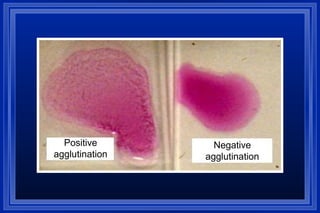
Brucellosis is a zoonotic disease caused by bacteria that primarily infects domestic animals and can be transmitted to humans. It is a global disease with high prevalence in parts of the Mediterranean, Middle East, Africa, and South America. Humans typically get infected by consuming raw dairy products or through contact with infected animal tissues and fluids. Symptoms are non-specific but include undulating fever, sweats, joint pain and swelling. Diagnosis involves serological tests or culture of blood and tissues. Treatment requires a combination of doxycycline and streptomycin or rifampin for several weeks. Prevention focuses on animal vaccination, safe food handling, and protective equipment for high risk workers.