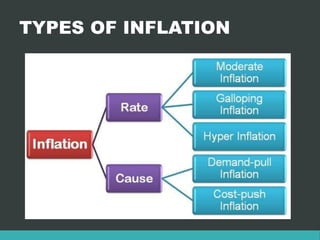
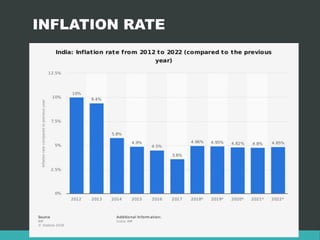
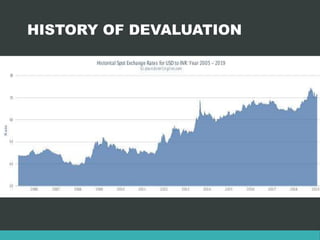
Inflation refers to a general continuous increase in the price level of goods and services in an economy over time. It can be caused by an increase in the money supply or aggregate demand. Negative effects include a decrease in purchasing power while positive effects include encouraging investment. Inflation can be classified as moderate, galloping or hyper based on its rate, and as demand-pull or cost-push based on its cause. Deflation is the opposite of inflation, where prices fall, while devaluation refers to decreasing the value of a currency relative to other currencies. Disinvestment refers to governments or organizations selling off assets or subsidiaries to reduce debt and introduce competition.