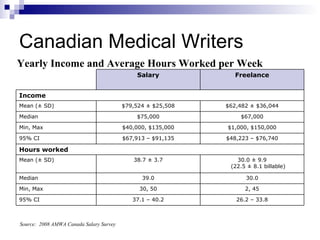
The document presents an overview of the pharmaceutical industry in Canada, highlighting its sales as only 2% of the global market and the primary focus of industry employment in Quebec and Ontario. It covers key statistics including leading pharmaceutical companies, therapeutic classes, and the demographics of Canadian medical writers, including their education and sectors of employment. Additionally, it discusses training opportunities, medical writing income, and the regulatory environment for pharmaceutical advertising in Canada.
![Medical Writing in Canada Presented at AMWA National Conference October 25, 2008, Louisvile, KY Amanda Strong [email_address] 514.239.2736 www.medicalcommunications.ca](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/medicalwritingcanada-amwa2008-091015103244-phpapp01/85/Medical-Writing-Canada-1-320.jpg)