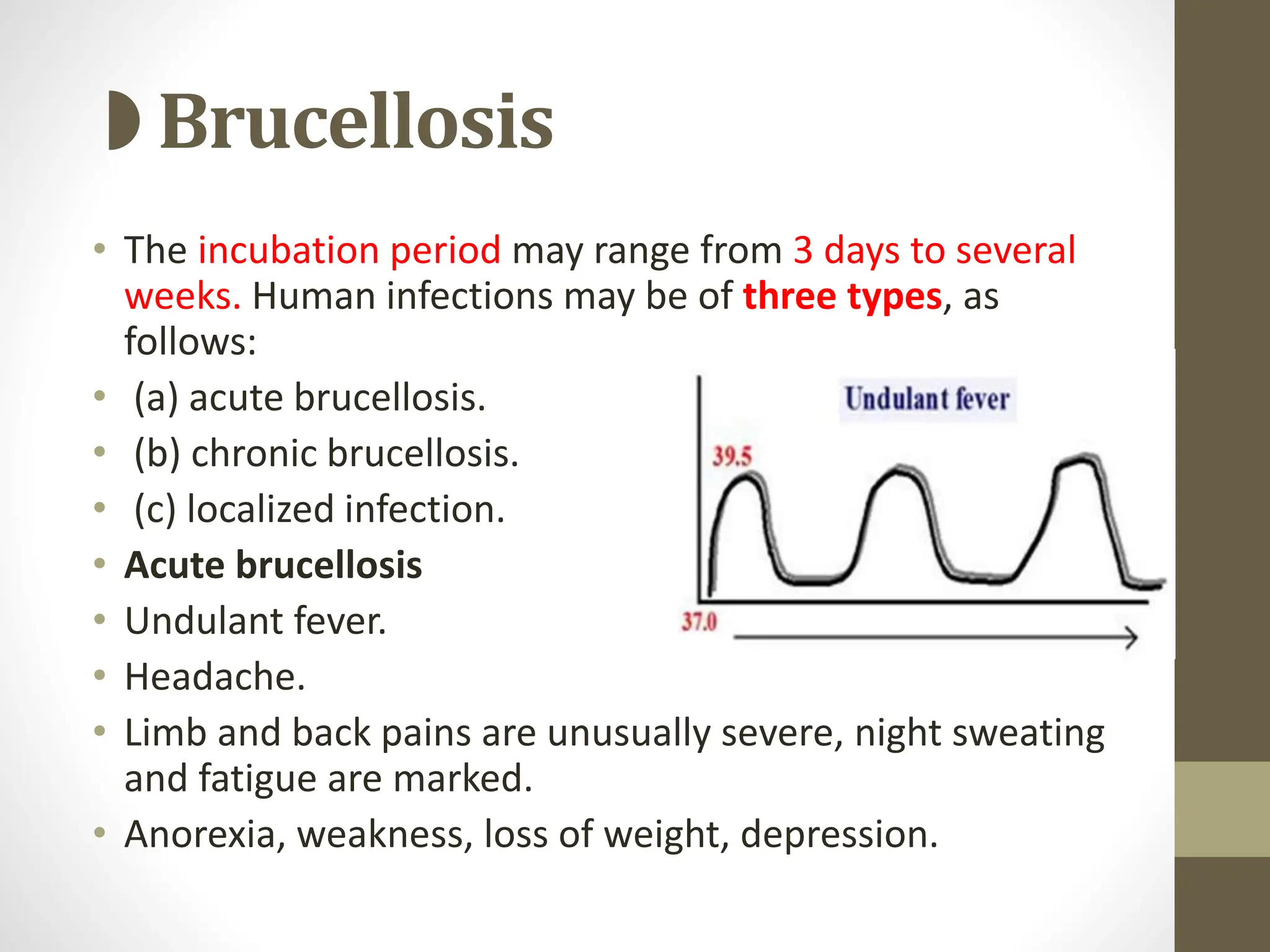
This document provides information on Brucella, the causative agent of brucellosis. It discusses that Brucella is a gram-negative coccobacillus that can infect various domestic animals and cause zoonotic infections in humans. The four main human pathogenic species are B. abortus, B. melitensis, B. suis, and B. canis. Brucellosis is transmitted to humans primarily through the consumption of contaminated, unpasteurized dairy products. The disease causes acute or chronic systemic infections and can occasionally lead to localized complications like endocarditis. Laboratory diagnosis involves culture and serological tests. Treatment involves prolonged courses of antibiotic combinations like doxycycline and rifamp