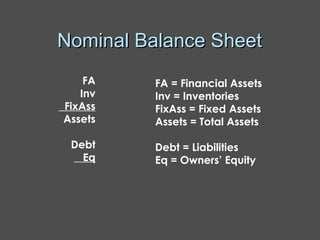
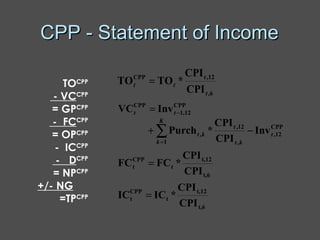
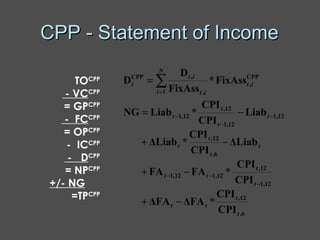
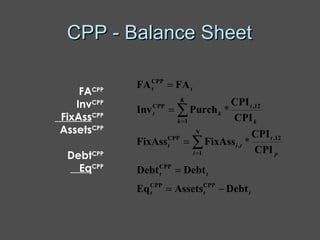
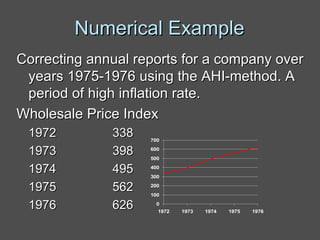
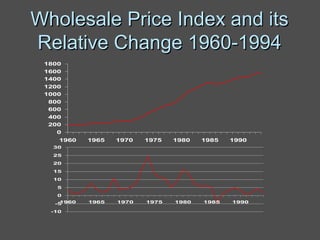
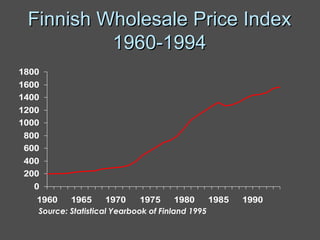
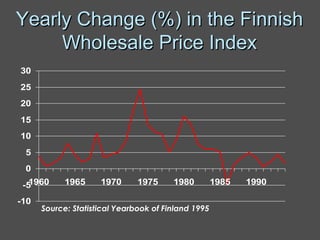
Inflation accounting aims to account for the effects of inflation on financial statements. There are several methods described in the document, including current purchasing power (CPP) accounting and current cost accounting (CCA). The Finnish AHI method combines elements of CPP and CCA - it uses a wholesale price index to adjust asset and liability values annually to the price level at mid-year. Adjustments are made to statement of income line items like variable costs and depreciation expense, as well as to asset and equity values on the balance sheet. A numerical example demonstrates application of the AHI method to correct annual reports for a company from 1975-1976, a period of high inflation.








![Nominal Statement of Income TO - VC = GP - FC = OP - IC - D = NP TO = Turnover VC = Variable Costs GP = Gross Profit FC = Fixed Costs OP = Operating Profit IC = Interest Costs D = Depreciation NP = Net Profit Below we also need: [ NG = Net Gain from Liabilities TP = Total Profit ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inflation-091025114556-phpapp02/85/Inflation-11-320.jpg)