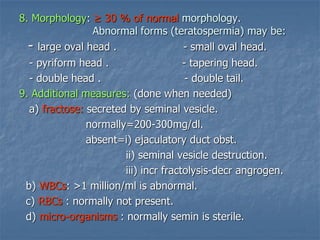
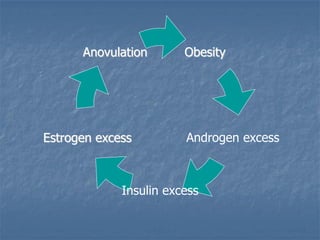
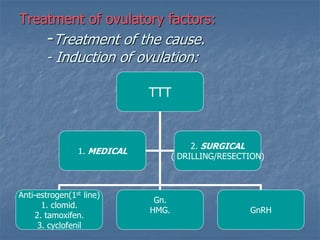
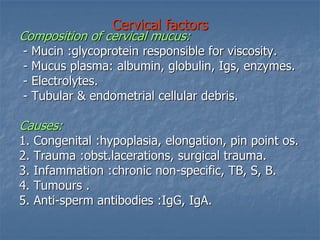
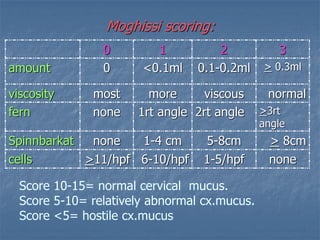
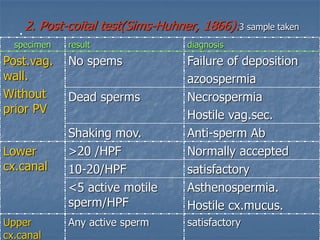
This document defines infertility and its causes. It discusses male and female factors of infertility in detail. For male factors, it covers pre-testicular, testicular, and post-testicular causes and evaluates male factor infertility through history, examination, semen analysis, and assessment of sperm function. For female factors, it discusses ovarian causes of anovulation including physiological and pathological causes. It also describes the treatment of ovulatory disorders, focusing on clomiphene citrate as a first-line induction of ovulation treatment.