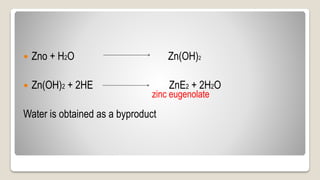
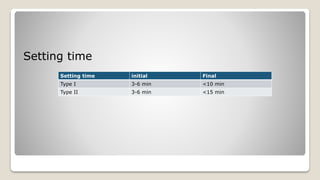
This document discusses inelastic impression materials, focusing on zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) impression paste. It describes the composition, setting reaction, properties, uses, and clinical implications of ZOE paste. It also summarizes several research studies related to ZOE paste, including factors that influence setting time, allergic reactions, efficacy of disinfection methods, techniques for implant impressions and bite registration, and the effects of tray design and storage on impression accuracy and stability.