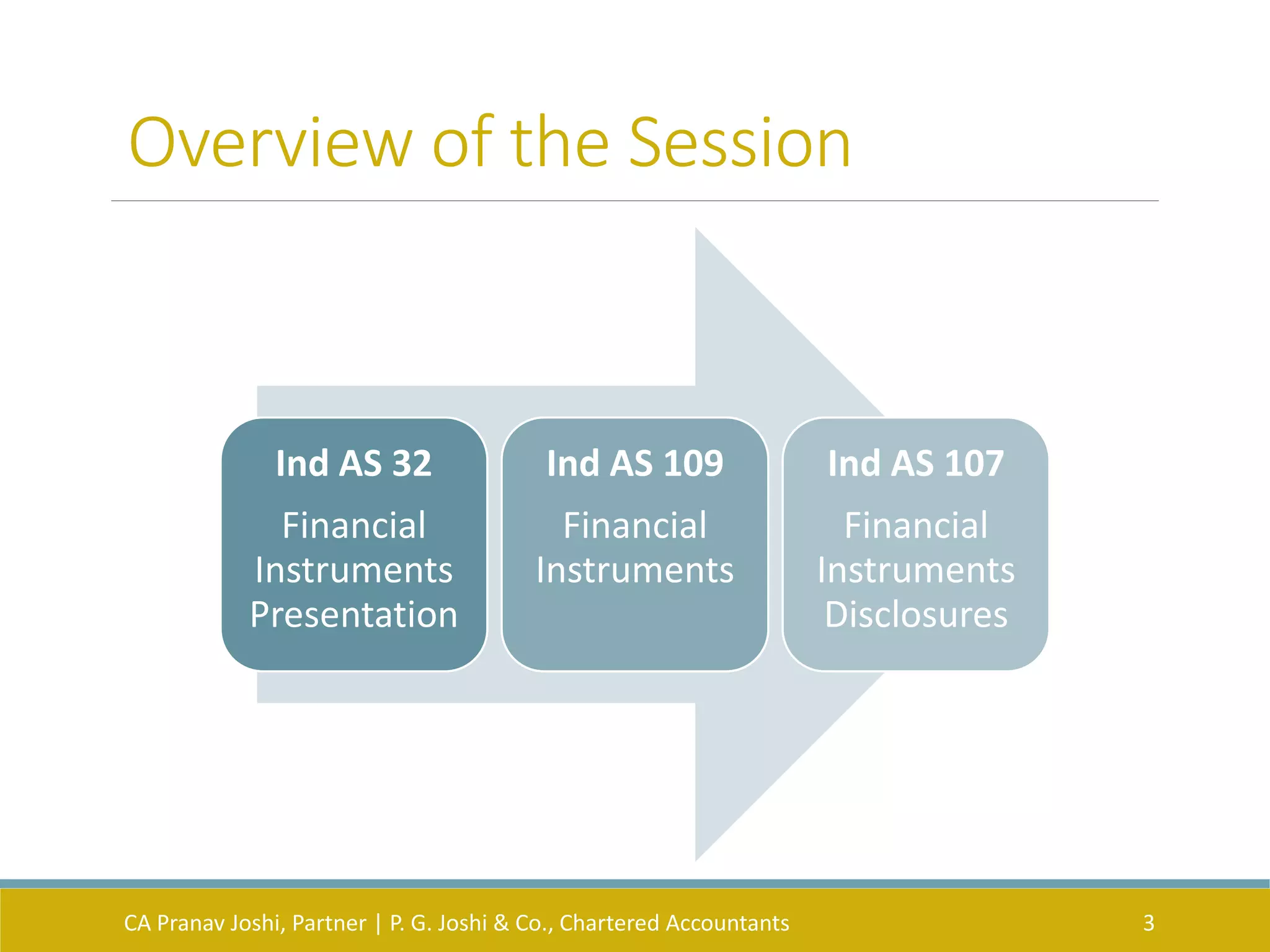
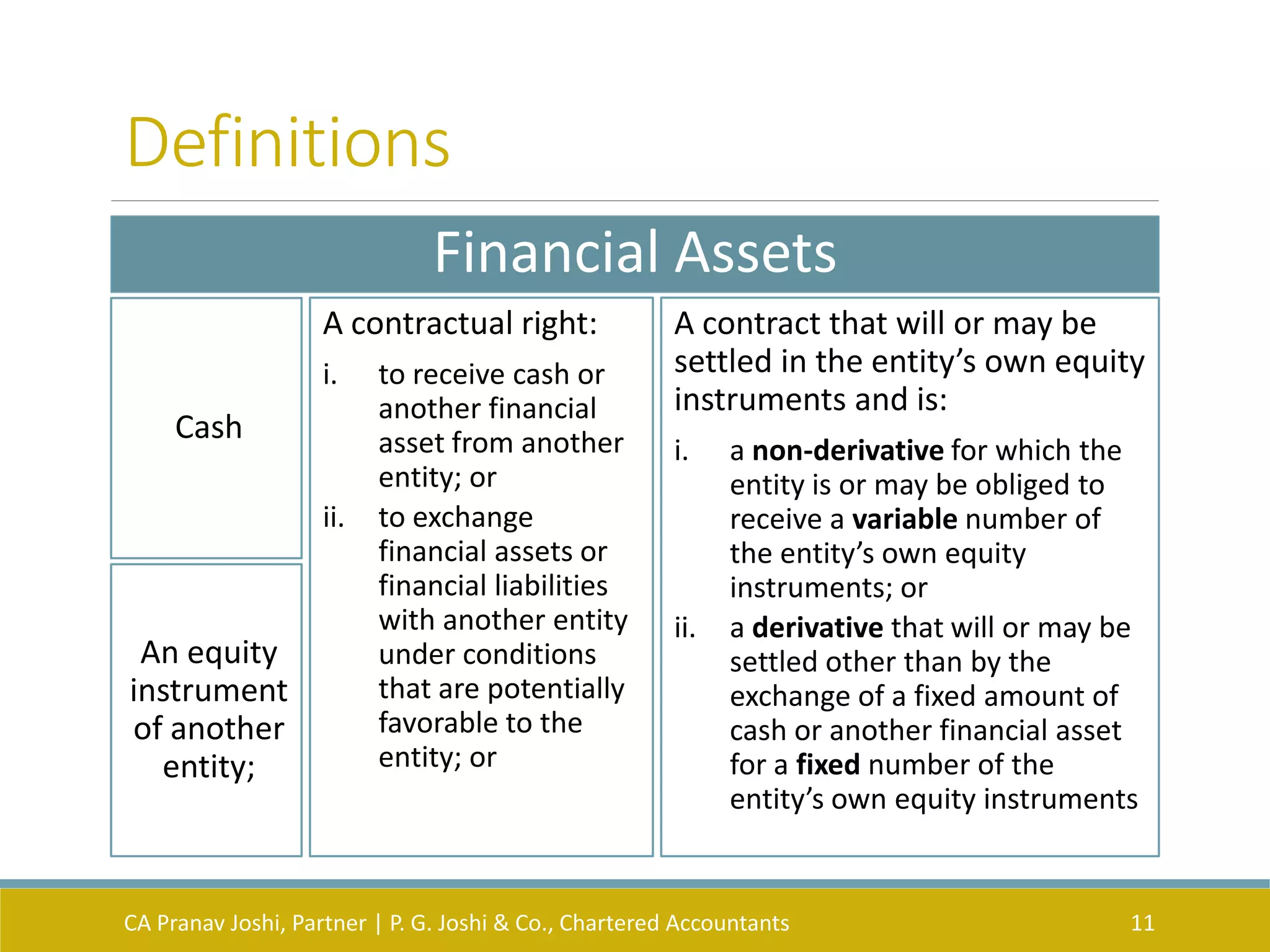
The document provides an overview of key Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) related to financial instruments: Ind AS 32 on presentation, Ind AS 109 on recognition and measurement, and Ind AS 107 on disclosures. It defines important terms, outlines the objectives and scope of each standard, and summarizes the classification, measurement, impairment and disclosure requirements for financial assets and financial liabilities. The presentation focuses on the central themes of each standard and exceptions are ignored unless specifically included.