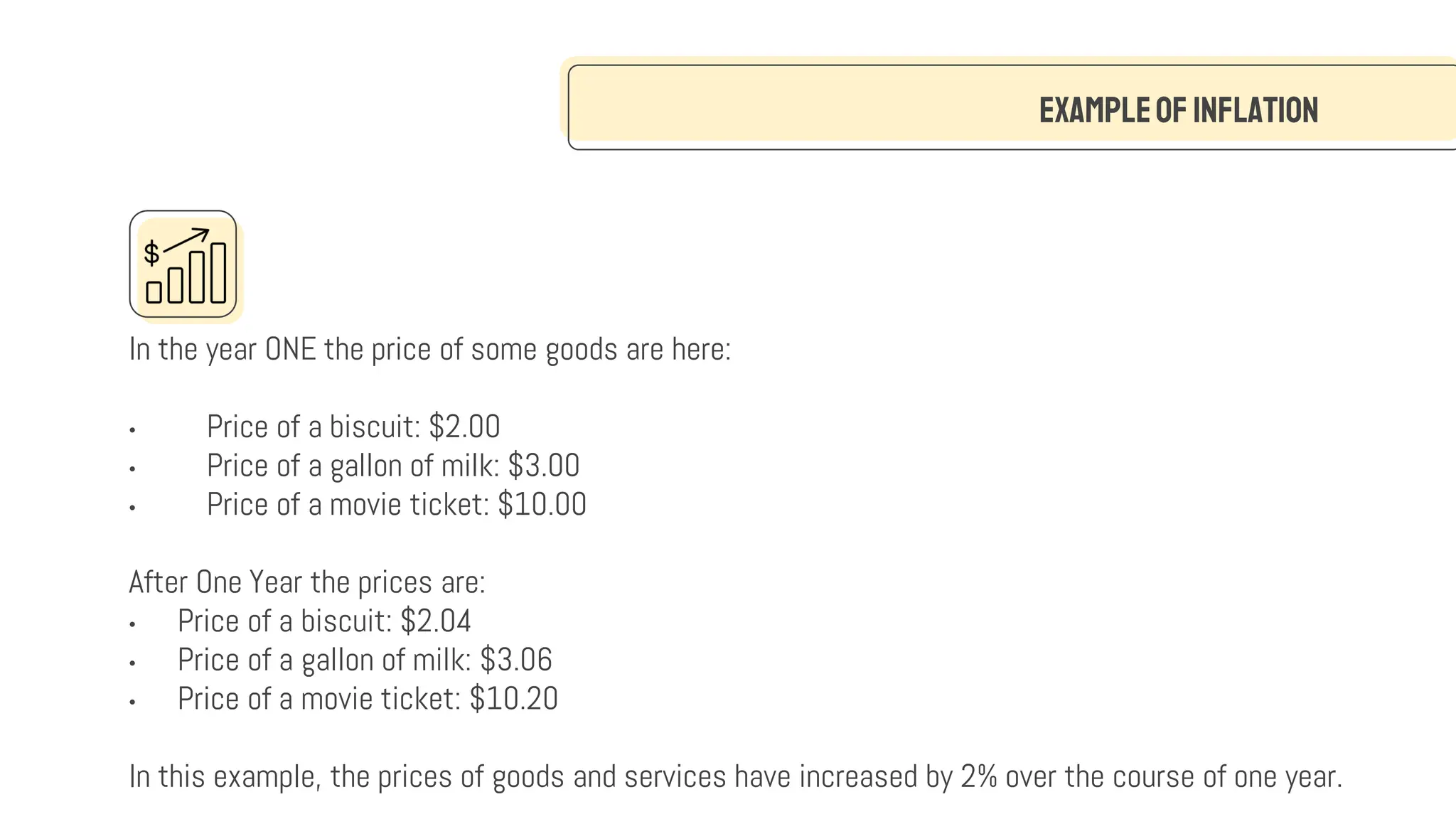
The document discusses inflation, defining it as the rate at which the prices of goods and services increase, leading to a decline in purchasing power. It explores various types of inflation such as demand-pull and cost-push inflation, along with their causes including built-in inflation and monetary inflation. It also examines the effects of inflation, highlighting its impact on purchasing power, economic uncertainty, interest rates, and international competitiveness.