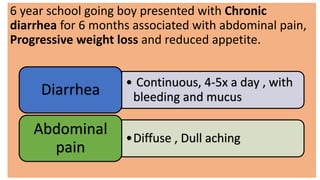
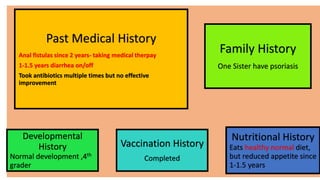
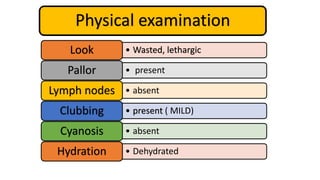
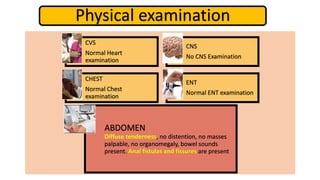
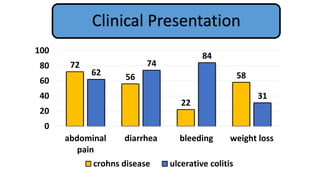
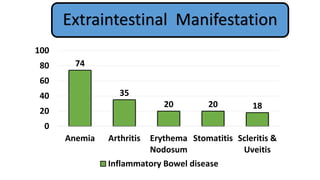
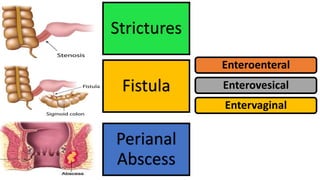
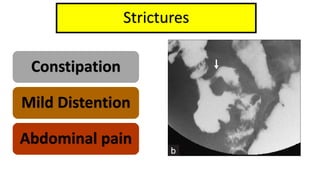
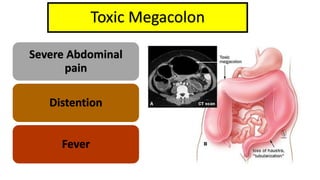
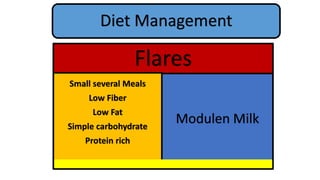
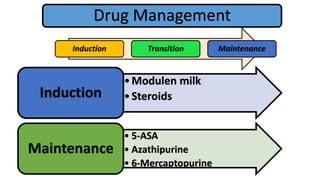
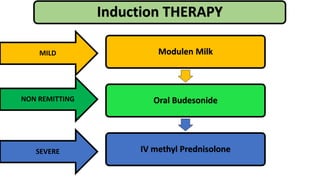
1. Fahad Fayyaz Butt, a 6-year-old boy, presented with chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss, and reduced appetite for 6 months. Physical examination found pallor, mild clubbing, diffuse abdominal tenderness, and anal fistulas.
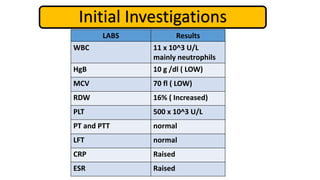
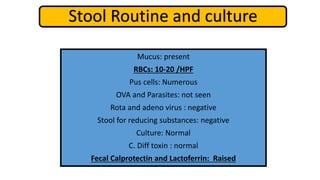
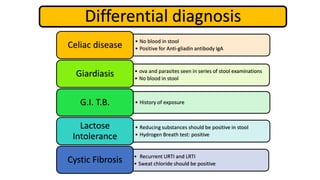
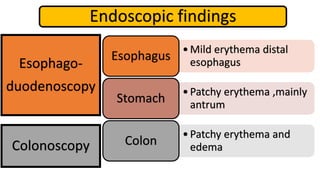
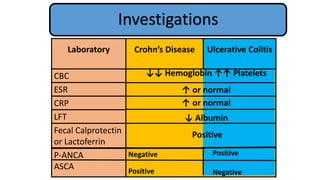
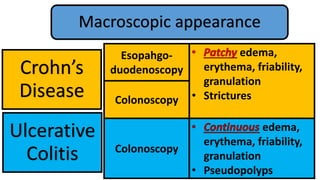
2. Initial investigations showed anemia, elevated inflammatory markers, and positive anti-gliadin antibodies. Endoscopy found patchy erythema in the esophagus, stomach, and colon.
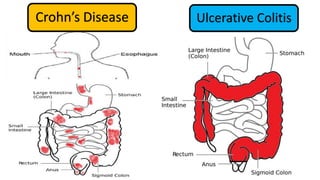
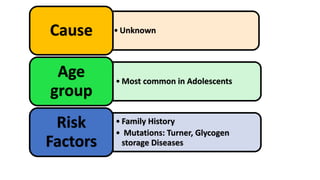
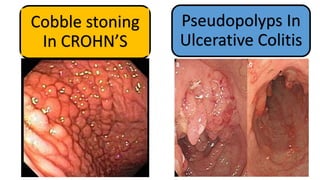
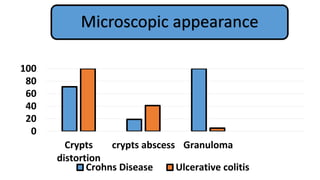
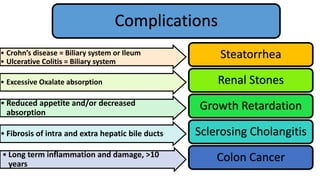
3. He was diagnosed with Crohn's disease based on his clinical presentation and endoscopic findings. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are the two main types of inflammatory bowel disease.