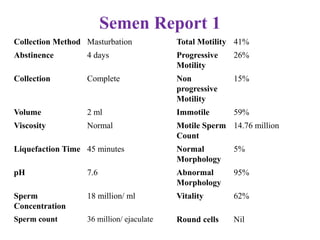
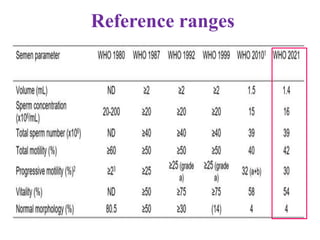
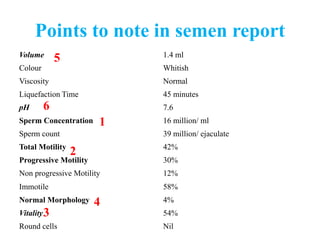
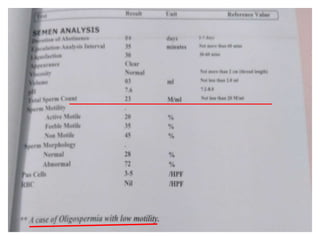
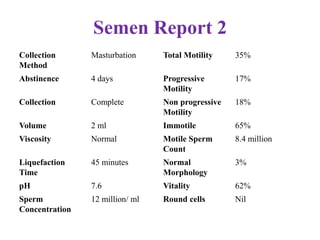
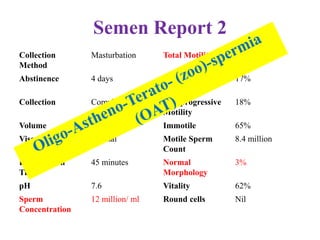
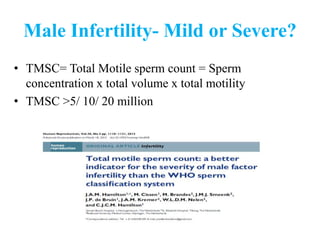
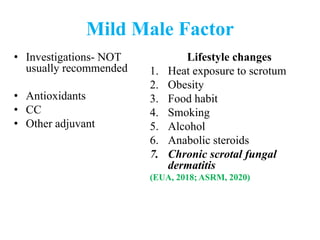
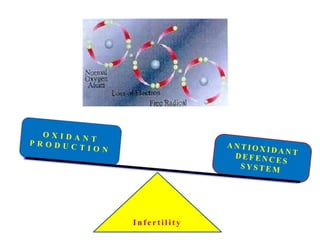
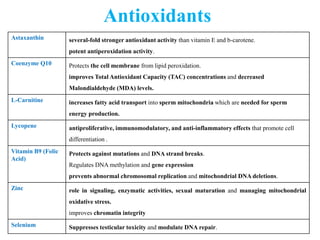
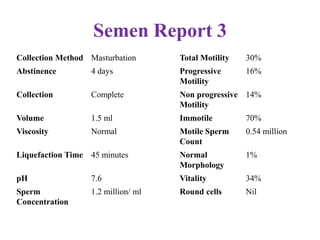
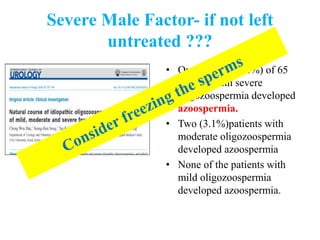
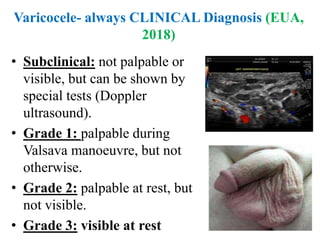
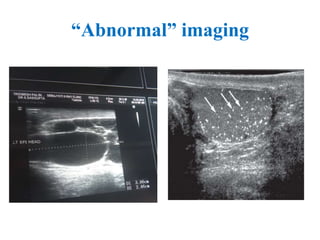
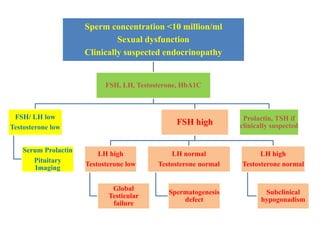
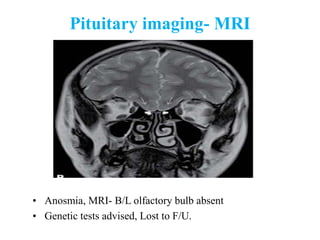
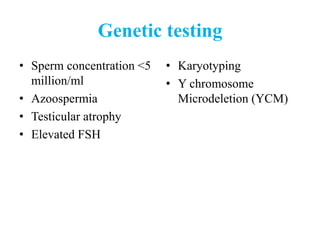
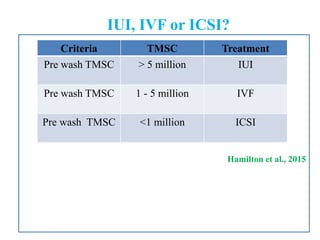
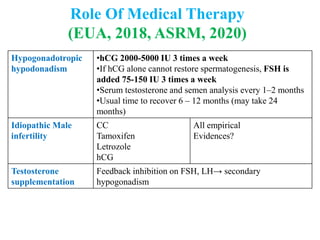
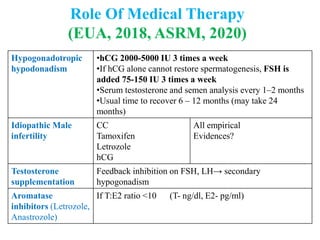
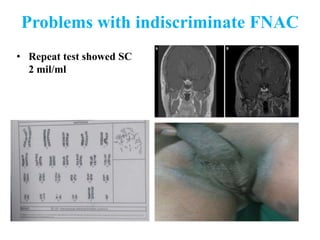
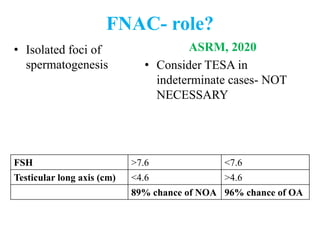
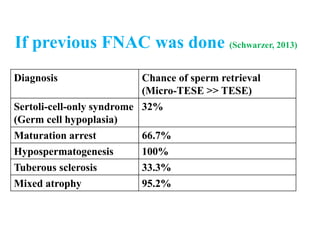
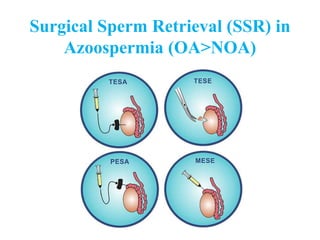
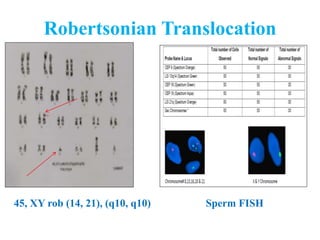
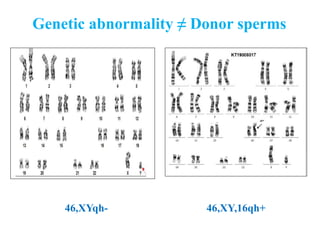
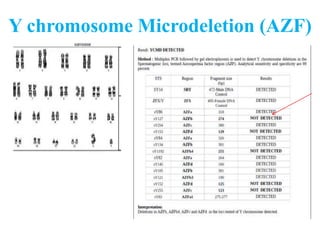
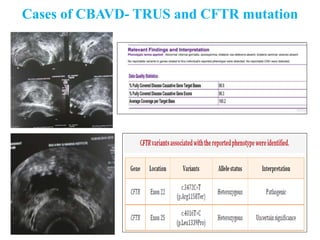
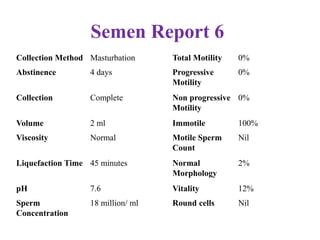
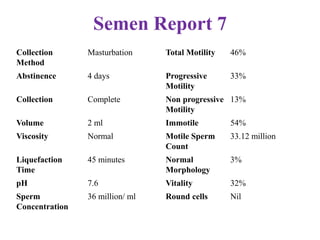
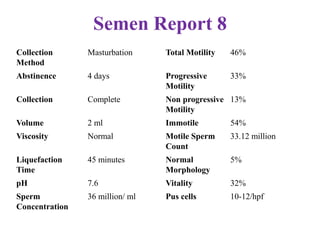
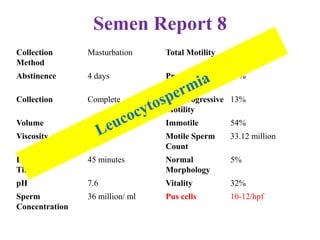
The document discusses abnormal semen analysis, including multiple semen reports with varying sperm parameters, and guidelines for further management based on the severity of male infertility. It emphasizes the role of antioxidants, lifestyle changes, and potential medical therapies while detailing the importance of further investigations in severe cases. Additionally, the document outlines the implications of abnormal findings and the need for appropriate follow-up actions such as donor sperm or specialized techniques for sperm retrieval.